- JavaScript事件处理(1)
- JavaScript事件处理
- Java中的事件处理(1)
- Java中的事件处理
- Jython-安装
- Jython-安装(1)
- jQuery-事件处理
- jQuery-事件处理(1)
- Jython-循环
- Jython-循环(1)
- Android-事件处理
- Android-事件处理(1)
- Jython-模块
- Jython-模块(1)
- Laravel-事件处理
- Laravel-事件处理(1)
- Jython教程(1)
- Jython教程
- 讨论Jython(1)
- 讨论Jython
- Jython-概述(1)
- Jython-概述
- Matplotlib 中的事件处理
- Matplotlib 中的事件处理(1)
- Jython-Java应用程序(1)
- Jython-Java应用程序
- Jython-菜单(1)
- Jython-菜单
- Spring中的事件处理
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-08 07:20:39 🧑 作者: Mango
Java swing中的事件处理要求控件(如JButton或JList等)应与各自的事件侦听器一起注册。事件监听器接口或相应的Adapter类需要被实现或被重写其事件处理方法而被子类化。在Jython中,事件处理非常简单。我们可以将任何函数作为与控件相对应的事件处理函数的属性来传递。
首先让我们看看如何用Java处理click事件。
首先,我们必须导入java.awt.event包。接下来,扩展JFrame的类必须实现ActionListener接口。
public class btnclick extends JFrame implements ActionListener
然后,我们必须声明JButton对象,将其添加到框架的ContentPane中,然后通过addActionListener()方法向ActionListener注册。
JButton b1 = new JButton("Click here");
getContentPane().add(b1);
b1.addActionListener(this);
现在,必须重写ActionListener接口的actionPerformed()方法以处理ActionEvent。
以下是整个Java代码-
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class btnclick extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
btnclick() {
JButton b1 = new JButton("Click here");
getContentPane().add(b1);
b1.addActionListener(this);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("Clicked");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
btnclick b = new btnclick();
b.setSize(300,200);
b.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
b.setVisible(true);
}
}
现在,我们将编写与相同代码等效的Jython代码。
首先,我们不需要导入ActionEvent或ActionListener,因为Jython的动态类型允许我们避免在代码中提及这些类。
其次,不需要实现或将ActionListener子类化。而是直接将所有用户定义的函数作为actionPerformed bean属性的值提供给JButton构造函数。
button = JButton('Click here!', actionPerformed = clickhere)
clickhere()函数定义为常规Jython函数,该函数处理按钮上的click事件。
def change_text(event):
print clicked!'
这是Jython的等效代码。
from javax.swing import JFrame, JButton
frame = JFrame("Hello")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(300,200)
def clickhere(event):
print "clicked"
btn = JButton("Add", actionPerformed = clickhere)
frame.add(btn)
frame.setVisible(True)
Java和Jython代码的输出是相同的。单击该按钮时,它将在控制台上打印“已单击”消息。

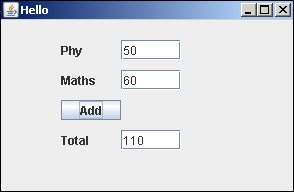
在下面的Jython代码中,在JFrame窗口上提供了两个JTextField对象,以在’phy’和’maths’中输入标记。单击JButton对象时将执行add()函数。
btn = JButton("Add", actionPerformed = add)
add()函数通过getText()方法读取两个文本字段的内容,并将它们解析为整数,以便可以执行加法运算。然后,将结果通过setText()方法放入第三个文本字段中。
def add(event):
print "add"
ttl = int(txt1.getText())+int(txt2.getText())
txt3.setText(str(ttl))
完整的代码如下-
from javax.swing import JFrame, JLabel, JButton, JTextField
