- Jython-函数
- Jython-安装(1)
- Jython-安装
- Jython-循环
- Jython-循环(1)
- Jython-模块
- Jython-模块(1)
- Jython教程
- Jython教程(1)
- wxPython-布局管理(1)
- wxPython-布局管理
- 讨论Jython(1)
- 讨论Jython
- Jython-概述(1)
- Jython-概述
- Jython-Java应用程序
- Jython-Java应用程序(1)
- Jython-菜单
- Jython-菜单(1)
- Jython-导入Java库
- Jython-导入Java库(1)
- Jython-对话框(1)
- Jython-对话框
- PyQt-布局管理
- PyQt-布局管理(1)
- Jython-JDBC
- Jython-JDBC(1)
- Jython-Servlet
- Jython-Servlet(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-08 07:19:47 🧑 作者: Mango
Java中的布局管理器是那些类,用于管理控件在诸如Frame,Dialog或Panel的容器对象中的放置。布局管理器会保持控件在框架中的相对位置,即使更改分辨率或调整框架本身的大小也是如此。
这些类实现Layout接口。在AWT库中定义了以下布局管理器-
- BorderLayout
- 流布局
- 网格布局
- 卡布局
- GridBagLayout
在Swing库中定义了以下布局管理器-
- BoxLayout
- 组布局
- ScrollPaneLayout
- SpringLayout
在以下示例中,我们将使用AWT布局管理器和挥杆布局管理器。
- 绝对布局
- 流程布局
- 网格布局
- 边框布局
- 盒子布局
- 组布局
现在让我们详细讨论每个。
绝对布局
在探索所有上述布局管理器之前,我们必须查看控件在容器中的绝对位置。我们必须将框架对象的布局方法设置为“无”。
frame.setLayout(None)
然后通过调用setBounds()方法放置控件。它需要四个参数-x位置,y位置,宽度和高度。
例如-将按钮对象放置在绝对位置并具有绝对大小。
btn = JButton("Add")
btn.setBounds(60,80,60,20)
同样,可以通过适当分配位置和大小来放置所有控件。此布局相对易于使用,但是当调整窗口大小或更改屏幕分辨率时执行程序时,无法保留其外观。
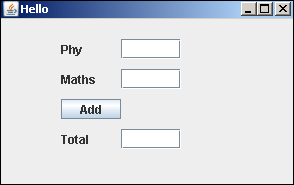
在以下Jython脚本中,使用三个Jlabel对象分别显示文本“ phy”,“数学”和“总计”。在这三个的前面-放置了JTextField对象。将一个Button对象放置在“总计”标签上方。
首先,创建的JFrame窗口的布局设置为none。
frame = JFrame("Hello")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(300,200)
frame.setLayout(None)
然后根据其绝对位置和大小添加不同的控件。完整的代码如下-
from javax.swing import JFrame, JLabel, JButton, JTextField
frame = JFrame("Hello")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(300,200)
frame.setLayout(None)
lbl1 = JLabel("Phy")
lbl1.setBounds(60,20,40,20)
txt1 = JTextField(10)
txt1.setBounds(120,20,60,20)
lbl2 = JLabel("Maths")
lbl2.setBounds(60,50,40,20)
txt2 = JTextField(10)
txt2.setBounds(120, 50, 60,20)
btn = JButton("Add")
btn.setBounds(60,80,60,20)
lbl3 = JLabel("Total")
lbl3.setBounds(60,110,40,20)
txt3 = JTextField(10)
txt3.setBounds(120, 110, 60,20)
frame.add(lbl1)
frame.add(txt1)
frame.add(lbl2)
frame.add(txt2)
frame.add(btn)
frame.add(lbl3)
frame.add(txt3)
frame.setVisible(True)
上面代码的输出如下。
Jython FlowLayout
FlowLayout是容器类的默认布局管理器。它从左到右,然后从上到下排列控制。
在以下示例中,将使用FlowLayout管理器在JFrame中显示Jlabel对象,JTextField对象和JButton对象。首先,让我们从javax.swing包和java.awt包中导入所需的类。
from javax.swing import JFrame, JLabel, JButton, JTextField
from java.awt import FlowLayout
然后创建一个JFrame对象并设置其Location以及size属性。
frame = JFrame("Hello")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(200,200)
Set the layout manager for the frame as FlowLayout.
