检测链表中的循环
给定一个链表,检查链表是否有循环。下图显示了一个带有循环的链表。
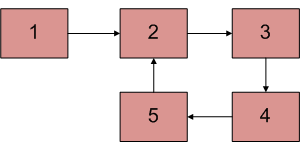
以下是执行此操作的不同方法。
解决方案 1:散列方法:
将链表一一遍历,不断将节点地址放入哈希表中。在任何时候,如果达到 NULL,则返回 false,如果当前节点中的下一个指向 Hash 中先前存储的任何节点,则返回 true。
C++
// C++ program to detect loop in a linked list
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Returns true if there is a loop in linked list
// else returns false.
bool detectLoop(struct Node* h)
{
unordered_set s;
while (h != NULL) {
// If this node is already present
// in hashmap it means there is a cycle
// (Because you we encountering the
// node for the second time).
if (s.find(h) != s.end())
return true;
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
s.insert(h);
h = h->next;
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
cout << "Loop found";
else
cout << "No Loop";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Geetanjali Java
// Java program to detect loop in a linked list
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedList {
static Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
static public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Returns true if there is a loop in linked
// list else returns false.
static boolean detectLoop(Node h)
{
HashSet s = new HashSet();
while (h != null) {
// If we have already has this node
// in hashmap it means their is a cycle
// (Because you we encountering the
// node second time).
if (s.contains(h))
return true;
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
s.add(h);
h = h.next;
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head;
if (detectLoop(head))
System.out.println("Loop found");
else
System.out.println("No Loop");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal. Python3
# Python3 program to detect loop
# in the linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize
# the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new
# node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print it
# the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print(temp.data, end=" ")
temp = temp.next
def detectLoop(self):
s = set()
temp = self.head
while (temp):
# If we have already has
# this node in hashmap it
# means their is a cycle
# (Because you we encountering
# the node second time).
if (temp in s):
return True
# If we are seeing the node for
# the first time, insert it in hash
s.add(temp)
temp = temp.next
return False
# Driver program for testing
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(20)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(10)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head
if(llist.detectLoop()):
print("Loop found")
else:
print("No Loop ")
# This code is contributed by Gitanjali.C#
// C# program to detect loop in a linked list
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class LinkedList {
// head of list
public Node head;
/* Linked list Node*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Returns true if there is a loop in linked
// list else returns false.
public static bool detectLoop(Node h)
{
HashSet s = new HashSet();
while (h != null) {
// If we have already has this node
// in hashmap it means their is a cycle
// (Because you we encountering the
// node second time).
if (s.Contains(h))
return true;
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
s.Add(h);
h = h.next;
}
return false;
}
/* Driver code*/
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head;
if (detectLoop(llist.head))
Console.WriteLine("Loop found");
else
Console.WriteLine("No Loop");
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
C++
// C++ program to detect loop in a linked list
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
int flag;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->flag = 0;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Returns true if there is a loop in linked list
// else returns false.
bool detectLoop(struct Node* h)
{
while (h != NULL) {
// If this node is already traverse
// it means there is a cycle
// (Because you we encountering the
// node for the second time).
if (h->flag == 1)
return true;
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, mark its flag as 1
h->flag = 1;
h = h->next;
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
cout << "Loop found";
else
cout << "No Loop";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Geetanjali Java
// Java program to detect loop in a linked list
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Link list node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
int flag;
};
static Node push(Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.flag = 0;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = head_ref;
// Move the head to point to the new node
head_ref = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// Returns true if there is a loop in linked
// list else returns false.
static boolean detectLoop(Node h)
{
while (h != null)
{
// If this node is already traverse
// it means there is a cycle
// (Because you we encountering the
// node for the second time).
if (h.flag == 1)
return true;
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, mark its flag as 1
h.flag = 1;
h = h.next;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 20);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 15);
head = push(head, 10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
System.out.print("Loop found");
else
System.out.print("No Loop");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiPython3
# Python3 program to detect loop in a linked list
''' Link list node '''
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.data = 0
self.next = None
self.flag = 0
def push(head_ref, new_data):
''' allocate node '''
new_node = Node();
''' put in the data '''
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.flag = 0;
''' link the old list off the new node '''
new_node.next = (head_ref);
''' move the head to point to the new node '''
(head_ref) = new_node;
return head_ref
# Returns true if there is a loop in linked list
# else returns false.
def detectLoop(h):
while (h != None):
# If this node is already traverse
# it means there is a cycle
# (Because you we encountering the
# node for the second time).
if (h.flag == 1):
return True;
# If we are seeing the node for
# the first time, mark its flag as 1
h.flag = 1;
h = h.next;
return False;
''' Driver program to test above function'''
if __name__=='__main__':
''' Start with the empty list '''
head = None;
head = push(head, 20);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 15);
head = push( head, 10)
''' Create a loop for testing '''
head.next.next.next.next = head;
if (detectLoop(head)):
print("Loop found")
else:
print("No Loop")
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program to detect loop in a linked list
using System;
class GFG{
// Link list node
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public int flag;
};
static Node push(Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.flag = 0;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = head_ref;
// Move the head to point to the new node
head_ref = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// Returns true if there is a loop in linked
// list else returns false.
static bool detectLoop(Node h)
{
while (h != null)
{
// If this node is already traverse
// it means there is a cycle
// (Because you we encountering the
// node for the second time).
if (h.flag == 1)
return true;
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, mark its flag as 1
h.flag = 1;
h = h.next;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 20);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 15);
head = push(head, 10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
Console.Write("Loop found");
else
Console.Write("No Loop");
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76Javascript
C++
// C++ program to detect loop in a linked list
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int detectLoop(Node* list)
{
Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
cout << "Loop found";
else
cout << "No Loop";
return 0;
}
// This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
// C program to detect loop in a linked list
#include
#include
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int detectLoop(struct Node* list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
printf("Loop found");
else
printf("No Loop");
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to detect loop in a linked list
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
void detectLoop()
{
Node slow_p = head, fast_p = head;
int flag = 0;
while (slow_p != null && fast_p != null
&& fast_p.next != null) {
slow_p = slow_p.next;
fast_p = fast_p.next.next;
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag == 1)
System.out.println("Loop found");
else
System.out.println("Loop not found");
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head;
llist.detectLoop();
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra. */Python
# Python program to detect loop in the linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print it the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
def detectLoop(self):
slow_p = self.head
fast_p = self.head
while(slow_p and fast_p and fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next.next
if slow_p == fast_p:
return
# Driver program for testing
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(20)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(10)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head
if(llist.detectLoop()):
print "Found Loop"
else:
print "No Loop"
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// C# program to detect loop in a linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
Boolean detectLoop()
{
Node slow_p = head, fast_p = head;
while (slow_p != null && fast_p != null
&& fast_p.next != null) {
slow_p = slow_p.next;
fast_p = fast_p.next.next;
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/* Driver code */
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head;
Boolean found = llist.detectLoop();
if (found) {
Console.WriteLine("Loop Found");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("No Loop");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi SinghJavascript
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
bool detectLoop(Node* head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node* temp = new Node;
while (head != NULL) {
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head->next == NULL) {
return false;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head->next == temp) {
return true;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node* nex = head->next;
// Make next point to temp
head->next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(1);
head->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next = newNode(3);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(5);
/* Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
bool found = detectLoop(head);
if (found)
cout << "Loop Found";
else
cout << "No Loop";
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to return first node of loop
class GFG {
static class Node {
int key;
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static boolean detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
while (head != null) {
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null) {
return false;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp) {
return true;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = newNode(1);
