检测和删除链表中的循环
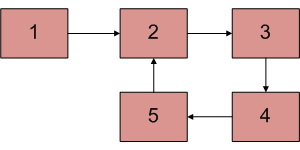
编写一个函数detectAndRemoveLoop()来检查给定的链表是否包含循环,如果存在循环,则删除循环并返回 true。如果列表不包含循环,则返回 false。下图显示了一个带有循环的链表。 detectAndRemoveLoop()必须将下面的列表更改为 1->2->3->4->5->NULL。
我们还建议阅读以下帖子作为此处讨论的解决方案的先决条件。
编写一个 C函数来检测链表中的循环
在尝试删除循环之前,我们必须检测它。上面帖子中讨论的技术可用于检测循环。要移除循环,我们需要做的就是获取指向循环最后一个节点的指针。例如,上图中值为 5 的节点。一旦我们有了指向最后一个节点的指针,我们就可以将这个节点的下一个节点设置为 NULL,循环就消失了。
我们可以轻松地使用哈希或访问节点技术(在上面提到的帖子中讨论过)来获取指向最后一个节点的指针。想法很简单:下一个已被访问(或散列)的第一个节点是最后一个节点。
我们还可以使用 Floyd Cycle Detection 算法来检测和删除循环。在弗洛伊德算法中,慢指针和快指针在循环节点相遇。我们可以使用这个循环节点来移除循环。当使用 Floyd 算法进行循环检测时,有以下两种不同的消除循环方法。
方法一(一一查)我们知道,当快慢指针在一个公共点相遇时,弗洛伊德循环检测算法就终止了。我们也知道这个公共点是循环节点之一(上图中的 2 或 3 或 4 或 5)。将 this 的地址存储在一个指针变量中,比如 ptr2。之后,从链表的头部开始,一一检查节点是否可以从 ptr2 到达。每当我们找到一个可达的节点时,我们就知道这个节点是链表中循环的起始节点,我们可以得到这个节点的前一个节点的指针。
C++
// C++ program to detect and remove loop in linked list
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to remove loop.
Used by detectAndRemoveLoop() */
void removeLoop(struct Node*, struct Node*);
/* This function detects and
removes loop in the list
If loop was there in the
list then it returns 1,
otherwise returns 0 */
int detectAndRemoveLoop(struct Node* list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next)
{
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
/* If slow_p and fast_p meet at
some point then
there is a loop */
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
removeLoop(slow_p, list);
/* Return 1 to indicate that loop is found */
return 1;
}
}
/* Return 0 to indeciate that ther is no loop*/
return 0;
}
/* Function to remove loop.
loop_node --> Pointer to
one of the loop nodes
head --> Pointer to the
start node of the linked list */
void removeLoop(struct Node* loop_node, struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* ptr1;
struct Node* ptr2;
/* Set a pointer to the beginning
of the Linked List and
move it one by one to find the
first node which is
part of the Linked List */
ptr1 = head;
while (1) {
/* Now start a pointer from
loop_node and check if
it ever reaches ptr2 */
ptr2 = loop_node;
while (ptr2->next != loop_node
&& ptr2->next != ptr1)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* If ptr2 reahced ptr1
then there is a loop. So
break the loop */
if (ptr2->next == ptr1)
break;
/* If ptr2 did't reach ptr1
then try the next node
* after ptr1 */
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
}
/* After the end of loop ptr2
is the last node of the
loop. So make next of ptr2 as NULL */
ptr2->next = NULL;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
struct Node* newNode(int key)
{
struct Node* temp = new Node();
temp->data = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
struct Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
cout << "Linked List after removing loop" << endl;
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code has been contributed by Striver C
// C program to detect and remove loop in linked list
#include
#include
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to remove loop.
