Java中的SortedMap接口与示例
SortedMap 是集合框架中的一个接口。该接口扩展了 Map 接口并提供了其元素的总排序(元素可以按键的排序顺序遍历)。实现这个接口的类是TreeMap。
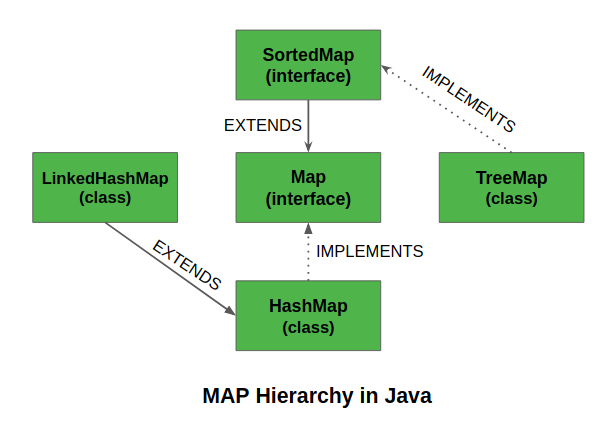
SortedMap 的主要特征是它按照键的自然顺序或指定的比较器对键进行排序。因此,当您想要满足以下条件的地图时,请考虑使用 TreeMap:
- 不允许空键或空值。
- 键按自然顺序或指定的比较器排序。
类型参数:
- K - 此映射维护的键的类型
- V – 映射值的类型
SortedMap 的父接口是 Map
SortedMap 的子接口是 ConcurrentNavigableMap
SortedMap 由 ConcurrentSkipListMap、TreeMap 实现。
宣言:
public interface SortedMap extends Map
{
Comparator comparator();
SortedMap subMap(K fromKey, K toKey);
SortedMap headMap(K toKey);
SortedMap tailMap(K fromKey);
K firstKey();
K lastKey();
}
例子:
Java
// Java code to demonstrate SortedMap Interface
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class SortedMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedMap sm
= new TreeMap();
sm.put(new Integer(2), "practice");
sm.put(new Integer(3), "quiz");
sm.put(new Integer(5), "code");
sm.put(new Integer(4), "contribute");
sm.put(new Integer(1), "geeksforgeeks");
Set s = sm.entrySet();
// Using iterator in SortedMap
Iterator i = s.iterator();
// Traversing map. Note that the traversal
// produced sorted (by keys) output .
while (i.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)i.next();
int key = (Integer)m.getKey();
String value = (String)m.getValue();
System.out.println("Key : " + key
+ " value : " + value);
}
}
} Java
// Java program add the elements in the SortedMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Default Initialization of a
// SortedMap
SortedMap tm1 = new TreeMap();
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap tm2
= new TreeMap();
// Inserting the Elements
tm1.put(3, "Geeks");
tm1.put(2, "For");
tm1.put(1, "Geeks");
tm2.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
tm2.put(new Integer(2), "For");
tm2.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
System.out.println(tm1);
System.out.println(tm2);
}
} Java
// Java program to change
// the elements in SortedMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap tm
= new TreeMap();
// Inserting the Elements
tm.put(3, "Geeks");
tm.put(2, "Geeks");
tm.put(1, "Geeks");
System.out.println(tm);
tm.put(2, "For");
System.out.println(tm);
}
} Java
// Java program to remove the
// elements from SortedMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap tm
= new TreeMap();
// Inserting the Elements
tm.put(3, "Geeks");
tm.put(2, "Geeks");
tm.put(1, "Geeks");
tm.put(4, "For");
System.out.println(tm);
tm.remove(4);
System.out.println(tm);
}
} Java
// Java program to iterate through SortedMap
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap tm
= new TreeMap();
// Inserting the Elements
tm.put(3, "Geeks");
tm.put(2, "For");
tm.put(1, "Geeks");
for (Map.Entry mapElement : tm.entrySet()) {
int key = (int)mapElement.getKey();
// Finding the value
String value = (String)mapElement.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// creation of SortedMap object using
// the TreeMap class
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedMap tm
= new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
public int compare(String a, String b)
{
return b.compareTo(a);
}
});
// Adding elements into the TreeMap
// using put()
tm.put("India", "1");
tm.put("Australia", "2");
tm.put("South Africa", "3");
// Displaying the TreeMap
System.out.println(tm);
// Removing items from TreeMap
// using remove()
tm.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("Map after removing "
+ "Australia:" + tm);
}
} 输出:
Key : 1 value : geeksforgeeks
Key : 2 value : practice
Key : 3 value : quiz
Key : 4 value : contribute
Key : 5 value : code
创建 SortedMap 对象
由于 SortedMap 是一个接口,因此无法创建 SortedMap 类型的对象。我们总是需要一个扩展这个列表的类来创建一个对象。而且,在Java 1.5 中引入泛型之后,可以限制可以存储在 SortedMap 中的对象类型。这个类型安全的映射可以定义为:
// Obj1, Obj2 are the type of the object to be stored in SortedMap
SortedMap
对 SortedMap 执行各种操作
由于 SortedMap 是一个接口,它只能与实现该接口的类一起使用。 TreeMap是实现 SortedMap 接口的类。现在,让我们看看如何在 TreeMap 上执行一些常用的操作。
1. 添加元素:为了向 SortedMap 添加元素,我们可以使用put()方法。但是,插入顺序不会保留在 TreeMap 中。在内部,对于每个元素,键都会按升序进行比较和排序。
Java
// Java program add the elements in the SortedMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Default Initialization of a
// SortedMap
SortedMap tm1 = new TreeMap();
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap tm2
= new TreeMap();
// Inserting the Elements
tm1.put(3, "Geeks");
tm1.put(2, "For");
tm1.put(1, "Geeks");
tm2.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
tm2.put(new Integer(2), "For");
tm2.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
System.out.println(tm1);
System.out.println(tm2);
}
}
输出:
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
2.更改元素:添加元素后,如果我们想更改元素,可以通过 put() 方法再次添加元素来完成。由于 SortedMap 中的元素是使用键索引的,因此可以通过简单地插入我们希望更改的键的更新值来更改键的值。
Java
// Java program to change
// the elements in SortedMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap tm
= new TreeMap();
// Inserting the Elements
tm.put(3, "Geeks");
tm.put(2, "Geeks");
tm.put(1, "Geeks");
System.out.println(tm);
tm.put(2, "For");
System.out.println(tm);
}
}
输出:
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}3.移除元素:为了从SortedMap中移除一个元素,我们可以使用remove()方法。此方法获取键值并从此 SortedMap 中删除该键的映射(如果它存在于映射中)。