head.next = newNode(2);
head.next.next = newNode(3);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(5);
// Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) /
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
boolean found = detectLoop(head);
if (found)
System.out.println("Loop Found");
else
System.out.println("No Loop");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduPython3
# Python3 program to return first node of loop
# A binary tree node has data, pointer to
# left child and a pointer to right child
# Helper function that allocates a new node
# with the given data and None left and
# right pointers
class newNode:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# A utility function to pra linked list
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(head.key, end=" ")
head = head.next
print()
# Function to detect first node of loop
# in a linked list that may contain loop
def detectLoop(head):
# Create a temporary node
temp = ""
while (head != None):
# This condition is for the case
# when there is no loop
if (head.next == None):
return False
# Check if next is already
# pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp):
return True
# Store the pointer to the next node
# in order to get to it in the next step
nex = head.next
# Make next poto temp
head.next = temp
# Get to the next node in the list
head = nex
return False
# Driver Code
head = newNode(1)
head.next = newNode(2)
head.next.next = newNode(3)
head.next.next.next = newNode(4)
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(5)
# Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3)
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next
found = detectLoop(head)
if (found):
print("Loop Found")
else:
print("No Loop")
# This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10C#
// C# program to return first node of loop
using System;
public class GFG {
public class Node {
public int key;
public Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null) {
Console.Write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Boolean detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
while (head != null) {
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null) {
return false;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp) {
return true;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(1);
head.next = newNode(2);
head.next.next = newNode(3);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(5);
// Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3)
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
Boolean found = detectLoop(head);
if (found) {
Console.WriteLine("Loop Found");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("No Loop");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi SinghJavascript
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
/*returns distance between first and last node every time
* last node moves forwars*/
int distance(Node* first, Node* last)
{
/*counts no of nodes between first and last*/
int counter = 0;
Node* curr;
curr = first;
while (curr != last) {
counter += 1;
curr = curr->next;
}
return counter + 1;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
bool detectLoop(Node* head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node* temp = new Node;
Node *first, *last;
/*first always points to head*/
first = head;
/*last pointer initially points to head*/
last = head;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between current
* position of first and last*/
int current_length = 0;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between previous
* position of first and last*/
int prev_length = -1;
while (current_length > prev_length && last != NULL) {
// set prev_length to current length then update the
// current length
prev_length = current_length;
// distance is calculated
current_length = distance(first, last);
// last node points the next node
last = last->next;
}
if (last == NULL) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(1);
head->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next = newNode(3);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(5);
/* Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
bool found = detectLoop(head);
if (found)
cout << "Loop Found";
else
cout << "No Loop Found";
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to return first node of loop
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class Node
{
int key;
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/*returns distance between first and last node every time
* last node moves forwars*/
static int distance(Node first, Node last)
{
/*counts no of nodes between first and last*/
int counter = 0;
Node curr;
curr = first;
while (curr != last)
{
counter += 1;
curr = curr.next;
}
return counter + 1;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static boolean detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
Node first, last;
/*first always points to head*/
first = head;
/*last pointer initially points to head*/
last = head;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between current
* position of first and last*/
int current_length = 0;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between previous
* position of first and last*/
int prev_length = -1;
while (current_length > prev_length && last != null)
{
// set prev_length to current length then update the
// current length
prev_length = current_length;
// distance is calculated
current_length = distance(first, last);
// last node points the next node
last = last.next;
}
if (last == null)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(1);
head.next = newNode(2);
head.next.next = newNode(3);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(5);
/* Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
boolean found = detectLoop(head);
if (found)
System.out.print("Loop Found");
else
System.out.print("No Loop Found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1C#
// C# program to return first node of loop
using System;
public class GFG
{
public
class Node
{
public
int key;
public
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
Console.Write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
/*returns distance between first and last node every time
* last node moves forwars*/
static int distance(Node first, Node last)
{
/*counts no of nodes between first and last*/
int counter = 0;
Node curr;
curr = first;
while (curr != last)
{
counter += 1;
curr = curr.next;
}
