检查两棵树是否互为镜像的迭代方法
给定两棵二叉树。问题是检查两个二叉树是否是彼此的镜像。
二叉树的镜像:二叉树的镜像 T 是另一个二叉树 M(T),所有非叶节点的左右子节点互换。
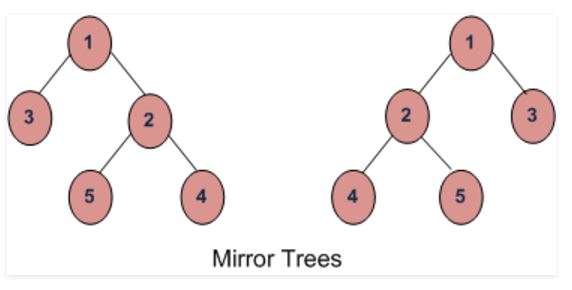
上图中的树是彼此的镜像。
我们已经讨论了检查两棵树是否镜像的递归解决方案。在这篇文章中讨论了迭代解决方案。
先决条件:使用栈迭代中序树遍历
方法:以下步骤是:
- 并行执行一棵树的迭代中序遍历和另一棵树的迭代反向中序遍历。
- 在这两次迭代遍历期间,检查相应节点是否具有相同的值。如果不相同,则它们不是彼此的镜子。
- 如果值相同,则检查在迭代中序遍历中的任何一点,根中的一个是否为空,另一个不为空。如果发生这种情况,那么它们就不是彼此的镜像。此检查确保它们是否具有相应的镜像结构。
- 否则,两棵树都是彼此的镜像。
反向中序遍历与中序遍历相反。在这种情况下,首先遍历右子树,然后是根,然后是左子树。
C++
// C++ implementation to check whether the two
// binary trees are mirrors of each other or not
#include
using namespace std;
// structure of a node in binary tree
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Utility function to create and return
// a new node for a binary tree
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node *temp = new Node();
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// function to check whether the two binary trees
// are mirrors of each other or not
string areMirrors(Node *root1, Node *root2)
{
stack st1, st2;
while (1)
{
// iterative inorder traversal of 1st tree and
// reverse inorder traversal of 2nd tree
while (root1 && root2)
{
// if the corresponding nodes in the two traversal
// have different data values, then they are not
// mirrors of each other.
if (root1->data != root2->data)
return "No";
st1.push(root1);
st2.push(root2);
root1 = root1->left;
root2 = root2->right;
}
// if at any point one root becomes null and
// the other root is not null, then they are
// not mirrors. This condition verifies that
// structures of tree are mirrors of each other.
if (!(root1 == NULL && root2 == NULL))
return "No";
if (!st1.empty() && !st2.empty())
{
root1 = st1.top();
root2 = st2.top();
st1.pop();
st2.pop();
/* we have visited the node and its left subtree.
Now, it's right subtree's turn */
root1 = root1->right;
/* we have visited the node and its right subtree.
Now, it's left subtree's turn */
root2 = root2->left;
}
// both the trees have been completely traversed
else
break;
}
// trees are mirrors of each other
return "Yes";
}
// Driver program to test above
int main()
{
// 1st binary tree formation
Node *root1 = newNode(1); /* 1 */
root1->left = newNode(3); /* / \ */
root1->right = newNode(2); /* 3 2 */
root1->right->left = newNode(5); /* / \ */
root1->right->right = newNode(4); /* 5 4 */
// 2nd binary tree formation
Node *root2 = newNode(1); /* 1 */
root2->left = newNode(2); /* / \ */
root2->right = newNode(3); /* 2 3 */
root2->left->left = newNode(4); /* / \ */
root2->left->right = newNode(5); /* 4 5 */
cout << areMirrors(root1, root2);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation to check whether the two
// binary trees are mirrors of each other or not
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
// structure of a node in binary tree
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
}
// Utility function to create and return
// a new node for a binary tree
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// function to check whether the two binary trees
// are mirrors of each other or not
static String areMirrors(Node root1, Node root2)
{
Stack st1 = new Stack ();
Stack st2 = new Stack ();
while (true)
{
// iterative inorder traversal of 1st tree and
// reverse inorder traversal of 2nd tree
while (root1 != null && root2 != null)
{
// if the corresponding nodes in the two traversal
// have different data values, then they are not
// mirrors of each other.
if (root1.data != root2.data)
return "No";
st1.push(root1);
st2.push(root2);
root1 = root1.left;
root2 = root2.right;
}
// if at any point one root becomes null and
// the other root is not null, then they are
// not mirrors. This condition verifies that
// structures of tree are mirrors of each other.
if (!(root1 == null && root2 == null))
return "No";
if (!st1.isEmpty() && !st2.isEmpty())
{
root1 = st1.peek();
root2 = st2.peek();
st1.pop();
st2.pop();
/* we have visited the node and its left subtree.
