- MATLAB 中的集成(1)
- MATLAB-集成(1)
- MATLAB中的饼图
- MATLAB 2-D图(1)
- 根 matlab (1)
- matlab 轴 - Matlab (1)
- MATLAB中的饼图(1)
- MATLAB 2-D图
- : 在 matlab (1)
- matlab 轴 - Matlab 代码示例
- 集成 - 任何代码示例
- Python的集成方法(1)
- Python的集成方法
- matlab 标签 - Matlab (1)
- matlab 获取数组值 - Matlab (1)
- 集成测试(1)
- 集成测试
- 集成测试
- 集成测试
- 集成测试 (1)
- matlab转python(1)
- matlab if - Matlab (1)
- matlab 标签 - Matlab 代码示例
- matlab 获取数组值 - Matlab 代码示例
- matlab 符号根 - Matlab (1)
- jquery 集成 - Html (1)
- matlab if - Matlab 代码示例
- matlab 创建图像 - Matlab (1)
- matlab 从矩阵中获取行 - Matlab (1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-03 09:59:31 🧑 作者: Mango
集成处理两种本质上不同的问题。
-
在第一种类型中,给出了函数的导数,我们想找到函数。因此,我们基本上扭转了分化的过程。这种逆过程称为反微分,或者找到原始函数,或者找到不定积分。
-
第二类问题包括相加大量非常小的数量,然后随着数量的大小接近零而取一个极限,而项的数量趋于无穷大。这个过程导致定积分的定义。
定积分用于查找面积,体积,重心,惯性矩,力完成的功以及许多其他应用。
使用MATLAB查找不定积分
根据定义,如果函数f(x)的导数是f’(x),那么我们说f’(x)相对于x的不定积分是f(x)。例如,由于x 2的导数(相对于x)为2x,因此可以说2x的不定积分为x 2 。
在符号中-
f’(x 2 )= 2x ,因此,
∫2xdx = x 2
不定积分不是唯一的,因为对于常数c的任何值,x 2 + c的导数也将是2x。
这用符号表示为-
∫2xdx = x 2 + c
其中,c被称为“任意常数”。
MATLAB提供了一个用于计算表达式积分的int命令。为了导出一个函数的不定积分的表达式,我们写:
int(f);
例如,从我们之前的示例中-
syms x
int(2*x)
MATLAB执行上述语句并返回以下结果-
ans =
x^2
例子1
在此示例中,让我们找到一些常用表达式的积分。创建一个脚本文件并在其中键入以下代码-
syms x n
int(sym(x^n))
f = 'sin(n*t)'
int(sym(f))
syms a t
int(a*cos(pi*t))
int(a^x)
运行文件时,它显示以下结果-
ans =
piecewise([n == -1, log(x)], [n ~= -1, x^(n + 1)/(n + 1)])
f =
sin(n*t)
ans =
-cos(n*t)/n
ans =
(a*sin(pi*t))/pi
ans =
a^x/log(a)
例子2
创建一个脚本文件并在其中键入以下代码-
syms x n
int(cos(x))
int(exp(x))
int(log(x))
int(x^-1)
int(x^5*cos(5*x))
pretty(int(x^5*cos(5*x)))
int(x^-5)
int(sec(x)^2)
pretty(int(1 - 10*x + 9 * x^2))
int((3 + 5*x -6*x^2 - 7*x^3)/2*x^2)
pretty(int((3 + 5*x -6*x^2 - 7*x^3)/2*x^2))
请注意, pretty函数以更易读的格式返回表达式。
运行文件时,它显示以下结果-
ans =
sin(x)
ans =
exp(x)
ans =
x*(log(x) - 1)
ans =
log(x)
ans =
(24*cos(5*x))/3125 + (24*x*sin(5*x))/625 - (12*x^2*cos(5*x))/125 + (x^4*cos(5*x))/5 - (4*x^3*sin(5*x))/25 + (x^5*sin(5*x))/5
2 4
24 cos(5 x) 24 x sin(5 x) 12 x cos(5 x) x cos(5 x)
----------- + ------------- - -------------- + ------------
3125 625 125 5
3 5