return counter + 1;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static bool detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
Node first, last;
/*first always points to head*/
first = head;
/*last pointer initially points to head*/
last = head;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between current
* position of first and last*/
int current_length = 0;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between previous
* position of first and last*/
int prev_length = -1;
while (current_length > prev_length && last != null)
{
// set prev_length to current length then update the
// current length
prev_length = current_length;
// distance is calculated
current_length = distance(first, last);
// last node points the next node
last = last.next;
}
if (last == null)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(1);
head.next = newNode(2);
head.next.next = newNode(3);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(5);
/* Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
bool found = detectLoop(head);
if (found)
Console.Write("Loop Found");
else
Console.Write("No Loop Found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1Javascript
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
bool detectLoop(Node* head)
{
// If the head is null we will return false
if (!head)
return 0;
else {
// Traversing the linked list
// for detecting loop
while (head) {
// If loop found
if (head->key == -1) {
return true;
}
// Changing the data of visited node to any
// value which is outside th given range here it
// is supposed the given range is (1 <= Data on
// Node <= 10^3)
else {
head->key = -1;
head = head->next;
}
}
// If loop not found return false
return 0;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(1);
head->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next = newNode(3);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(5);
/* Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
bool found = detectLoop(head);
cout << found << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to return first node of loop
import java.util.*;
class LinkedList{
// Head of list
static Node head;
// Linked list Node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
static public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static boolean detectLoop(Node h)
{
// If the head is null we will return false
if (head == null)
return false;
else
{
// Traversing the linked list
// for detecting loop
while (head != null)
{
// If loop found
if (head.data == -1)
{
return true;
}
// Changing the data of visited node to any
// value which is outside th given range
// here it is supposed the given range is (1
// <= Data on Node <= 10^3)
else
{
head.data = -1;
head = head.next;
}
}
// If loop not found return false
return false;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(1);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(5);
/* Create a loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next;
if (detectLoop(llist.head))
System.out.println("1");
else
System.out.println("0");
}
}
// This code is contributed by RohitOberoiPython3
# Python program to return first node of loop
class Node:
def __init__(self,d):
self.data = d
self.next = None
head = None
def push(new_data):
global head
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = head
head=new_node
def detectLoop(h):
global head
if (head == None):
return False
else:
while (head != None):
if (head.data == -1):
return True
else:
head.data = -1
head = head.next
return False
push(1);
push(2);
push(3);
push(4);
push(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next
if (detectLoop(head)):
print("1")
else:
print("0")
# This code is contributed by patel2127.C#
// C# program to return first node of loop
using System;
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
public class GFG{
// Head of list
static Node head;
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
static public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static bool detectLoop(Node h)
{
// If the head is null we will return false
if (head == null)
return false;
else
{
// Traversing the linked list
// for detecting loop
while (head != null)
{
// If loop found
if (head.data == -1)
{
return true;
}
// Changing the data of visited node to any
// value which is outside th given range
// here it is supposed the given range is (1
// <= Data on Node <= 10^3)
else
{
head.data = -1;
head = head.next;
}
}
// If loop not found return false
return false;
}
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main (){
push(1);
push(2);
push(3);
push(4);
push(5);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
if (detectLoop(head))
Console.WriteLine("1");
else
Console.WriteLine("0");
}
}Javascript
Loop found复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
只需要遍历一次循环。 - 辅助空间: O(n)。
n 是在 hashmap 中存储值所需的空间。
解决方案2 :这个问题可以通过修改链表数据结构来解决,不用hashmap。
方法:这个解决方案需要修改基本的链表数据结构。
- 每个节点都有一个访问过的标志。
- 遍历链表并继续标记访问过的节点。
- 如果您再次看到访问过的节点,则存在循环。此解决方案在 O(n) 中有效,但需要每个节点的附加信息。
- 不需要修改基本数据结构的这种解决方案的变体可以使用散列来实现,只需将访问节点的地址存储在散列中,如果您看到散列中已经存在的地址,则存在一个循环。
C++
// C++ program to detect loop in a linked list
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
int flag;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->flag = 0;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Returns true if there is a loop in linked list
// else returns false.
bool detectLoop(struct Node* h)
{
while (h != NULL) {
// If this node is already traverse
// it means there is a cycle
// (Because you we encountering the
// node for the second time).
if (h->flag == 1)
return true;
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, mark its flag as 1
h->flag = 1;
h = h->next;
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
cout << "Loop found";
else
cout << "No Loop";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Geetanjali
Java
// Java program to detect loop in a linked list
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Link list node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
int flag;
};
static Node push(Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.flag = 0;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = head_ref;
// Move the head to point to the new node
head_ref = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// Returns true if there is a loop in linked
// list else returns false.
static boolean detectLoop(Node h)
{
while (h != null)
{
// If this node is already traverse
// it means there is a cycle
// (Because you we encountering the
// node for the second time).