Used by detectAndRemoveLoop() */
void removeLoop(struct Node*, struct Node*);
/* This function detects and
removes loop in the list
If loop was there in the
list then it returns 1,
otherwise returns 0 */
int detectAndRemoveLoop(struct Node* list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next)
{
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
/* If slow_p and fast_p
meet at some point then
there is a loop */
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
removeLoop(slow_p, list);
/* Return 1 to indicate
that loop is found */
return 1;
}
}
/* Return 0 to indeciate that ther is no loop*/
return 0;
}
/* Function to remove loop.
loop_node --> Pointer to one of the loop nodes
head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list */
void removeLoop(struct Node* loop_node, struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* ptr1;
struct Node* ptr2;
/* Set a pointer to the beginning of the Linked List and
move it one by one to find the first node which is
part of the Linked List */
ptr1 = head;
while (1) {
/* Now start a pointer from loop_node and check if
it ever reaches ptr2 */
ptr2 = loop_node;
while (ptr2->next != loop_node
&& ptr2->next != ptr1)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* If ptr2 reahced ptr1 then there is a loop. So
break the loop */
if (ptr2->next == ptr1)
break;
/* If ptr2 did't reach ptr1 then try the next node
* after ptr1 */
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
}
/* After the end of loop ptr2 is the last node of the
loop. So make next of ptr2 as NULL */
ptr2->next = NULL;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
struct Node* newNode(int key)
{
struct Node* temp
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
struct Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to detect and remove loop in linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null && fast != null
&& fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same point then loop
// is present
if (slow == fast) {
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node curr)
{
Node ptr1 = null, ptr2 = null;
/* Set a pointer to the beginning of the Linked List
and move it one by one to find the first node which
is part of the Linked List */
ptr1 = curr;
while (1 == 1) {
/* Now start a pointer from loop_node and check
if it ever reaches ptr2 */
ptr2 = loop;
while (ptr2.next != loop && ptr2.next != ptr1) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* If ptr2 reahced ptr1 then there is a loop. So
break the loop */
if (ptr2.next == ptr1) {
break;
}
/* If ptr2 did't reach ptr1 then try the next
* node after ptr1 */
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
}
/* After the end of loop ptr2 is the last node of
the loop. So make next of ptr2 as NULL */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
System.out.println(
"Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank JaiswalPython
# Python program to detect and remove loop in linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def detectAndRemoveLoop(self):
slow_p = fast_p = self.head
while(slow_p and fast_p and fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next.next
# If slow_p and fast_p meet at some poin
# then there is a loop
if slow_p == fast_p:
self.removeLoop(slow_p)
# Return 1 to indicate that loop if found
return 1
# Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop
return 0
# Function to remove loop
# loop node-> Pointer to one of the loop nodes
# head --> Pointer to the start node of the
# linked list
def removeLoop(self, loop_node):
# Set a pointer to the beginning of the linked
# list and move it one by one to find the first
# node which is part of the linked list
ptr1 = self.head
while(1):
# Now start a pointer from loop_node and check
# if it ever reaches ptr2
ptr2 = loop_node
while(ptr2.next != loop_node and ptr2.next != ptr1):
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# If ptr2 reached ptr1 then there is a loop.
# So break the loop
if ptr2.next == ptr1:
break
ptr1 = ptr1.next
# After the end of loop ptr2 is the lsat node of
# the loop. So make next of ptr2 as NULL
ptr2.next = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to prit the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
# Driver code
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(10)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(20)
llist.push(50)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next
llist.detectAndRemoveLoop()
print "Linked List after removing loop"
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// C# program to detect and remove loop in linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
public Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null && fast != null
&& fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same point then loop
// is present
if (slow == fast) {
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node curr)
{
Node ptr1 = null, ptr2 = null;
/* Set a pointer to the beginning of the Linked List
and move it one by one to find the first node which
is part of the Linked List */
ptr1 = curr;
while (1 == 1) {
/* Now start a pointer from loop_node and check
if it ever reaches ptr2 */
ptr2 = loop;
while (ptr2.next != loop && ptr2.next != ptr1) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* If ptr2 reahced ptr1 then there is a loop. So
break the loop */
if (ptr2.next == ptr1) {
break;
}
/* If ptr2 did't reach ptr1 then try the next
* node after ptr1 */
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
}
/* After the end of loop ptr2 is the last node of
the loop. So make next of ptr2 as NULL */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
list.head.next.next.next.next.next
= list.head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(list.head);
Console.WriteLine(
"Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
C++
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to remove loop. */
void removeLoop(struct Node*, struct Node*);
/* This function detects and removes loop in the list
If loop was there in the list then it returns 1,
otherwise returns 0 */
int detectAndRemoveLoop(struct Node* list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
// Iterate and find if loop exists or not
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
/* If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then there
is a loop */
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
removeLoop(slow_p, list);
/* Return 1 to indicate that loop is found */
return 1;
}
}
/* Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop*/
return 0;
}
/* Function to remove loop.