from java.awt import Dimension
frame = JFrame("Hello")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(300,200)
frame.setLayout(None)
def add(event):
print "add"
ttl = int(txt1.getText())+int(txt2.getText())
txt3.setText(str(ttl))
lbl1 = JLabel("Phy")
lbl1.setBounds(60,20,40,20)
txt1 = JTextField(10)
txt1.setBounds(120,20,60,20)
lbl2 = JLabel("Maths")
lbl2.setBounds(60,50,40,20)
txt2 = JTextField(10)
txt2.setBounds(120, 50, 60,20)
btn = JButton("Add", actionPerformed = add)
btn.setBounds(60,80,60,20)
lbl3 = JLabel("Total")
lbl3.setBounds(60,110,40,20)
txt3 = JTextField(10)
txt3.setBounds(120, 110, 60,20)
frame.add(lbl1)
frame.add(txt1)
frame.add(lbl2)
frame.add(txt2)
frame.add(btn)
frame.add(lbl3)
frame.add(txt3)
frame.setVisible(True)
当从命令提示符处执行以上代码时,将出现以下窗口。输入“ Phy”,“数学”的标记,然后单击“添加”按钮。结果将相应显示。
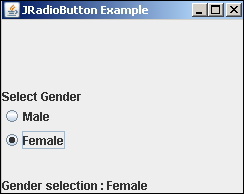
Jython JRadioButton事件
JRadioButton类在javax.swing包中定义。它创建具有打开或关闭状态的可选切换按钮。如果在ButtonGroup中添加了多个单选按钮,则它们的选择是互斥的。
在下面的示例中,将JRadioButton类的两个对象和两个JLabel添加到垂直BoxLayout中的Jpanel容器中。在JRadioButton对象的构造函数中,将OnCheck()函数设置为actionPerformed属性的值。单击单选按钮以更改其状态时,将执行此函数。
rb1 = JRadioButton("Male", True,actionPerformed = OnCheck)
rb2 = JRadioButton("Female", actionPerformed = OnCheck)
请注意,单选按钮的默认状态为false(未选中)。创建按钮rb1时,其初始状态为True(选中)。
将两个单选按钮添加到单选按钮组中,以使它们互斥,这样,如果选择了一个,则自动取消选择另一个。
grp = ButtonGroup()
grp.add(rb1)
grp.add(rb2)
这两个单选按钮以及两个标签将被添加到垂直布局的面板对象中,该对象在rb2和lbl2之间的高度为25个像素。
panel = JPanel()
panel.setLayout(BoxLayout(panel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS))
panel.add(Box.createVerticalGlue())
panel.add(lbl)
panel.add(rb1)
panel.add(rb2)
panel.add(Box.createRigidArea(Dimension(0,25)))
panel.add(lbl1)
该面板将添加到顶级JFrame对象,该对象的visible属性最后设置为“ True”。
frame = JFrame("JRadioButton Example")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(250,200)
frame.setVisible(True)
The complete code of radio.py is given below:
from javax.swing import JFrame, JPanel, JLabel, BoxLayout, Box
from java.awt import Dimension
from javax.swing import JRadioButton,ButtonGroup
frame = JFrame("JRadioButton Example")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(250,200)
panel = JPanel()
panel.setLayout(BoxLayout(panel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS))
frame.add(panel)
def OnCheck(event):
lbl1.text = ""
if rb1.isSelected():
lbl1.text = lbl1.text+"Gender selection : Male"
else:
lbl1.text = lbl1.text+"Gender selection : Female "
lbl = JLabel("Select Gender")
rb1 = JRadioButton("Male", True,actionPerformed = OnCheck)
rb2 = JRadioButton("Female", actionPerformed = OnCheck)
grp = ButtonGroup()
grp.add(rb1)
grp.add(rb2)