if (h.flag == 1)
return true;
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, mark its flag as 1
h.flag = 1;
h = h.next;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 20);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 15);
head = push(head, 10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
System.out.print("Loop found");
else
System.out.print("No Loop");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program to detect loop in a linked list
''' Link list node '''
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.data = 0
self.next = None
self.flag = 0
def push(head_ref, new_data):
''' allocate node '''
new_node = Node();
''' put in the data '''
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.flag = 0;
''' link the old list off the new node '''
new_node.next = (head_ref);
''' move the head to point to the new node '''
(head_ref) = new_node;
return head_ref
# Returns true if there is a loop in linked list
# else returns false.
def detectLoop(h):
while (h != None):
# If this node is already traverse
# it means there is a cycle
# (Because you we encountering the
# node for the second time).
if (h.flag == 1):
return True;
# If we are seeing the node for
# the first time, mark its flag as 1
h.flag = 1;
h = h.next;
return False;
''' Driver program to test above function'''
if __name__=='__main__':
''' Start with the empty list '''
head = None;
head = push(head, 20);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 15);
head = push( head, 10)
''' Create a loop for testing '''
head.next.next.next.next = head;
if (detectLoop(head)):
print("Loop found")
else:
print("No Loop")
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# program to detect loop in a linked list
using System;
class GFG{
// Link list node
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public int flag;
};
static Node push(Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.flag = 0;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = head_ref;
// Move the head to point to the new node
head_ref = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// Returns true if there is a loop in linked
// list else returns false.
static bool detectLoop(Node h)
{
while (h != null)
{
// If this node is already traverse
// it means there is a cycle
// (Because you we encountering the
// node for the second time).
if (h.flag == 1)
return true;
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, mark its flag as 1
h.flag = 1;
h = h.next;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 20);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 15);
head = push(head, 10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
Console.Write("Loop found");
else
Console.Write("No Loop");
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76
Javascript
Loop found复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
只需要遍历一次循环。 - 辅助空间: O(1)。
不需要额外的空间。
解决方案 3 :Floyd 的循环查找算法
方法:这是最快的方法,如下所述:
- 使用两个指针遍历链表。
- 将一个指针(slow_p)移动一个,将另一个指针(fast_p)移动两个。
- 如果这些指针在同一节点相遇,则存在循环。如果指针不满足,则链表没有循环。
下图显示了detectloop函数在代码中的工作方式:
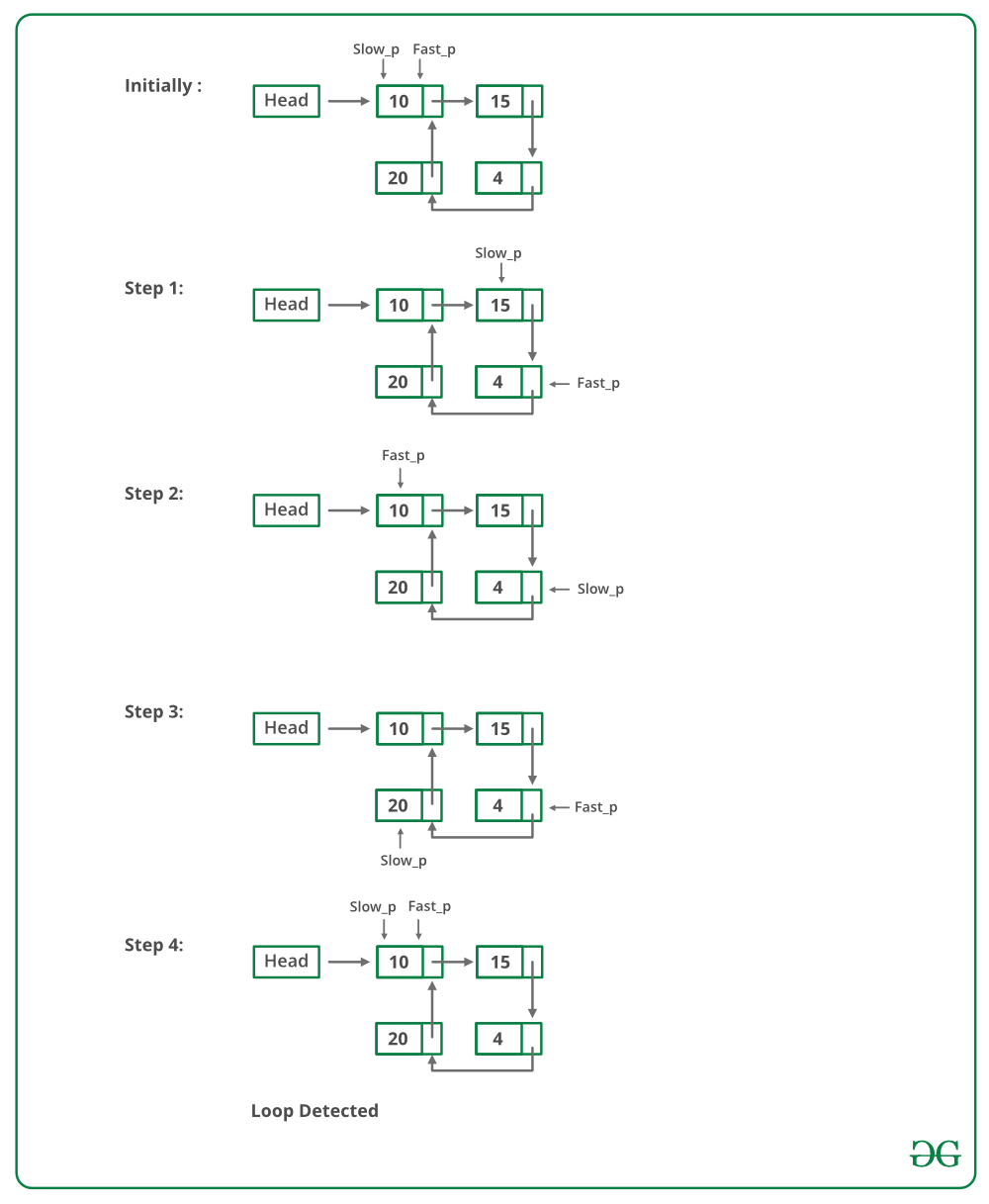
弗洛伊德循环查找算法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to detect loop in a linked list
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int detectLoop(Node* list)
{
Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
cout << "Loop found";
else
cout << "No Loop";
return 0;
}
// This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// C program to detect loop in a linked list
#include
#include
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int detectLoop(struct Node* list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
printf("Loop found");
else
printf("No Loop");
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to detect loop in a linked list
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
void detectLoop()
{
Node slow_p = head, fast_p = head;
int flag = 0;
while (slow_p != null && fast_p != null
&& fast_p.next != null) {
slow_p = slow_p.next;
fast_p = fast_p.next.next;
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag == 1)
System.out.println("Loop found");
else
System.out.println("Loop not found");
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head;
llist.detectLoop();
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra. */
Python
# Python program to detect loop in the linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print it the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
def detectLoop(self):
slow_p = self.head
fast_p = self.head
while(slow_p and fast_p and fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next.next
if slow_p == fast_p:
return
# Driver program for testing
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(20)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(10)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head
if(llist.detectLoop()):
print "Found Loop"
else:
print "No Loop"
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
C#
// C# program to detect loop in a linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
Boolean detectLoop()
{
Node slow_p = head, fast_p = head;
while (slow_p != null && fast_p != null
&& fast_p.next != null) {
slow_p = slow_p.next;
fast_p = fast_p.next.next;
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/* Driver code */
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head;
Boolean found = llist.detectLoop();
if (found) {
Console.WriteLine("Loop Found");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("No Loop");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Javascript
Loop found复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
只需要遍历一次循环。 - 辅助空间: O(1)。
不需要空间。
上述算法是如何工作的?