loop_node --> Pointer to one of the loop nodes
head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list */
void removeLoop(struct Node* loop_node, struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* ptr1 = loop_node;
struct Node* ptr2 = loop_node;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
unsigned int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1->next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2->next != ptr1)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2->next = NULL;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
// Print the list after loop removal
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
struct Node* newNode(int key)
{
struct Node* temp = new Node();
temp->data = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
struct Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
cout << "Linked List after removing loop \n";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code has been contributed by Striver C
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to remove loop. */
void removeLoop(struct Node*, struct Node*);
/* This function detects and removes loop in the list
If loop was there in the list then it returns 1,
otherwise returns 0 */
int detectAndRemoveLoop(struct Node* list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
// Iterate and find if loop exists or not
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
/* If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then there
is a loop */
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
removeLoop(slow_p, list);
/* Return 1 to indicate that loop is found */
return 1;
}
}
/* Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop*/
return 0;
}
/* Function to remove loop.
loop_node --> Pointer to one of the loop nodes
head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list */
void removeLoop(struct Node* loop_node, struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* ptr1 = loop_node;
struct Node* ptr2 = loop_node;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
unsigned int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1->next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2->next != ptr1)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2->next = NULL;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
// Print the list after loop removal
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
struct Node* newNode(int key)
{
struct Node* temp = new Node();
temp->data = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
struct Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
cout << "Linked List after removing loop \n";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code has been contributed by Striver Java
// Java program to detect and remove loop in linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same point then loop is present
if (slow == fast) {
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node head)
{
Node ptr1 = loop;
Node ptr2 = loop;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1.next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2.next != ptr1) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank JaiswalPython
# Python program to detect and remove loop in linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def detectAndRemoveLoop(self):
slow_p = fast_p = self.head
while(slow_p and fast_p and fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next.next
# If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then
# there is a loop
if slow_p == fast_p:
self.removeLoop(slow_p)
# Return 1 to indicate that loop is found
return 1
# Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop
return 0
# Function to remove loop
# loop_node --> pointer to one of the loop nodes
# head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list
def removeLoop(self, loop_node):
ptr1 = loop_node
ptr2 = loop_node
# Count the number of nodes in loop
k = 1
while(ptr1.next != ptr2):
ptr1 = ptr1.next
k += 1
# Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = self.head
# And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = self.head
for i in range(k):
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Move both pointers at the same place
# they will meet at loop starting node
while(ptr2 != ptr1):
ptr1 = ptr1.next
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Get pointer to the last node
