- 别名 mysql (1)
- 别名 mysql 代码示例
- SQL |别名
- SQL |别名
- SQL |别名(1)
- SQL |别名(1)
- Linux别名
- Linux别名(1)
- Laravel 帆别名 (1)
- D编程-别名
- D编程-别名(1)
- Oracle别名(1)
- Oracle别名
- laravel 帆别名 - PHP (1)
- PostgreSQL – 别名(1)
- PostgreSQL列别名(1)
- PostgreSQL – 别名
- PostgreSQL列别名
- PostgreSQL别名(1)
- PostgreSQL别名
- Powershell-别名
- Powershell-别名(1)
- Laravel 帆别名 - 任何代码示例
- laravel 帆别名 - PHP 代码示例
- 别名导入 javascript (1)
- 更改命令别名 (1)
- git 别名 - Shell-Bash (1)
- Linux 中的别名命令及示例(1)
- Linux 中的别名命令及示例
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-19 02:12:24 🧑 作者: Mango
MySQL别名
MySQL中的别名用于为表或表中的列提供临时名称,以用于特定查询。它用作表示表或列名称的昵称。它使查询简短明了。
当表或列名不是实时的用户友好时,这将非常有用。它使列的名称更具可读性。 MySQL别名只能在查询期间存在。
MySQL别名的优点
以下是MySQL中别名的优点:
- 在查询中要使用多个表的情况下,这是首选方法。
- 它提供了非常有用和灵活的功能,使我们能够快速完成复杂的任务。
- 它使列名或表名更具可读性。
- 在查询中使用该功能时,此函数很有用。
- 它还可以使我们合并两个或多个列。
- 当列名很大或不可读时,它也很有用。
句法
以下是MySQL中使用的别名的基本语法:
对于列
SELECT col_name AS alias_name FROM table_name;
对于表
SELECT col_name1, col_name2,... FROM table_name AS alias_name;
参数说明
下表详细说明了参数:
| Parameter | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Column_Name | It is the column name that we are going to create an alias name. |
| Table_Name | It is the table name that we are going to create an alias name. |
| Alias_Name | It is the temporary name that we are going to assign for the column or table. |
| AS | It is optional. If you have not specified it, there is no effect on the query execution. It is a programmer choice that they use it during the aliasing of the column name, but not aliasing in the table name. |
如果要给别名提供空格,则必须将其用引号引起来。通常最好在列名(而不是表名)中使用别名作为空格。以下语法对其进行了更清晰的说明:
SELECT col_name AS 'alias_name' FROM table_name;
现在,我们将了解别名在MySQL中是如何工作的。让我们首先使用以下查询创建一个名为“ Student_info”的表:
CREATE TABLE Student_info(
stud_id int PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
stud_code varchar(15),
stud_name varchar(35),
subject varchar(25),
marks int
);
创建表后,我们需要插入一条记录。假设此表包含以下数据:
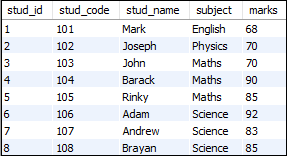
说明列别名
如果要使用“ Roll No”作为别名从上表中获取stud_code,请执行以下语句:
mysql> SELECT stud_code AS Roll_No FROM Student_info;
它将返回如下输出:
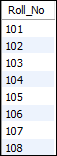
同样,如果我们想使用“ Roll No”来获取stud_code,其中“ Roll No”包含空格和标记为乐谱,请执行以下语句:
mysql> SELECT stud_code AS 'Roll No', marks AS scores FROM Student_info;
它将返回如下输出:
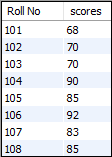
这是另一个示例,它将返回分数大于70的学生姓名和科目。
mysql> SELECT stud_name AS 'Student Name', subject AS 'Subject', marks
FROM Student_info
HAVING marks > 70
ORDER BY stud_name;
成功执行后,我们可以看到结果集仅包含标记大于70的那些记录。

说明表别名
它允许我们用不同的名称指定表名称。通常,表别名用于多个表,并使用JOIN操作连接它们。
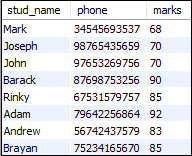
假设我们的数据库有一个名为“ Students”的表,其中包含以下数据:
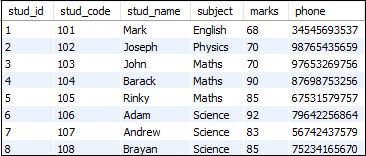
该语句将使用表别名返回记录:
mysql> SELECT Student_details.stud_name, Student_details.phone, Student_details.marks
FROM Students AS Student_details;
它将给出以下输出:
让我们看另一个示例,以了解使用JOIN操作的表别名。假设我们的数据库还有一个名为“ Student_detail”的表,其中包含以下数据:
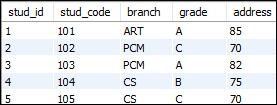
在两个表中,我们可以看到它们包含相同的一列“ stud_code”。如果我们在没有表别名的情况下使用它,它将给出一个错误消息:一个子句中的列“ stud_code”是不明确的。
因此,如果要避免此类错误,请使用表别名概念。该语句更清楚地说明了这一点:
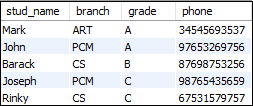
mysql> SELECT stud_name, branch, grade, phone
FROM Students AS S
INNER JOIN Student_detail AS D
ON S.stud_code=D.stud_code
ORDER BY grade;
成功执行以上语句后,我们将获得以下输出:
如果您不想在查询中使用别名概念,则MySQL使用表名来标识列名。此过程使语句冗长且可读性较差,如下所示:
mysql> SELECT stud_name, branch, grade, phone
FROM Students INNER JOIN Student_detail
ON Students.stud_code=Student_detail.stud_code
ORDER BY grade;