Solidity – 构造函数
构造函数是任何面向对象的编程语言中的一种特殊方法,每当初始化类的对象时都会调用它。 Solidity 则完全不同,Solidity 在智能合约内部提供了一个构造函数声明,它只在合约部署时调用一次,用于初始化合约状态。如果没有明确定义的构造函数,则编译器会创建默认构造函数。
创建构造函数
构造函数是使用构造函数关键字定义的,没有任何函数名,后跟访问修饰符。它是一个可选函数,用于初始化合约的状态变量。构造函数可以是内部的或公共的,内部构造函数将合约标记为抽象的。
句法:
constructor() {
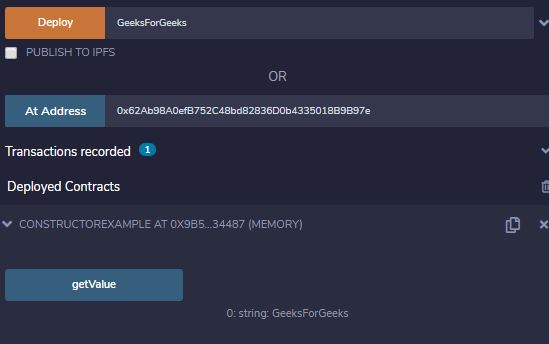
} 示例:在下面的示例中,在合约构造函数示例中,创建了一个构造函数来初始化状态变量str。
Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// creating a constructor
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract constructorExample {
// Declaring state variable
string str;
// Creating a constructor
// to set value of 'str'
constructor() public {
str = "GeeksForGeeks";
}
// Defining function to
// return the value of 'str'
function getValue(
) public view returns (
string memory) {
return str;
}
}Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Constructor in Inheritance
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Base {
// Declaring variable
uint data;
// Defining a constructor
constructor(uint _data) public {
data = _data;
}
// Defining function
function Print(
) public returns(string memory){
return "Direct Initialization";
}
}
// Child contract inheriting
// the parent contract 'Base'
contract Derived is Base(2){
// Defining a constructor
constructor() public {}
// Defining function to access
// variable of parent contract
function getData(
) external returns(uint){
uint result = data ** 2;
return result;
}
}
// Caller contract
contract caller{
// Creating an object of child contract
Derived c = new Derived();
// Accessing functions of parent
// and child contract using
// object of child contract
function getResult() public returns(uint){
c.Print();
return c.getData();
}
}Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Indirect Initialization
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Base {
// Declaring state variable
string str;
// Defining a constructor
constructor(
string memory _str) public {
str = _str;
}
// Defining a function
function Print(
) public returns(string memory){
return "Indirect Initialization";
}
}
// Child contract inheriting
// parent contract 'Base'
contract Derived is Base {
// Defining a constructor
constructor(
string memory _info) Base(
string(abi.encodePacked(
_info, _info))) public {}
// Defining function to
// return value of parent
// contract variable 'str'
function getStr(
) public view returns(string memory){
return str;
}
}
// Caller contract
contract caller {
// Creating an object of
// child contract
Derived c
= new Derived("GeeksForGeeks");
//Defining a function to access
// functions of the parent
//contract and child contract
function getResult() public view{
c.Print();
c.getStr();
}
}Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Need of constructors
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract constructorExample {
// Declaring state variable
string str;
address private owner
= 0x62Ab98A0efB752C48bd82836D0b4335018B9B97e;
// Defining constructor
constructor(string memory string) public {
if(msg.sender == owner){
str = string;