while(ptr2.next != ptr1):
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Set the next node of the loop ending node
# to fix the loop
ptr2.next = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
# Driver program
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(10)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(20)
llist.push(50)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next
llist.detectAndRemoveLoop()
print "Linked List after removing loop"
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// A C# program to detect and remove loop in linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same
// point then loop is present
if (slow == fast) {
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node head)
{
Node ptr1 = loop;
Node ptr2 = loop;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1.next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2.next != ptr1) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = list.head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(list.head);
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
C++
// C++ program to detect and remove loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node* head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return;
Node *slow = head, *fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
// Search for loop using slow and
// fast pointers
while (fast && fast->next) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast)
{
slow = head;
// this check is needed when slow
// and fast both meet at the head of the LL
// eg: 1->2->3->4->5 and then
// 5->next = 1 i.e the head of the LL
if(slow == fast) {
while(fast->next != slow) fast = fast->next;
}
else {
while (slow->next != fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast->next = NULL; /* remove loop */
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = head;
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to detect
// and remove loop in linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return;
Node slow = node, fast = node;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = node;
if (slow != fast) {
while (slow.next != fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast.next = null; /* remove loop */
}
/* This case is added if fast and slow pointer meet at first position. */
else {
while(fast.next != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
}
fast.next = null;
}
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank JaiswalPython
# Python program to detect and remove loop
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def detectAndRemoveLoop(self):
if self.head is None:
return
if self.head.next is None:
return
slow = self.head
fast = self.head
# Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps respectively
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast is not None):
if fast.next is None:
break
if slow == fast:
break
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# if loop exists
if slow == fast:
slow = self.head
if ptr1 == ptr2:
while ptr2.next != ptr1:
ptr2 = ptr2.next
else:
while (slow.next != fast.next):
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
# Sinc fast.next is the looping point
fast.next = None # Remove loop
# Utility function to print the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
# Driver program
llist = LinkedList()
llist.head = Node(50)
llist.head.next = Node(20)
llist.head.next.next = Node(15)
llist.head.next.next.next = Node(4)
llist.head.next.next.next.next = Node(10)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next
llist.detectAndRemoveLoop()
print "Linked List after removing loop"
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// C# program to detect and remove loop in linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
public Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return;
Node slow = node, fast = node;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = node;
while (slow.next != fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast.next = null; /* remove loop */
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = list.head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(list.head);
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-JiC++
// C++ program to detect and remove loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
void hashAndRemove(Node* head)
{
// hash map to hash addresses of the linked list nodes
unordered_map node_map;
// pointer to last node
Node* last = NULL;
while (head != NULL) {
// if node not present in the map, insert it in the map
if (node_map.find(head) == node_map.end()) {
node_map[head]++;
last = head;
head = head->next;
}
// if present, it is a cycle, make the last node's next pointer NULL
else {
last->next = NULL;
break;
}
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = head;
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
// printList(head);
hashAndRemove(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to detect and remove loop in a linked list
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedList {
static Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
static public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Returns true if the loop is removed from the linked
// list else returns false.
static boolean removeLoop(Node h)
{
HashSet s = new HashSet();
Node prev = null;
while (h != null) {
// If we have already has this node
// in hashmap it means their is a cycle and we
// need to remove this cycle so set the next of
// the previous pointer with null.
if (s.contains(h)) {
prev.next = null;
return true;
}
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
else {
s.add(h);
prev = h;
h = h.next;
}
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head;
if (removeLoop(head)) {
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop");
llist.printList(head);
}
else
System.out.println("No Loop found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Animesh Nag. 输出:
Linked List after removing loop
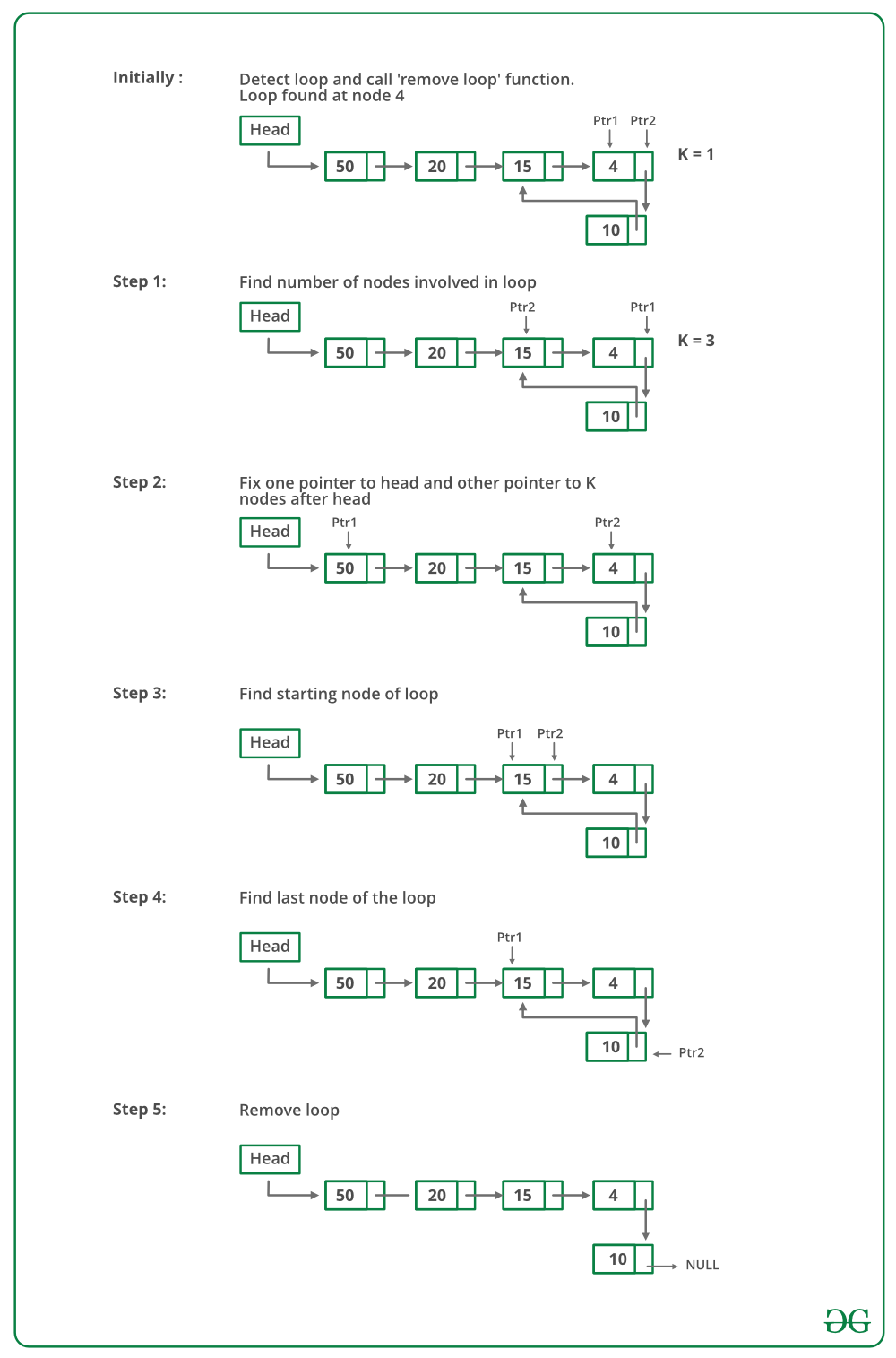
50 20 15 4 10 方法二(更好的解决方案)
- 该方法还依赖于 Floyd's Cycle 检测算法。
- 使用 Floyd 循环检测算法检测循环并获取指向循环节点的指针。
- 计算循环中的节点数。让计数为k。
- 将一个指针固定到头部,另一个指向头部的第 k 个节点。
- 以相同的速度移动两个指针,它们将在循环起始节点相遇。
- 获取指向循环最后一个节点的指针并将其下一个设为 NULL。
感谢 WgpShashank 提出这种方法。
下图是代码中“删除循环”函数的试运行:
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to remove loop. */
void removeLoop(struct Node*, struct Node*);
/* This function detects and removes loop in the list
If loop was there in the list then it returns 1,
otherwise returns 0 */
int detectAndRemoveLoop(struct Node* list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
// Iterate and find if loop exists or not
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
/* If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then there
is a loop */
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
removeLoop(slow_p, list);
/* Return 1 to indicate that loop is found */
return 1;
}
}
/* Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop*/
return 0;
}
/* Function to remove loop.
loop_node --> Pointer to one of the loop nodes
head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list */
void removeLoop(struct Node* loop_node, struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* ptr1 = loop_node;
struct Node* ptr2 = loop_node;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
unsigned int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1->next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2->next != ptr1)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2->next = NULL;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
// Print the list after loop removal
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
struct Node* newNode(int key)
{
struct Node* temp = new Node();
temp->data = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
struct Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
cout << "Linked List after removing loop \n";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code has been contributed by Striver
C
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to remove loop. */
void removeLoop(struct Node*, struct Node*);
/* This function detects and removes loop in the list
If loop was there in the list then it returns 1,
otherwise returns 0 */
int detectAndRemoveLoop(struct Node* list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
// Iterate and find if loop exists or not
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
/* If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then there
is a loop */
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
removeLoop(slow_p, list);
/* Return 1 to indicate that loop is found */
return 1;
}
}
/* Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop*/
return 0;
}
/* Function to remove loop.