Now, it's right subtree's turn */
root1 = root1.right;
/* we have visited the node and its right subtree.
Now, it's left subtree's turn */
root2 = root2.left;
}
// both the trees have been completely traversed
else
break;
}
// trees are mirrors of each other
return "Yes";
}
// Driver program to test above
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 1st binary tree formation
Node root1 = newNode(1); /* 1 */
root1.left = newNode(3); /* / \ */
root1.right = newNode(2); /* 3 2 */
root1.right.left = newNode(5); /* / \ */
root1.right.right = newNode(4); /* 5 4 */
// 2nd binary tree formation
Node root2 = newNode(1); /* 1 */
root2.left = newNode(2); /* / \ */
root2.right = newNode(3); /* 2 3 */
root2.left.left = newNode(4); /* / \ */
root2.left.right = newNode(5); /* 4 5 */
System.out.println(areMirrors(root1, root2));
}
} Python3
# Python3 implementation to check whether
# the two binary trees are mirrors of each
# other or not
# Utility function to create and return
# a new node for a binary tree
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = self.right = None
# function to check whether the two binary
# trees are mirrors of each other or not
def areMirrors(root1, root2):
st1 = []
st2 = []
while (1):
# iterative inorder traversal of 1st tree
# and reverse inorder traversal of 2nd tree
while (root1 and root2):
# if the corresponding nodes in the
# two traversal have different data
# values, then they are not mirrors
# of each other.
if (root1.data != root2.data):
return "No"
st1.append(root1)
st2.append(root2)
root1 = root1.left
root2 = root2.right
# if at any point one root becomes None and
# the other root is not None, then they are
# not mirrors. This condition verifies that
# structures of tree are mirrors of each other.
if (not (root1 == None and root2 == None)):
return "No"
if (not len(st1) == 0 and not len(st2) == 0):
root1 = st1[-1]
root2 = st2[-1]
st1.pop(-1)
st2.pop(-1)
# we have visited the node and its left
# subtree. Now, it's right subtree's turn
root1 = root1.right
# we have visited the node and its right
# subtree. Now, it's left subtree's turn
root2 = root2.left
# both the trees have been
# completely traversed
else:
break
# trees are mirrors of each other
return "Yes"
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 1st binary tree formation
root1 = newNode(1) # 1
root1.left = newNode(3) # / \
root1.right = newNode(2) # 3 2
root1.right.left = newNode(5)# / \
root1.right.right = newNode(4) # 5 4
# 2nd binary tree formation
root2 = newNode(1) # 1
root2.left = newNode(2) # / \
root2.right = newNode(3) # 2 3
root2.left.left = newNode(4)# / \
root2.left.right = newNode(5)# 4 5
print(areMirrors(root1, root2))
# This code is contributed by pranchalKC#
// C# implementation to check whether the two
// binary trees are mirrors of each other or not
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG
{
// structure of a node in binary tree
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
}
// Utility function to create and return
// a new node for a binary tree
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// function to check whether the two binary trees
// are mirrors of each other or not
static String areMirrors(Node root1, Node root2)
{
Stack st1 = new Stack ();
Stack st2 = new Stack ();
while (true)
{
// iterative inorder traversal of 1st tree and
// reverse inorder traversal of 2nd tree
while (root1 != null && root2 != null)
{
// if the corresponding nodes in the two traversal
// have different data values, then they are not
// mirrors of each other.
if (root1.data != root2.data)
return "No";
st1.Push(root1);
st2.Push(root2);
root1 = root1.left;
root2 = root2.right;
}
// if at any point one root becomes null and
// the other root is not null, then they are
// not mirrors. This condition verifies that
// structures of tree are mirrors of each other.
if (!(root1 == null && root2 == null))
return "No";
if (st1.Count != 0 && st2.Count != 0)
{
root1 = st1.Peek();
root2 = st2.Peek();
st1.Pop();
st2.Pop();
/* we have visited the node and its left subtree.
Now, it's right subtree's turn */
root1 = root1.right;
/* we have visited the node and its right subtree.
Now, it's left subtree's turn */
root2 = root2.left;
}
// both the trees have been completely traversed
else
break;
}
// trees are mirrors of each other
return "Yes";
}
// Driver program to test above
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// 1st binary tree formation
Node root1 = newNode(1); /* 1 */
root1.left = newNode(3); /* / \ */
root1.right = newNode(2); /* 3 2 */
root1.right.left = newNode(5); /* / \ */
root1.right.right = newNode(4); /* 5 4 */
// 2nd binary tree formation
Node root2 = newNode(1); /* 1 */
root2.left = newNode(2); /* / \ */
root2.right = newNode(3); /* 2 3 */
root2.left.left = newNode(4); /* / \ */
root2.left.right = newNode(5); /* 4 5 */
Console.WriteLine(areMirrors(root1, root2));
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
输出:
Yes时间复杂度: O(n)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v70YxIpP
-IY