}
}
// Defining function to
// return value of 'str'
function getValue() public view returns (
string memory) {
return str;
}
}输出 :
继承中的构造函数
如果未定义构造函数,则调用默认构造函数,但如果构造函数在父合约中定义并具有一些参数,则子合约也应向构造函数提供所需的参数。如果子合约没有将任何参数传递给父构造函数,则子合约将成为抽象合约。调用父合约的构造函数有两种方式:
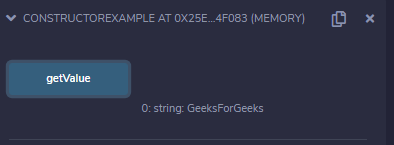
1、直接初始化:在下面的例子中,直接初始化方法用于初始化父类的构造函数。
坚固性
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Constructor in Inheritance
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Base {
// Declaring variable
uint data;
// Defining a constructor
constructor(uint _data) public {
data = _data;
}
// Defining function
function Print(
) public returns(string memory){
return "Direct Initialization";
}
}
// Child contract inheriting
// the parent contract 'Base'
contract Derived is Base(2){
// Defining a constructor
constructor() public {}
// Defining function to access
// variable of parent contract
function getData(
) external returns(uint){
uint result = data ** 2;
return result;
}
}
// Caller contract
contract caller{
// Creating an object of child contract
Derived c = new Derived();
// Accessing functions of parent
// and child contract using
// object of child contract
function getResult() public returns(uint){
c.Print();
return c.getData();
}
}
输出 :
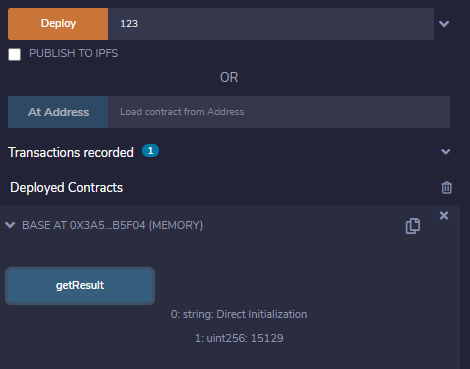
2. 间接初始化:在下面的例子中,使用Base(字符串(abi.encodePacked(_info, _info)))的间接初始化来初始化基类的构造函数。
坚固性
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Indirect Initialization
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Base {
// Declaring state variable
string str;
// Defining a constructor
constructor(
string memory _str) public {
str = _str;
}
// Defining a function
function Print(
) public returns(string memory){
return "Indirect Initialization";
}
}
// Child contract inheriting
// parent contract 'Base'
contract Derived is Base {
// Defining a constructor
constructor(
string memory _info) Base(
string(abi.encodePacked(
_info, _info))) public {}
// Defining function to
// return value of parent
// contract variable 'str'
function getStr(
) public view returns(string memory){
return str;
}
}
// Caller contract
contract caller {
// Creating an object of
// child contract
Derived c
= new Derived("GeeksForGeeks");
//Defining a function to access
// functions of the parent
//contract and child contract
function getResult() public view{
c.Print();
c.getStr();
}
}
输出 :
构造函数的需要
构造函数在智能合约中非常有用,可以在运行时定义参数值,也可以限制方法调用。 Solidity 不支持构造函数重载,它一次只允许一个构造函数。
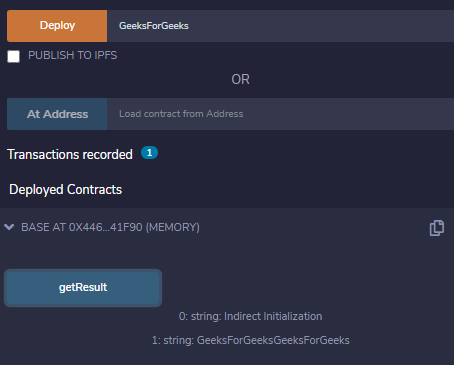
示例:在下面的示例中,合约构造函数示例包含一个构造函数,以演示构造函数的必要性。
坚固性
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Need of constructors
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract constructorExample {
// Declaring state variable
string str;
address private owner
= 0x62Ab98A0efB752C48bd82836D0b4335018B9B97e;
// Defining constructor
constructor(string memory string) public {
if(msg.sender == owner){
str = string;
}
}
// Defining function to
// return value of 'str'
function getValue() public view returns (
string memory) {
return str;
}
}
输出 :