n叉树的镜像
给定一棵树,其中每个节点都包含可变数量的子节点,将树转换为其镜像。下图显示了一个示例。
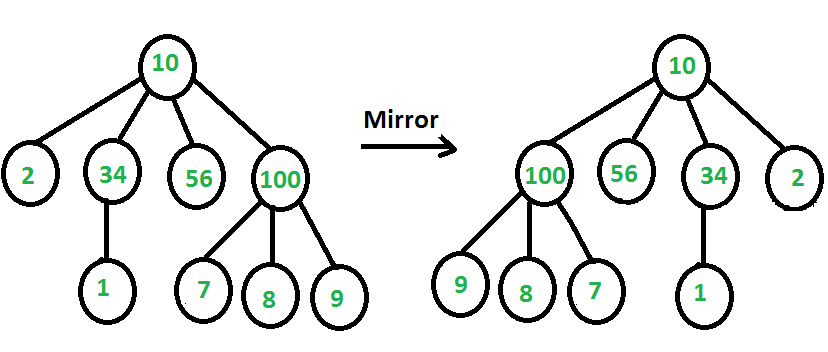
我们强烈建议您最小化您的浏览器并首先自己尝试。
树的节点表示为一个键和一个可变大小的子指针数组。这个想法类似于二叉树的镜像。对于每个节点,我们首先对其所有子节点进行递归,然后反转子指针数组。我们也可以通过其他方式来完成这些步骤,即先反转子指针数组,然后为子指针递归。
下面是上述想法的 C++ 实现。
C++
// C++ program to mirror an n-ary tree
#include
using namespace std;
// Represents a node of an n-ary tree
struct Node
{
int key;
vectorchild;
};
// Function to convert a tree to its mirror
void mirrorTree(Node * root)
{
// Base case: Nothing to do if root is NULL
if (root==NULL)
return;
// Number of children of root
int n = root->child.size();
// If number of child is less than 2 i.e.
// 0 or 1 we do not need to do anything
if (n < 2)
return;
// Calling mirror function for each child
for (int i=0; ichild[i]);
// Reverse vector (variable sized array) of child
// pointers
reverse(root->child.begin(), root->child.end());
}
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node *newNode(int key)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
return temp;
}
// Prints the n-ary tree level wise
void printNodeLevelWise(Node * root)
{
if (root==NULL)
return;
// Create a queue and enqueue root to it
queueq;
q.push(root);
// Do level order traversal. Two loops are used
// to make sure that different levels are printed
// in different lines
while (!q.empty())
{
int n = q.size();
while (n>0)
{
// Dequeue an item from queue and print it
Node * p = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << p->key << " ";
// Enqueue all childrent of the dequeued item
for (int i=0; ichild.size(); i++)
q.push(p->child[i]);
n--;
}
cout << endl; // Separator between levels
}
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
/* Let us create below tree
* 10
* / / \ \
* 2 34 56 100
* | / | \
* 1 7 8 9
*/
Node *root = newNode(10);
(root->child).push_back(newNode(2));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(34));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(56));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(100));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode(1));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode(7));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode(8));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode(9));
cout << "Level order traversal Before Mirroring\n";
printNodeLevelWise(root);
mirrorTree(root);
cout << "\nLevel order traversal After Mirroring\n";
printNodeLevelWise(root);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python program to mirror an n-ary tree
# Represents a node of an n-ary tree
class Node :
# Utility function to create a new tree node
def __init__(self ,key):
self.key = key
self.child = []
# Function to convert a tree to its mirror
def mirrorTree(root):
# Base Case : nothing to do if root is None
if root is None:
return
# Number of children of root
n = len(root.child)
# If number of child is less than 2 i.e.
# 0 or 1 we don't need to do anything
if n <2 :
return
# Calling mirror function for each child
for i in range(n):
mirrorTree(root.child[i]);
# Reverse variable sized array of child pointers
root.child.reverse()
# Prints the n-ary tree level wise
def printNodeLevelWise(root):
if root is None:
return
# create a queue and enqueue root to it
queue = []
queue.append(root)
# Do level order traversal. Two loops are used
# to make sure that different levels are printed
# in different lines
while(len(queue) >0):
n = len(queue)
while(n > 0) :
# Dequeue an item from queue and print it
p = queue[0]
queue.pop(0)
print(p.key,end=" ")
# Enqueue all children of the dequeued item
for index, value in enumerate(p.child):
queue.append(value)
n -= 1
print() # Separator between levels
# Driver Program
""" Let us create below tree
* 10
* / / \ \
* 2 34 56 100
* | / | \
* 1 7 8 9
"""
root = Node(10)
root.child.append(Node(2))
root.child.append(Node(34))
root.child.append(Node(56))
root.child.append(Node(100))
root.child[2].child.append(Node(1))
root.child[3].child.append(Node(7))
root.child[3].child.append(Node(8))
root.child[3].child.append(Node(9))
print ("Level order traversal Before Mirroring")
printNodeLevelWise(root)
mirrorTree(root)
print ("\nLevel Order traversal After Mirroring")
printNodeLevelWise(root)Javascript
输出:
Level order traversal Before Mirroring
10
2 34 56 100
1 7 8 9
Level order traversal After Mirroring
10
100 56 34 2
9 8 7 1