- Java RMI应用程序
- Java RMI应用程序(1)
- 如何运行Java RMI 应用程序
- 如何运行Java RMI 应用程序(1)
- Java RMI-GUI应用程序(1)
- Java RMI-GUI应用程序
- Java RMI教程(1)
- Java RMI教程
- Java RMI-简介(1)
- Java RMI-简介
- 讨论Java RMI(1)
- 讨论Java RMI
- java rmi 示例客户端服务器 - Java (1)
- Java RMI-有用的资源
- Java RMI-有用的资源(1)
- java rmi 示例客户端服务器 - Java 代码示例
- Java中的远程方法调用RMI
- Java中的远程方法调用RMI(1)
- Java RMI(远程方法调用)
- Java RMI(远程方法调用)(1)
- Java RMI-快速指南
- Java RMI-快速指南(1)
- Java的.rmi.Naming类在Java中(1)
- Java的.rmi.Naming类在Java中
- Java中的Java .rmi.MarshalledObject 类
- Java的.rmi.RMISecurityManager类在Java中(1)
- Java的.rmi.RMISecurityManager类在Java中
- Java中的Java .rmi.MarshalledObject 类(1)
- Spring和RMI集成
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-15 03:20:43 🧑 作者: Mango
在上一章中,我们创建了一个示例RMI应用程序,其中客户端调用一个显示GUI窗口(JavaFX)的方法。
在本章中,我们将以一个示例为例,说明客户端程序如何在服务器上的MySQL数据库中检索表的记录。
假设我们在数据库详细信息中有一个名为student_data的表,如下所示。
+----+--------+--------+------------+---------------------+
| ID | NAME | BRANCH | PERCENTAGE | EMAIL |
+----+--------+--------+------------+---------------------+
| 1 | Ram | IT | 85 | ram123@gmail.com |
| 2 | Rahim | EEE | 95 | rahim123@gmail.com |
| 3 | Robert | ECE | 90 | robert123@gmail.com |
+----+--------+--------+------------+---------------------+
假设用户名是myuser ,密码是password 。
创建学生班
如下所示,使用setter和getter方法创建一个Student类。
public class Student implements java.io.Serializable {
private int id, percent;
private String name, branch, email;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getBranch() {
return branch;
}
public int getPercent() {
return percent;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setID(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setBranch(String branch) {
this.branch = branch;
}
public void setPercent(int percent) {
this.percent = percent;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
定义远程接口
定义远程接口。在这里,我们定义了一个名为Hello的远程接口,其中包含一个名为getStudents()的方法。此方法返回一个列表,其中包含Student类的对象。
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.util.*;
// Creating Remote interface for our application
public interface Hello extends Remote {
public List getStudents() throws Exception;
}
开发实施类
创建一个类并实现上面创建的接口。
在这里,我们实现了Remote接口的getStudents()方法。调用此方法时,它将检索名为student_data的表的记录。使用其setter方法将这些值设置为Student类,将其添加到列表对象并返回该列表。
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
// Implementing the remote interface
public class ImplExample implements Hello {
// Implementing the interface method
public List getStudents() throws Exception {
List list = new ArrayList();
// JDBC driver name and database URL
String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/details";
// Database credentials
String USER = "myuser";
String PASS = "password";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
//Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully...");
//Execute a query
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM student_data";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//Extract data from result set
while(rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String branch = rs.getString("branch");
int percent = rs.getInt("percentage");
String email = rs.getString("email");
// Setting the values
Student student = new Student();
student.setID(id);
student.setName(name);
student.setBranch(branch);
student.setPercent(percent);
student.setEmail(email);
list.add(student);
}
rs.close();
return list;
}
}
服务器程序
RMI服务器程序应实现远程接口或扩展实现类。在这里,我们应该创建一个远程对象并将其绑定到RMI注册中心。
以下是此应用程序的服务器程序。在这里,我们将扩展上面创建的类,创建一个远程对象,并使用绑定名称hello将其注册到RMI注册表。
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
public class Server extends ImplExample {
public Server() {}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
// Instantiating the implementation class
ImplExample obj = new ImplExample();
// Exporting the object of implementation class (
here we are exporting the remote object to the stub)
Hello stub = (Hello) UnicastRemoteObject.exportObject(obj, 0);
// Binding the remote object (stub) in the registry
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry();
registry.bind("Hello", stub);
System.err.println("Server ready");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Server exception: " + e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
客户程序
以下是此应用程序的客户端程序。在这里,我们正在获取远程对象并调用名为getStudents()的方法。它从列表对象中检索表的记录并显示它们。
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.*;
public class Client {
private Client() {}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
try {
// Getting the registry
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(null);
// Looking up the registry for the remote object
Hello stub = (Hello) registry.lookup("Hello");
// Calling the remote method using the obtained object
List list = (List)stub.getStudents();
for (Student s:list)v {
// System.out.println("bc "+s.getBranch());
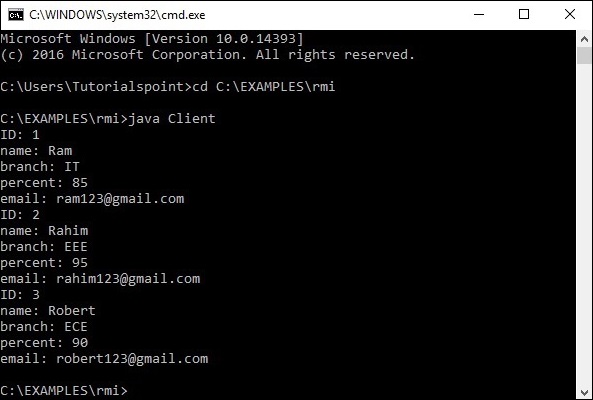
System.out.println("ID: " + s.getId());
System.out.println("name: " + s.getName());
System.out.println("branch: " + s.getBranch());
System.out.println("percent: " + s.getPercent());
System.out.println("email: " + s.getEmail());
}
// System.out.println(list);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Client exception: " + e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行示例的步骤
以下是运行我们的RMI示例的步骤。
步骤1-打开存储所有程序的文件夹,并编译所有Java文件,如下所示。
Javac *.java
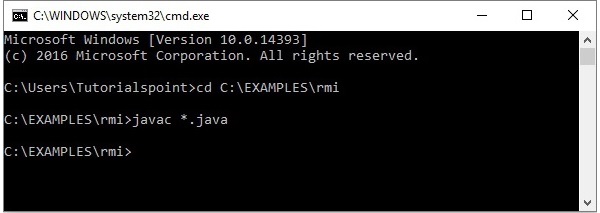
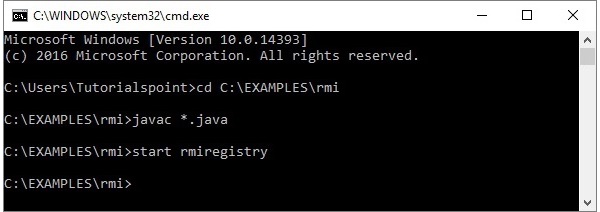
步骤2-使用以下命令启动rmi注册表。
start rmiregistry
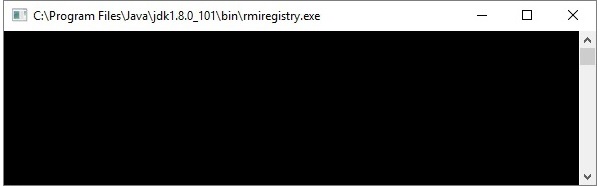
如下所示,这将在另一个窗口上启动rmi注册表。
步骤3-运行服务器类文件,如下所示。
Java Server
步骤4-运行客户端类文件,如下所示。
java Client