MATLAB – 数据类型
MATLAB 是一个平台,它为数百万工程师和科学家提供使用编程和数值计算算法分析数据并帮助创建模型的平台。数据类型是由它们可以存储在其中的值定义的特定类型的数据项,通常在它们使用的编程语言中。
在 MATLAB 中定义数据类型
在 MATLAB 中,我们不需要任何类型的声明语句,当它获取任何新变量名称时,它会创建变量并为其分配适当的内存空间,但如果变量名称已经存在,它将用新内容替换原始内容并将其分配给需要时提供新的存储空间。
Syntax: variable name = a value (or an expression)
示例:
Matlab
% MATLAB code for variable initialization
Geeks = 7;Matlab
% MATLAB code for random matrix generation
rng default
A = randi(5,5) % It will generate random matrix of 15x5
B = A < 9 % The result is a logical matrix.
% Each value in B represents a logical 1 (true)
% or logical 0 (false) state to indicate whether
% the corresponding element of A fulfills the condition A < 9.
% For example, A(1,1) is 13, so B(1,1) is logical 0 (false).
% However, A(1,2) is 2, so B(1,2) is logical 1 (true).Matlab
% MATLAB code for showing String results
str = "Welcome to GeeksforGeeks, "
"Welcome!"" and lets start coding."
fprintf(str);Matlab
% MATLAB code for numeric type
str = 'Hello World';
int8(str)Matlab
% MATLAB code for Table
T = table(Name,QuestionAttempted,CodingScore);
data = {'Atul Sisodiya',22,100};
Tnew = [Tnew;data];Matlab
C = {1, 2, 3}Matlab
geek(1).name = ("Atul Sisodiya");
geek(1).coding = 100;
geek输出:

MATLAB 中的数据类型
在 MATLAB 中,数据可以存储为不同的类型,数值、文本、复数等。为了存储这些数据,MATLAB 具有不同的类,这些类具有不同的特性。 MATLAB 总共提供了 16 种基本数据类型。

逻辑类型
逻辑类型是用逻辑值 0 和 1 表示的 True 和 false 值。任何数值(非复数)都可以转换为逻辑表示。
Syntax:G = logical (x)
示例:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code for random matrix generation
rng default
A = randi(5,5) % It will generate random matrix of 15x5
B = A < 9 % The result is a logical matrix.
% Each value in B represents a logical 1 (true)
% or logical 0 (false) state to indicate whether
% the corresponding element of A fulfills the condition A < 9.
% For example, A(1,1) is 13, so B(1,1) is logical 0 (false).
% However, A(1,2) is 2, so B(1,2) is logical 1 (true).
输出:

字符和字符串类型
在 MATLAB 中,字符和字符串数组为文本类型数据提供存储。与称为数字数组的数字序列相比,字符串是字符数组。
Syntax: s = ‘String’
例子:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code for showing String results
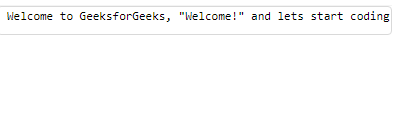
str = "Welcome to GeeksforGeeks, "
"Welcome!"" and lets start coding."
fprintf(str);
输出:
数字类型-
整数和浮点数据属于这种类型,描述如下。 Negative numbers = -1.79769 x 10308 to -2.22507 x 10-308 Positive numbers = 2.22507 x 10-308 to 1.79769 x 10308 Negative numbers = -1.79769 x 10308 to -2.22507 x 10-308 Positive numbers = 2.22507 x 10-308 to 1.79769 x 10308Data Type Short Description Features double Double-precision arrays single Single-precision arrays int8 8-bit signed integer arrays int16 16-bit signed integer arrays int32 32-bit signed integer arrays int64 64-bit signed integer arrays uint8 8-bit unsigned integer arrays unit16 16-bit unsigned integer arrays uint32 32-bit unsigned integer arrays uint64 64-bit unsigned integer arrays
例子:
MATLAB
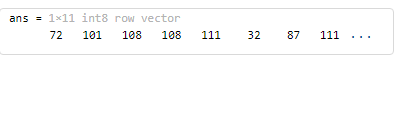
% MATLAB code for numeric type
str = 'Hello World';
int8(str)
输出:
桌子
该表包含行和列变量。每个变量可以是不同的数据类型和不同的大小,但每个变量需要具有相同的行数。函数范围用于访问数据以创建、编辑和读取表数据。
Syntax:T = table(ColumnName1,ColumnName2);
例子:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code for Table
T = table(Name,QuestionAttempted,CodingScore);
data = {'Atul Sisodiya',22,100};
Tnew = [Tnew;data];
输出:
Table array
2x3
Name QuestionAttempted CodingScore
Atul Sisodiya 22 100细胞
元胞数组是一种 MATLAB 数据类型,其中包含称为元胞的索引数据容器。单元格可以包含任何类型的数据,通常包含不同长度的字符向量、数字、任意大小的数字数组。一组单元格包含在 () 中,并且通过使用 {} 完成对单元格的访问,该 {} 用于创建、编辑或删除任何单元格函数。
Syntax: c = { }
例子:
MATLAB
C = {1, 2, 3}
输出:

结构
在结构中,数据容器用于对相关数据及其类型进行分组,这些数据称为字段。字段可以包含任何类型的数据。在结构中,使用点符号访问数据。
Syntax: structname.fieldName
例子:
MATLAB
geek(1).name = ("Atul Sisodiya");
geek(1).coding = 100;
geek
输出:

函数句柄
函数句柄在 MATLAB 中主要用于将函数(数字或字符)传递给另一个函数。用于间接调用函数的变量可以命名为函数句柄。
要创建函数句柄,使用“@”运算符。
示例:要创建一个函数句柄来计算 x^2 + y^2,使用的函数是:
输出:
