📌 相关文章
- 取证 (1)
- Python取证-网络取证
- Python取证-网络取证(1)
- Python取证-移动取证
- Python取证-移动取证(1)
- Python中的哈希函数(1)
- Python取证-内存和取证(1)
- Python取证-内存和取证
- Linux中的Python取证(1)
- Linux中的Python取证
- Python取证-安装Python(1)
- Python取证-安装Python
- Python取证-基本取证应用(1)
- Python取证-基本取证应用
- Python代码示例中的哈希函数
- Python取证-索引(1)
- Python取证-索引
- Python取证Python模块
- Python取证Python模块(1)
- Python取证-搜索(1)
- Python取证-搜索
- 取证 - 任何代码示例
- Python取证教程(1)
- Python取证教程
- Python取证-云的实现(1)
- Python取证-云的实现
- Python取证-简介(1)
- Python取证-简介
- Python哈希表
📜 Python取证-哈希函数
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-06 05:28:00 🧑 作者: Mango
散列函数被定义为在一个大的数据量映射到一个固定的值与指定的长度的函数。此函数确保相同的输入导致相同的输出,该输出实际上定义为哈希和。哈希值包括具有特定信息的特征。
该函数实际上是无法恢复的。因此,几乎不可能进行任何类似暴力攻击的第三方攻击。同样,这种算法称为单向密码算法。
理想的加密哈希函数具有四个主要属性-
- 计算任何给定输入的哈希值必须很容易。
- 从其哈希值生成原始输入必须是不可行的。
- 在不更改哈希的情况下修改输入必须是不可行的。
- 找到具有相同哈希值的两个不同输入必须是不可行的。
例
考虑以下示例,该示例有助于使用十六进制格式的字符来匹配密码。
import uuid
import hashlib
def hash_password(password):
# userid is used to generate a random number
salt = uuid.uuid4().hex #salt is stored in hexadecimal value
return hashlib.sha256(salt.encode() + password.encode()).hexdigest() + ':' + salt
def check_password(hashed_password, user_password):
# hexdigest is used as an algorithm for storing passwords
password, salt = hashed_password.split(':')
return password == hashlib.sha256(salt.encode()
+ user_password.encode()).hexdigest()
new_pass = raw_input('Please enter required password ')
hashed_password = hash_password(new_pass)
print('The string to store in the db is: ' + hashed_password)
old_pass = raw_input('Re-enter new password ')
if check_password(hashed_password, old_pass):
print('Yuppie!! You entered the right password')
else:
print('Oops! I am sorry but the password does not match')
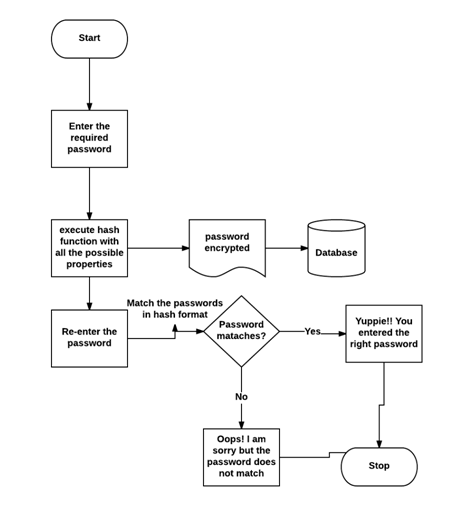
流程图
我们借助以下流程图解释了该程序的逻辑-
输出
我们的代码将产生以下输出-
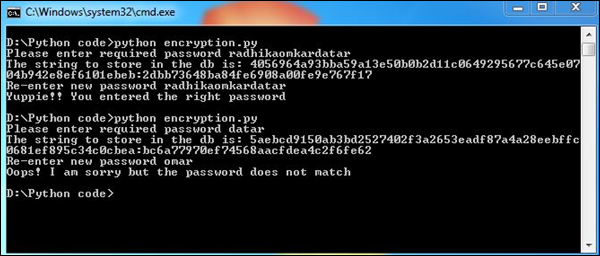
输入两次的密码与哈希函数匹配。这样可以确保两次输入的密码准确无误,这有助于收集有用的数据并将其保存为加密格式。