loop_node --> Pointer to one of the loop nodes
head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list */
void removeLoop(struct Node* loop_node, struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* ptr1 = loop_node;
struct Node* ptr2 = loop_node;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
unsigned int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1->next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2->next != ptr1)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2->next = NULL;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
// Print the list after loop removal
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
struct Node* newNode(int key)
{
struct Node* temp = new Node();
temp->data = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
struct Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
cout << "Linked List after removing loop \n";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code has been contributed by Striver
Java
// Java program to detect and remove loop in linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same point then loop is present
if (slow == fast) {
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node head)
{
Node ptr1 = loop;
Node ptr2 = loop;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1.next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2.next != ptr1) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
Python
# Python program to detect and remove loop in linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def detectAndRemoveLoop(self):
slow_p = fast_p = self.head
while(slow_p and fast_p and fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next.next
# If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then
# there is a loop
if slow_p == fast_p:
self.removeLoop(slow_p)
# Return 1 to indicate that loop is found
return 1
# Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop
return 0
# Function to remove loop
# loop_node --> pointer to one of the loop nodes
# head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list
def removeLoop(self, loop_node):
ptr1 = loop_node
ptr2 = loop_node
# Count the number of nodes in loop
k = 1
while(ptr1.next != ptr2):
ptr1 = ptr1.next
k += 1
# Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = self.head
# And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = self.head
for i in range(k):
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Move both pointers at the same place
# they will meet at loop starting node
while(ptr2 != ptr1):
ptr1 = ptr1.next
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Get pointer to the last node
while(ptr2.next != ptr1):
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Set the next node of the loop ending node
# to fix the loop
ptr2.next = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
# Driver program
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(10)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(20)
llist.push(50)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next
llist.detectAndRemoveLoop()
print "Linked List after removing loop"
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
C#
// A C# program to detect and remove loop in linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same
// point then loop is present
if (slow == fast) {
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node head)
{
Node ptr1 = loop;
Node ptr2 = loop;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1.next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2.next != ptr1) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = list.head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(list.head);
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
输出:
Linked List after removing loop
50 20 15 4 10 方法三(优化方法二:不计算循环中的节点)
我们不需要计算 Loop 中的节点数。检测到循环后,如果我们从头开始慢指针并以相同的速度移动慢指针和快指针,直到快不相遇,它们将在循环开始时相遇。
这是如何运作的?
在弗洛伊德循环查找算法之后的某个时间点让慢速和快速相遇。下图显示了找到循环时的情况。
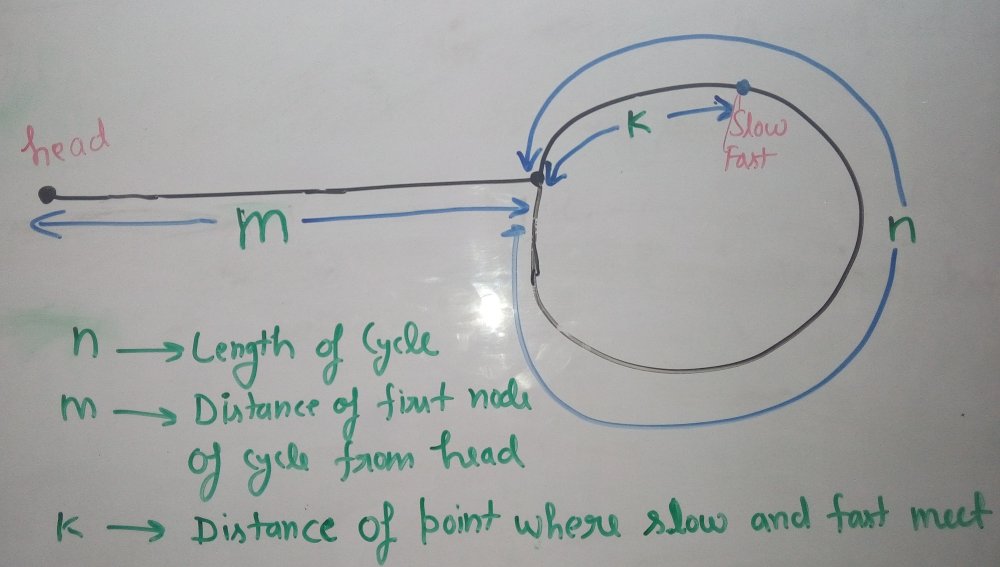
我们可以从上图中得出以下结论
Distance traveled by fast pointer = 2 * (Distance traveled
by slow pointer)
(m + n*x + k) = 2*(m + n*y + k)
Note that before meeting the point shown above, fast
was moving at twice speed.
x --> Number of complete cyclic rounds made by
fast pointer before they meet first time
y --> Number of complete cyclic rounds made by
slow pointer before they meet first time从上面的等式,我们可以得出以下结论
m + k = (x-2y)*n
Which means m+k is a multiple of n.
