用Java将 HashMap 写入文本文件
Java中的 HashMap 类实现了 Serializable 接口,以便可以使用ObjectOutputStream将其对象写入或序列化到文件中。但是,它生成的输出文件不是人类可读的格式,并且可能包含垃圾字符。
序列化:将对象及其属性和内容写入文件的过程。它在内部将对象转换为字节流。
反序列化:它是从文件中读取对象及其属性以及对象内容的过程。
If we want to write a HashMap object to a plain text file, we need a simple and understandable code to write on the HashMap and then insert the Map into the Text File. We can write the code in the form of key-Value Pair of a map Object to a File and each line File will contain the Key-Value Pair
方法
- 在下面的类中,我们将 HashMap 内容存储在 hashmap.ser 序列化文件中。
- 一旦我们运行下面的代码,它就会生成一个 hashmap.ser 文件。该文件将在下一个类中用于反序列化。
- hashmap.ser 序列化文件可以存储到任何位置,并描述它的位置,如下所示
- 所以我们需要 Location 在其中写入 HashMap。
- 因此,需要提供外部位置来存储 HashMap
final static String outputFilePath = "F:/Serialisation/write.txt";创建字符串键和字符串值对的 HashMap
HashMap map = new HashMap(); 创建文件对象:
File file = new File(outputFilePath);使用文件对象,我们将使用函数BufferedWriter (File_Path)编写 HashMap 输入
bf = new BufferedWriter( new FileWriter(file));然后最后关闭文件
bf.close();写入文件
Java
// Java program to write HashMap to a file
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
final static String outputFilePath
= "F:/Serialisation/write.txt";
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create new HashMap
HashMap map
= new HashMap();
// key-value pairs
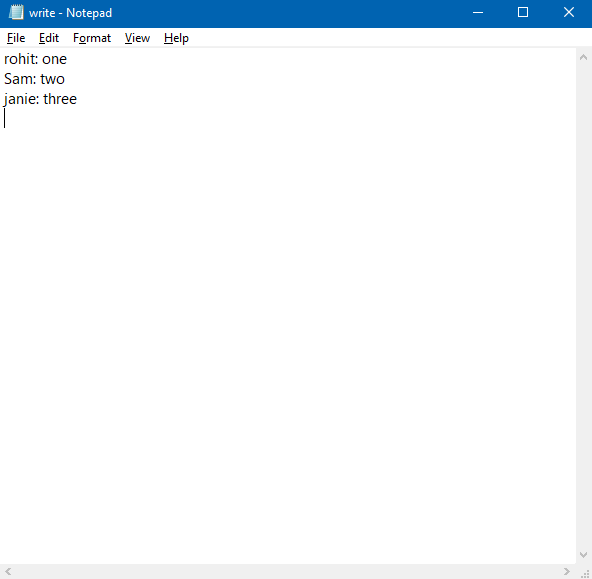
map.put("rohit", "one");
map.put("Sam", "two");
map.put("jainie", "three");
// new file object
File file = new File(outputFilePath);
BufferedWriter bf = null;
try {
// create new BufferedWriter for the output file
bf = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
// iterate map entries
for (Map.Entry entry :
map.entrySet()) {
// put key and value separated by a colon
bf.write(entry.getKey() + ":"
+ entry.getValue());
// new line
bf.newLine();
}
bf.flush();
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
// always close the writer
bf.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
} 输出: