使用 Catch 处理异常的Java程序
例外是程序执行时发生的事件。由于此异常,程序的正常流程将受到干扰。每当方法中发生异常时,该方法都会创建一个对象并将该对象发送到运行时系统。比如需要打开的文件没有找到、类没有找到异常、算术异常、SQL异常等。
要处理这些异常,有 4 种标准技术:
- 试着抓
- 扔
- 投掷
- 使用 HandlerExceptionResolver 接口(仅在 Spring 框架中)
Catch 用法如下所述:
句法:
try {
// Put the code in the try block which may occur any
// kind of exception
}
catch (ExceptionName e) {
// handle the exception
}
下面讨论两个例子:
- 使用预定义的异常类
- 使用定义自己的异常类
示例 1:使用带有预定义异常类的 catch
这是由 try 和 catch 块处理的预定义异常的示例。
Java
// Importing Classes/Files
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Importing Scanner Class for user input
import java.util.Scanner;
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Taking input from user
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// Taking input of first number
System.out.println("Enter the first number");
Integer number1 = input.nextInt();
// Taking input of second number
System.out.println("Enter the second number");
Integer number2 = input.nextInt();
// Considering values in order to show execution
// number1 = 30; number2 = 10;
try {
// Dividing both the numbers
int result = number1 / number2;
// If number2 = 0, method will create the object
// of ArithmeticException class and throw it
System.out.println("Result is " + result);
// Printing the result
}
// If there is any exception in the try block
// then catch will handle the exception
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
// Message printed after catching the exception
System.out.println("Dividing by zero");
}
}
}Java
// Java Program to Use catch to handle the exception
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Taking input from keyboard/user
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// Enter any name
System.out.println("Enter the name");
String name = input.next();
try {
// Enter age
System.out.println("Enter the age");
// Using nextInt function to read integer
Integer age = input.nextInt();
if (age <= 18) {
MyException me = new MyException();
throw me;
// If age is less then equal to 18 then the
// object of MyException class will be throw
// here
}
else
// If age is greater then 18 i.e no exception is
// there then try block will execute
{
System.out.println("name:" + name);
System.out.println("age:" + age);
}
}
catch (MyException e)
// If the exception will occur then the object that
// throw in the try block will be copied in to this
// object
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
// User defined MyException class
class MyException extends RuntimeException {
public String toString()
{
// toString method will get Override here
return "Age must be greater then 18";
}
}输出:
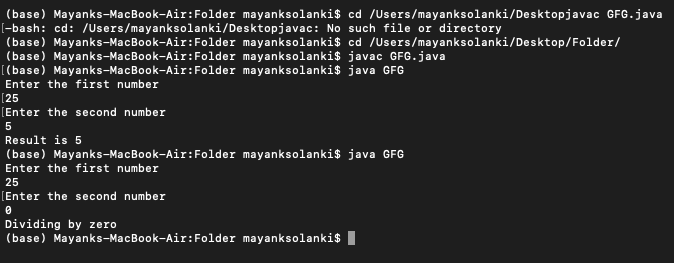
示例 2:通过定义异常类来使用 catch
在这个例子中,异常是用户定义的,其中异常类的写法如下:
Java
// Java Program to Use catch to handle the exception
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Taking input from keyboard/user
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// Enter any name
System.out.println("Enter the name");
String name = input.next();
try {
// Enter age
System.out.println("Enter the age");
// Using nextInt function to read integer
Integer age = input.nextInt();
if (age <= 18) {
MyException me = new MyException();
throw me;
// If age is less then equal to 18 then the
// object of MyException class will be throw
// here
}
else
// If age is greater then 18 i.e no exception is
// there then try block will execute
{
System.out.println("name:" + name);
System.out.println("age:" + age);
}
}
catch (MyException e)
// If the exception will occur then the object that
// throw in the try block will be copied in to this
// object
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
// User defined MyException class
class MyException extends RuntimeException {
public String toString()
{
// toString method will get Override here
return "Age must be greater then 18";
}
}
Input 1:
Enter the name : Geek
Enter the age: 18
Output:
Age must be greater then 18 // Age is equal to 18 so the exception is occured
Input 2:
Enter the name : Geek
Enter the age: 20
Output:
name: Geek
age:20 // Age is greater then 18 so no exception.