请参阅:Floyd 的慢速和快速指针方法是如何工作的?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Aup0kOWoMVg
方案四:不修改链表数据结构,标记访问过的节点
在此方法中,创建了一个临时节点。遍历的每个节点的下一个指针指向这个临时节点。这样,我们使用节点的下一个指针作为标志来指示该节点是否已被遍历。检查每个节点以查看下一个节点是否指向临时节点。在循环的第一个节点的情况下,我们第二次遍历它时,这个条件为真,因此我们发现循环存在。如果我们遇到一个指向 null 的节点,则循环不存在。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
bool detectLoop(Node* head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node* temp = new Node;
while (head != NULL) {
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head->next == NULL) {
return false;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head->next == temp) {
return true;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node* nex = head->next;
// Make next point to temp
head->next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(1);
head->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next = newNode(3);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(5);
/* Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
bool found = detectLoop(head);
if (found)
cout << "Loop Found";
else
cout << "No Loop";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to return first node of loop
class GFG {
static class Node {
int key;
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static boolean detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
while (head != null) {
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null) {
return false;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp) {
return true;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = newNode(1);
head.next = newNode(2);
head.next.next = newNode(3);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(5);
// Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) /
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
boolean found = detectLoop(head);
if (found)
System.out.println("Loop Found");
else
System.out.println("No Loop");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program to return first node of loop
# A binary tree node has data, pointer to
# left child and a pointer to right child
# Helper function that allocates a new node
# with the given data and None left and
# right pointers
class newNode:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# A utility function to pra linked list
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(head.key, end=" ")
head = head.next
print()
# Function to detect first node of loop
# in a linked list that may contain loop
def detectLoop(head):
# Create a temporary node
temp = ""
while (head != None):
# This condition is for the case
# when there is no loop
if (head.next == None):
return False
# Check if next is already
# pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp):
return True
# Store the pointer to the next node
# in order to get to it in the next step
nex = head.next
# Make next poto temp
head.next = temp
# Get to the next node in the list
head = nex
return False
# Driver Code
head = newNode(1)
head.next = newNode(2)
head.next.next = newNode(3)
head.next.next.next = newNode(4)
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(5)
# Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3)
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next
found = detectLoop(head)
if (found):
print("Loop Found")
else:
print("No Loop")
# This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10
C#
// C# program to return first node of loop
using System;
public class GFG {
public class Node {
public int key;
public Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null) {
Console.Write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Boolean detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
while (head != null) {
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null) {
return false;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp) {
return true;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(1);
head.next = newNode(2);
head.next.next = newNode(3);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(5);
// Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3)
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
Boolean found = detectLoop(head);
if (found) {
Console.WriteLine("Loop Found");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("No Loop");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Javascript
Loop Found复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
只需要遍历一次循环。 - 辅助空间: O(1)。
不需要空间。
解决方案 5:存储长度
在这个方法中,创建了两个指针,first(总是指向head)和last。每次最后一个指针移动时,我们计算 first 和 last 之间的节点数,并检查当前节点数 > 先前节点数,如果是,我们继续移动最后一个指针,否则意味着我们已经到达循环的末尾,所以我们相应地返回输出。
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
/*returns distance between first and last node every time
* last node moves forwars*/
int distance(Node* first, Node* last)
{
/*counts no of nodes between first and last*/
int counter = 0;
Node* curr;
curr = first;
while (curr != last) {
counter += 1;
curr = curr->next;
}
return counter + 1;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
bool detectLoop(Node* head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node* temp = new Node;
Node *first, *last;
/*first always points to head*/
first = head;
/*last pointer initially points to head*/
last = head;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between current
* position of first and last*/
int current_length = 0;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between previous
* position of first and last*/
int prev_length = -1;
while (current_length > prev_length && last != NULL) {
// set prev_length to current length then update the
// current length
prev_length = current_length;
// distance is calculated
current_length = distance(first, last);
// last node points the next node
last = last->next;
}
if (last == NULL) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(1);
head->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next = newNode(3);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(5);
/* Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
bool found = detectLoop(head);
if (found)
cout << "Loop Found";
else
cout << "No Loop Found";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to return first node of loop
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class Node
{
int key;
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/*returns distance between first and last node every time
* last node moves forwars*/
static int distance(Node first, Node last)
{
/*counts no of nodes between first and last*/
int counter = 0;
Node curr;
curr = first;
while (curr != last)
{
counter += 1;
curr = curr.next;
}
return counter + 1;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static boolean detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