Java
// Java program to remove the
// elements from SortedMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap tm
= new TreeMap();
// Inserting the Elements
tm.put(3, "Geeks");
tm.put(2, "Geeks");
tm.put(1, "Geeks");
tm.put(4, "For");
System.out.println(tm);
tm.remove(4);
System.out.println(tm);
}
}
输出:
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks, 4=For}
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}4.遍历SortedMap:遍历Map有多种方式。最著名的方法是使用增强的 for 循环并获取密钥。键的值是通过使用 getValue() 方法找到的。
Java
// Java program to iterate through SortedMap
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap tm
= new TreeMap();
// Inserting the Elements
tm.put(3, "Geeks");
tm.put(2, "For");
tm.put(1, "Geeks");
for (Map.Entry mapElement : tm.entrySet()) {
int key = (int)mapElement.getKey();
// Finding the value
String value = (String)mapElement.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
}
}
输出:
1 : Geeks
2 : For
3 : Geeks实现 SortedMap 接口的类是 TreeMap。
在集合框架中实现的 TreeMap 类是 SortedMap 接口的实现,而 SortedMap 扩展了 Map 接口。它的行为类似于一个简单的映射,不同之处在于它以排序格式存储键。 TreeMap 使用树数据结构进行存储。对象按排序的升序存储。但是我们也可以通过传递一个比较器以降序存储。让我们看看如何使用这个类创建一个 SortedMap 对象。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// creation of SortedMap object using
// the TreeMap class
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedMap tm
= new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
public int compare(String a, String b)
{
return b.compareTo(a);
}
});
// Adding elements into the TreeMap
// using put()
tm.put("India", "1");
tm.put("Australia", "2");
tm.put("South Africa", "3");
// Displaying the TreeMap
System.out.println(tm);
// Removing items from TreeMap
// using remove()
tm.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("Map after removing "
+ "Australia:" + tm);
}
}
输出:
{South Africa=3, India=1, Australia=2}
Map after removing Australia:{South Africa=3, India=1}SortedMap 接口的方法
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| comparator() | Returns the comparator used to order the keys in this map, or null if this map uses the natural ordering of its keys. |
| entrySet() | Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map. |
| firstKey() | Returns the first (lowest) key currently in this map. |
| headMap(K toKey) | Returns a view of the portion of this map whose keys are strictly less than toKey. |
| keySet() | Returns a Set view of the keys contained in this map. |
| lastKey() | Returns the last (highest) key currently in this map. |
| subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) | Returns a view of the portion of this map whose keys range from fromKey, inclusive, to toKey, exclusive. |
| tailMap(K fromKey) | Returns a view of the portion of this map whose keys are greater than or equal to fromKey. |
| values() | Returns a Collection view of the values contained in this map. |
从接口Java.util.Map 继承的方法
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| clear() | This method is used to clear and remove all of the elements or mappings from a specified Map collection. |
| containsKey(Object) | This method is used to check whether a particular key is being mapped into the Map or not. It takes the key element as a parameter and returns True if that element is mapped in the map. |
| containsValue(Object) | This method is used to check whether a particular value is being mapped by a single or more than one key in the Map. It takes the value as a parameter and returns True if that value is mapped by any of the key in the map. |
| entrySet() | This method is used to create a set out of the same elements contained in the map. It basically returns a set view of the map or we can create a new set and store the map elements into them. |
| equals(Object) | This method is used to check for equality between two maps. It verifies whether the elements of one map passed as a parameter is equal to the elements of this map or not. |
| get(Object) | This method is used to retrieve or fetch the value mapped by a particular key mentioned in the parameter. It returns NULL when the map contains no such mapping for the key. |
| hashCode() | This method is used to generate a hashCode for the given map containing key and values. |
| isEmpty() | This method is used to check if a map is having any entry for key and value pairs. If no mapping exists, then this returns true. |
| keySet() | This method is used to return a Set view of the keys contained in this map. The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are reflected in the set, and vice-versa. |
| put(Object, Object) | This method is used to associate the specified value with the specified key in this map. |
| putAll(Map) | This method is used to copy all of the mappings from the specified map to this map. |
| remove(Object) | This method is used to remove the mapping for a key from this map if it is present in the map. |
| size() | This method is used to return the number of key/value pairs available in the map. |
| values() | This method is used to create a collection out of the values of the map. It basically returns a Collection view of the values in the HashMap. |