frame.setLayout(FlowLayout())
现在为JLabel,JTextfield和JButton类声明对象。
label = JLabel("Welcome to Jython Swing")
txt = JTextField(30)
btn = JButton("ok")
最后,通过调用JFrame类的add()方法将这些控件添加到框架中。
frame.add(label)
frame.add(txt)
frame.add(btn)
要显示框架,请将其visible属性设置为true。完整的Jython脚本及其输出如下所示-
from javax.swing import JFrame, JLabel, JButton, JTextField
from java.awt import FlowLayout
frame = JFrame("Hello")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(200,200)
frame.setLayout(FlowLayout())
label = JLabel("Welcome to Jython Swing")
txt = JTextField(30)
btn = JButton("ok")
frame.add(label)
frame.add(txt)
frame.add(btn)
frame.setVisible(True)
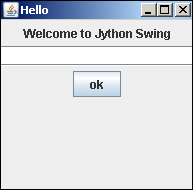
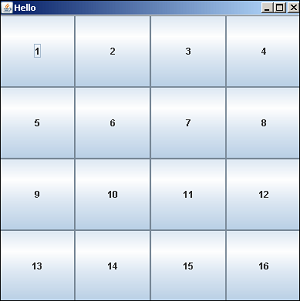
Jython GridLayout
Gridlayout管理器允许将控件放置在矩形网格中。一个控件放置在网格的每个单元格中。
在下面的示例中,将GridLayout应用于JFrame对象,将其分为4行4列。 JButton对象将放置在网格的每个单元格中。
让我们首先导入所需的库-
from javax.swing import JFrame, JButton
from java.awt import GridLayout
然后创建JFrame容器-
frame = JFrame("Hello")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(400,400)
现在,通过将GridLayout的尺寸指定为4 x 4来应用它。
frame.setLayout(GridLayout(4,4))
现在,我们应该使用两个FOR循环,每个循环从1到4,因此在随后的单元格中放置了16个JButton对象。
k = 0
frame.setLayout(GridLayout(4,4))
for i in range(1,5):
for j in range(1,5):
k = k+1
frame.add(JButton(str(k)))
最后将框架的可见性设置为true。完整的Jython代码如下。
from javax.swing import JFrame, JButton
from java.awt import GridLayout
frame = JFrame("Hello")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setLocation(100,100)
frame.setSize(400,400)
frame.setLayout(GridLayout(4,4))
k = 0
for i in range(1,5):
for j in range(1,5):
k = k+1
frame.add(JButton(str(k)))
frame.setVisible(True)
上面代码的输出如下-
Jython BorderLayout
BorderLayout管理器将容器分为五个地理区域和位置,每个区域中都有一个组件。这些区域由定义的常量表示,如下所示-
- BorderLayout.NORTH
- BorderLayout.SOUTH
- 边框版式
- BorderLayout.WEST
- BorderLayout.CENTER
让我们考虑以下示例-

Jython BoxLayout
BoxLayout类在javax.swing包中定义。它用于垂直或水平排列容器中的组件。方向由以下常数确定-
- X_AXIS
- Y_AXIS
- LINE_AXIS
- PAGE_AXIS
整数常数指定容器组件应沿其放置的轴。当容器具有默认的组件方向时,LINE_AXIS指定从左到右排列组件,而PAGE_AXIS指定从上到下排列组件。
在以下示例中,(JPanel类的)面板被添加到JFrame对象中。向其应用了垂直BoxLayout,并向其添加了另外两个面板(顶部和底部)。这两个内部面板有两个按钮,每个按钮都添加在水平Boxlayout中。
让我们首先创建顶级JFrame窗口。
frame = JFrame()
frame.setTitle("Buttons")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setSize(300, 150)
声明JPanel对象具有垂直的BoxLayout。将其添加到顶级框架中。
panel = JPanel()
panel.setLayout(BoxLayout(panel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS))
frame.add(panel)
在此面板中,又添加了两个面板的顶部和底部。它们每个都水平添加了两个JButton对象,并用25个像素的空格分隔它们。
###top panel
top = JPanel()
top.setLayout(BoxLayout(top, BoxLayout.X_AXIS))
b1 = JButton("OK")
b2 = JButton("Close")
top.add(Box.createVerticalGlue())
top.add(b1)
top.add(Box.createRigidArea(Dimension(25, 0)))
top.add(b2)
类似地,构造底部面板。
###bottom panel
bottom = JPanel()
bottom.setLayout(BoxLayout(bottom, BoxLayout.X_AXIS))
b3 = JButton("Open")
b4 = JButton("Save")
bottom.add(b3)
bottom.add(Box.createRigidArea(Dimension(25, 0)))
bottom.add(b4)
bottom.add(Box.createVerticalGlue())
请注意, createRigidArea()函数用于在两个按钮之间创建25像素的间距。同样, createVerticalGlue()函数占用布局中的前导或尾随空间。
首先,添加顶部和底部面板并将框架的可见性属性设置为true。完整的代码如下-
from java.awt import Dimension
from javax.swing import JButton, JFrame,JPanel,BoxLayout,Box
frame = JFrame()
frame.setTitle("Buttons")