Thus we can write, m + k = i*n or m = i*n - k.
Hence, distance moved by slow pointer: m, is equal to distance moved by fast pointer:
i*n - k or (i-1)*n + n - k (cover the loop completely i-1 times and start from n-k).因此,如果我们再次以相同的速度移动两个指针,使得一个指针(比如慢速)从链表的头节点开始,另一个指针(比如快)从汇合点开始。当慢指针到达循环开始时(已经进行了 m 步),快指针也会移动 m 步,因为它们现在以相同的速度移动。由于 m+k 是 n 的倍数并且从 k 开始快速开始,因此它们会在开始时相遇。他们之前也能见面吗?否,因为慢指针在 m 步后第一次进入循环。
C++
// C++ program to detect and remove loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node* head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return;
Node *slow = head, *fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
// Search for loop using slow and
// fast pointers
while (fast && fast->next) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast)
{
slow = head;
// this check is needed when slow
// and fast both meet at the head of the LL
// eg: 1->2->3->4->5 and then
// 5->next = 1 i.e the head of the LL
if(slow == fast) {
while(fast->next != slow) fast = fast->next;
}
else {
while (slow->next != fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast->next = NULL; /* remove loop */
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = head;
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to detect
// and remove loop in linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return;
Node slow = node, fast = node;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = node;
if (slow != fast) {
while (slow.next != fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast.next = null; /* remove loop */
}
/* This case is added if fast and slow pointer meet at first position. */
else {
while(fast.next != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
}
fast.next = null;
}
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
Python
# Python program to detect and remove loop
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def detectAndRemoveLoop(self):
if self.head is None:
return
if self.head.next is None:
return
slow = self.head
fast = self.head
# Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps respectively
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast is not None):
if fast.next is None:
break
if slow == fast:
break
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# if loop exists
if slow == fast:
slow = self.head
if ptr1 == ptr2:
while ptr2.next != ptr1:
ptr2 = ptr2.next
else:
while (slow.next != fast.next):
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
# Sinc fast.next is the looping point
fast.next = None # Remove loop
# Utility function to print the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
# Driver program
llist = LinkedList()
llist.head = Node(50)
llist.head.next = Node(20)
llist.head.next.next = Node(15)
llist.head.next.next.next = Node(4)
llist.head.next.next.next.next = Node(10)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next
llist.detectAndRemoveLoop()
print "Linked List after removing loop"
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
C#
// C# program to detect and remove loop in linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
public Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return;
Node slow = node, fast = node;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = node;
while (slow.next != fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast.next = null; /* remove loop */
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = list.head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(list.head);
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
输出:
Linked List after removing loop
50 20 15 4 10 方法四 Hashing:对链表节点的地址进行Hash
我们可以在无序映射中散列链表节点的地址,并检查该元素是否已存在于映射中。如果它存在,我们已经到达一个已经存在一个循环的节点,因此我们需要使最后一个节点的下一个指针为NULL。
C++
// C++ program to detect and remove loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
void hashAndRemove(Node* head)
{
// hash map to hash addresses of the linked list nodes
unordered_map node_map;
// pointer to last node
Node* last = NULL;
while (head != NULL) {
// if node not present in the map, insert it in the map
if (node_map.find(head) == node_map.end()) {
node_map[head]++;
last = head;
head = head->next;
}
// if present, it is a cycle, make the last node's next pointer NULL
else {
last->next = NULL;
break;
}
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = head;
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
// printList(head);
hashAndRemove(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to detect and remove loop in a linked list
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedList {
static Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
static public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Returns true if the loop is removed from the linked
// list else returns false.
static boolean removeLoop(Node h)
{
HashSet s = new HashSet();
Node prev = null;
while (h != null) {
// If we have already has this node
// in hashmap it means their is a cycle and we
// need to remove this cycle so set the next of
// the previous pointer with null.
if (s.contains(h)) {
prev.next = null;
return true;
}
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
else {
s.add(h);
prev = h;
h = h.next;
}
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head;
if (removeLoop(head)) {
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop");
llist.printList(head);
}
else
System.out.println("No Loop found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Animesh Nag.
Linked List after removing loop
50 20 15 4 10 我们感谢 Shubham Agrawal 提出这个解决方案。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。