Node first, last;
/*first always points to head*/
first = head;
/*last pointer initially points to head*/
last = head;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between current
* position of first and last*/
int current_length = 0;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between previous
* position of first and last*/
int prev_length = -1;
while (current_length > prev_length && last != null)
{
// set prev_length to current length then update the
// current length
prev_length = current_length;
// distance is calculated
current_length = distance(first, last);
// last node points the next node
last = last.next;
}
if (last == null)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(1);
head.next = newNode(2);
head.next.next = newNode(3);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(5);
/* Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
boolean found = detectLoop(head);
if (found)
System.out.print("Loop Found");
else
System.out.print("No Loop Found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
C#
// C# program to return first node of loop
using System;
public class GFG
{
public
class Node
{
public
int key;
public
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
Console.Write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
/*returns distance between first and last node every time
* last node moves forwars*/
static int distance(Node first, Node last)
{
/*counts no of nodes between first and last*/
int counter = 0;
Node curr;
curr = first;
while (curr != last)
{
counter += 1;
curr = curr.next;
}
return counter + 1;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static bool detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
Node first, last;
/*first always points to head*/
first = head;
/*last pointer initially points to head*/
last = head;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between current
* position of first and last*/
int current_length = 0;
/*current_length stores no of nodes between previous
* position of first and last*/
int prev_length = -1;
while (current_length > prev_length && last != null)
{
// set prev_length to current length then update the
// current length
prev_length = current_length;
// distance is calculated
current_length = distance(first, last);
// last node points the next node
last = last.next;
}
if (last == null)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(1);
head.next = newNode(2);
head.next.next = newNode(3);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(5);
/* Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
bool found = detectLoop(head);
if (found)
Console.Write("Loop Found");
else
Console.Write("No Loop Found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
Loop Found复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n 2 )
- 辅助空间: O(1)
另一种方法:
- 这是给定问题的最简单方法,我们唯一要做的就是为链表中不在给定范围内的节点的每个数据分配一个新值。
- 例子 假设 (1 <= 节点上的数据 <= 10^3) 然后在访问节点后将数据分配为 -1,因为它超出了给定的范围。
按照下面给出的代码更好地理解:
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
bool detectLoop(Node* head)
{
// If the head is null we will return false
if (!head)
return 0;
else {
// Traversing the linked list
// for detecting loop
while (head) {
// If loop found
if (head->key == -1) {
return true;
}
// Changing the data of visited node to any
// value which is outside th given range here it
// is supposed the given range is (1 <= Data on
// Node <= 10^3)
else {
head->key = -1;
head = head->next;
}
}
// If loop not found return false
return 0;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(1);
head->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next = newNode(3);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(5);
/* Create a loop for testing(5 is pointing to 3) */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
bool found = detectLoop(head);
cout << found << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to return first node of loop
import java.util.*;
class LinkedList{
// Head of list
static Node head;
// Linked list Node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
static public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static boolean detectLoop(Node h)
{
// If the head is null we will return false
if (head == null)
return false;
else
{
// Traversing the linked list
// for detecting loop
while (head != null)
{
// If loop found
if (head.data == -1)
{
return true;
}
// Changing the data of visited node to any
// value which is outside th given range
// here it is supposed the given range is (1
// <= Data on Node <= 10^3)
else
{
head.data = -1;
head = head.next;
}
}
// If loop not found return false
return false;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(1);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(5);
/* Create a loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next;
if (detectLoop(llist.head))
System.out.println("1");
else
System.out.println("0");
}
}
// This code is contributed by RohitOberoi
蟒蛇3
# Python program to return first node of loop
class Node:
def __init__(self,d):
self.data = d
self.next = None
head = None
def push(new_data):
global head
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = head
head=new_node
def detectLoop(h):
global head
if (head == None):
return False
else:
while (head != None):
if (head.data == -1):
return True
else:
head.data = -1
head = head.next
return False
push(1);
push(2);
push(3);
push(4);
push(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next
if (detectLoop(head)):
print("1")
else:
print("0")
# This code is contributed by patel2127.
C#
// C# program to return first node of loop
using System;
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
public class GFG{
// Head of list
static Node head;
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
static public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static bool detectLoop(Node h)
{
// If the head is null we will return false
if (head == null)
return false;
else
{
// Traversing the linked list
// for detecting loop
while (head != null)
{
// If loop found
if (head.data == -1)
{
return true;
}
// Changing the data of visited node to any
// value which is outside th given range
// here it is supposed the given range is (1
// <= Data on Node <= 10^3)
else
{
head.data = -1;
head = head.next;
}
}
// If loop not found return false
return false;
}
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main (){
push(1);
push(2);
push(3);
push(4);
push(5);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
if (detectLoop(head))
Console.WriteLine("1");
else
Console.WriteLine("0");
}
}
Javascript
1时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。