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
frame.setSize(300, 150)
panel = JPanel()
panel.setLayout(BoxLayout(panel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS))
frame.add(panel)
###top panel
top = JPanel()
top.setLayout(BoxLayout(top, BoxLayout.X_AXIS))
b1 = JButton("OK")
b2 = JButton("Close")
top.add(Box.createVerticalGlue())
top.add(b1)
top.add(Box.createRigidArea(Dimension(25, 0)))
top.add(b2)
###bottom panel
bottom = JPanel()
bottom.setLayout(BoxLayout(bottom, BoxLayout.X_AXIS))
b3 = JButton("Open")
b4 = JButton("Save")
bottom.add(b3)
bottom.add(Box.createRigidArea(Dimension(25, 0)))
bottom.add(b4)
bottom.add(Box.createVerticalGlue())
panel.add(bottom)
panel.add(top)
frame.setVisible(True)
上面的代码将生成以下输出。

Jython GroupLayout
GroupLayout管理器以分层方式将组件分组。分组由两个类SequentialGroup和ParallelGroup完成,它们均在Java中实现了Group接口。
布局过程分为两个步骤。第一步,将组件与水平轴一起放置,而第二步与垂直轴一起放置。每个组件必须在布局中定义两次。
有两种类型的安排,顺序安排和并行安排。在这两种方法中,我们都可以顺序或并行排列组件。在水平排列中,行称为顺序组,列称为并行组。另一方面,在平行排列中,元素的行是平行的组和一列,称为顺序。
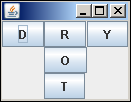
在下面的示例中,以这样的方式排列了五个按钮,使得三个分别出现在行和列中。首先,在JFrame窗口中添加一个Jpanel对象,并将其布局设置为Grouplayout。
frame = JFrame()
panel = JPanel()
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
layout = GroupLayout(panel)
panel.setLayout(layout)
然后构造JButton对象-
buttonD = JButton("D")
buttonR = JButton("R")
buttonY = JButton("Y")
buttonO = JButton("O")
buttonT = JButton("T")
接下来,我们创建一个名为LeftToRight的SequentialGroup ,向其添加buttonD和buttonY。在它们之间放置一个ParallelGroup ColumnMiddle(垂直添加了其他三个按钮)。
leftToRight = layout.createSequentialGroup()
leftToRight.addComponent(buttonD)
columnMiddle = layout.createParallelGroup()
columnMiddle.addComponent(buttonR)
columnMiddle.addComponent(buttonO)
columnMiddle.addComponent(buttonT)
leftToRight.addGroup(columnMiddle)
leftToRight.addComponent(buttonY)
现在是垂直SequentialGroup的定义,称为TopToBottom。添加一个包含三个按钮的ParallelGroup行,然后垂直放置两个按钮。
topToBottom = layout.createSequentialGroup()
rowTop = layout.createParallelGroup()
rowTop.addComponent(buttonD)
rowTop.addComponent(buttonR)
rowTop.addComponent(buttonY)
topToBottom.addGroup(rowTop)
topToBottom.addComponent(buttonO)
topToBottom.addComponent(buttonT)
最后,水平设置LeftToRight组,垂直将TopToBottom组设置为布局对象。完整的代码如下-
from javax.swing import JButton, JFrame,JPanel,GroupLayout
frame = JFrame()
panel = JPanel()
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
layout = GroupLayout(panel)
panel.setLayout(layout)
buttonD = JButton("D")
buttonR = JButton("R")
buttonY = JButton("Y")
buttonO = JButton("O")
buttonT = JButton("T")
leftToRight = layout.createSequentialGroup()
leftToRight.addComponent(buttonD)
columnMiddle = layout.createParallelGroup()
columnMiddle.addComponent(buttonR)
columnMiddle.addComponent(buttonO)
columnMiddle.addComponent(buttonT)
leftToRight.addGroup(columnMiddle)
leftToRight.addComponent(buttonY)
topToBottom = layout.createSequentialGroup()
rowTop = layout.createParallelGroup()
rowTop.addComponent(buttonD)
rowTop.addComponent(buttonR)
rowTop.addComponent(buttonY)
topToBottom.addGroup(rowTop)
topToBottom.addComponent(buttonO)
topToBottom.addComponent(buttonT)
layout.setHorizontalGroup(leftToRight)
layout.setVerticalGroup(topToBottom)
frame.add(panel)
frame.pack()
frame.setVisible(True)
上面代码的输出如下-