4 x sin(5 x) x sin(5 x)
------------- + -----------
25 5
ans =
-1/(4*x^4)
ans =
tan(x)
2
x (3 x - 5 x + 1)
ans =
- (7*x^6)/12 - (3*x^5)/5 + (5*x^4)/8 + x^3/2
6 5 4 3
7 x 3 x 5 x x
- ---- - ---- + ---- + --
12 5 8 2
使用MATLAB查找定积分
根据定义,定积分基本上是和的极限。我们使用定积分来查找面积,例如曲线和x轴之间的面积以及两条曲线之间的面积。定积分也可以在其他情况下使用,其中所需的数量可以表示为总和的极限。
通过传递要计算积分的限制, int函数可用于确定积分。
计算
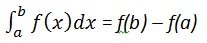
我们写,
int(x, a, b)
例如,计算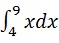 我们写-
我们写-
int(x, 4, 9)
MATLAB执行上述语句并返回以下结果-
ans =
65/2
以下是上述计算的八度等效-
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
f = x;
c = [1, 0];
integral = polyint(c);
a = polyval(integral, 9) - polyval(integral, 4);
display('Area: '), disp(double(a));
八度执行代码并返回以下结果-
Area:
32.500
可以使用Octave提供的quad()函数给出替代解决方案,如下所示:
pkg load symbolic
symbols
f = inline("x");
[a, ierror, nfneval] = quad(f, 4, 9);
display('Area: '), disp(double(a));
八度执行代码并返回以下结果-
Area:
32.500
例子1
让我们计算在x轴和曲线y = x 3 -2x + 5以及纵坐标x = 1和x = 2之间封闭的面积。
所需面积由-
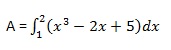
创建一个脚本文件并输入以下代码-
f = x^3 - 2*x +5;
a = int(f, 1, 2)
display('Area: '), disp(double(a));
运行文件时,它显示以下结果-
a =
23/4
Area:
5.7500
以下是上述计算的八度等效-
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
f = x^3 - 2*x +5;
c = [1, 0, -2, 5];
integral = polyint(c);
a = polyval(integral, 2) - polyval(integral, 1);
display('Area: '), disp(double(a));
八度执行代码并返回以下结果-
Area:
5.7500
可以使用Octave提供的quad()函数给出替代解决方案,如下所示:
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
f = inline("x^3 - 2*x +5");
[a, ierror, nfneval] = quad(f, 1, 2);
display('Area: '), disp(double(a));
八度执行代码并返回以下结果-
Area:
5.7500
例子2
找出曲线下的面积:f(x)= x 2 cos(x)对于-4≤x≤9。
创建一个脚本文件并编写以下代码-
f = x^2*cos(x);
ezplot(f, [-4,9])
a = int(f, -4, 9)
disp('Area: '), disp(double(a));
运行文件时,MATLAB绘制图形-
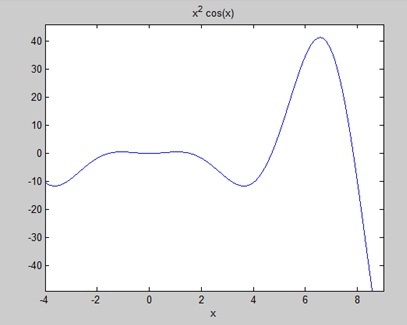
输出如下-
a =
8*cos(4) + 18*cos(9) + 14*sin(4) + 79*sin(9)
Area:
0.3326
以下是上述计算的八度等效-
pkg load symbolic
symbols
x = sym("x");
f = inline("x^2*cos(x)");
ezplot(f, [-4,9])
print -deps graph.eps
[a, ierror, nfneval] = quad(f, -4, 9);
display('Area: '), disp(double(a));