lbl1 = JLabel("Gender Selection :")
panel.add(Box.createVerticalGlue())
panel.add(lbl)
panel.add(rb1)
panel.add(rb2)
panel.add(Box.createRigidArea(Dimension(0,25)))
panel.add(lbl1)
frame.setVisible(True)
运行上面的Jython脚本并更改单选按钮的选择。该选择将出现在底部的标签中。
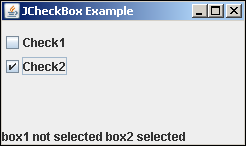
Jython JCheckBox事件
像JRadioButton一样,JCheckBox对象也是一个可选按钮,除了其标题外,还带有一个矩形的可选中框。通常,这用于为用户提供从项目列表中选择多个选项的机会。
在下面的示例中,将两个复选框和一个来自swing包的标签添加到垂直BoxLayout中的JPanel中。底部的标签显示两个复选框的即时选择状态。
这两个复选框都使用构造函数声明,该构造函数的actionPerformed属性设置为OnCheck()函数。
box1 = JCheckBox("Check1", actionPerformed = OnCheck)
box2 = JCheckBox("Check2", actionPerformed = OnCheck)
OnCheck()函数验证每个复选框的选择状态,并在底部的标签上显示相应的消息。
def OnCheck(event):
lbl1.text = ""
if box1.isSelected():
lbl1.text = lbl1.text + "box1 selected "
else:
lbl1.text = lbl1.text + "box1 not selected "
if box2.isSelected():
lbl1.text = lbl1.text + "box2 selected"
else:
lbl1.text = lbl1.text + "box2 not selected"
将这些框和一个JLabel对象添加到JPanel中,并在它们之间添加50像素高的空格。
panel = JPanel()
panel.setLayout(BoxLayout(panel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS))
panel.add(Box.createVerticalGlue())
panel.add(box1)
panel.add(box2)
panel.add(Box.createRigidArea(Dimension(0,50)))
panel.add(lbl1)
面板本身被添加到顶级JFrame窗口中,该窗口最后将visible属性设置为true。
frame = JFrame("JCheckBox Example")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(250,150)
frame.add(panel)
frame.setVisible(True)
运行上面的代码,并尝试使用复选框。两个复选框的瞬时状态都显示在底部。
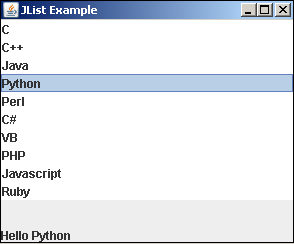
Jython JList事件
swing包中的JList控件为用户提供了可供选择的滚动项目列表。 JComboBox提供项目的下拉列表。在Java中,通过在ListSelectionListener中实现valueChanged()方法来处理选择事件。在Jython中,事件处理程序分配给JList对象的valueChanged属性。
在以下示例中,将JList对象和标签添加到BorderLayout中的JFrame中。 JList中填充了一个元组中的项目集合。它的valueChanged属性设置为listSelect()函数。
lang = ("C", "C++", "Java", "Python", "Perl", "C#", "VB", "PHP", "Javascript", "Ruby")
lst = JList(lang, valueChanged = listSelect)
事件处理程序函数获取所选项目的索引,并从JList对象获取相应的项目,以显示在底部的标签上。
def listSelect(event):
index = lst.selectedIndex
lbl1.text = "Hello" + lang[index]
使用BorderLayout将JList和JLabel对象添加到JFrame。
整个代码如下-
from javax.swing import JFrame, JPanel, JLabel, JList
from java.awt import BorderLayout
frame = JFrame("JList Example")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(300,250)
frame.setLayout(BorderLayout())
def listSelect(event):
index = lst.selectedIndex
lbl1.text = "Hello" + lang[index]
lang = ("C", "C++", "Java", "Python", "Perl", "C#", "VB", "PHP", "Javascript", "Ruby")
lst = JList(lang, valueChanged = listSelect)
lbl1 = JLabel("box1 not selected box2 not selected")
frame.add(lst, BorderLayout.NORTH)
frame.add(lbl1, BorderLayout.SOUTH)
frame.setVisible(True)
以下代码的输出如下。