晶体场论
配位化合物由中心的金属原子或离子组成,周围环绕着许多带相反电荷的离子或中性分子。配位连接将这些离子或分子与金属原子或离子连接起来。当溶解在水中时,它们不会解离成简单的离子。
晶体场论
H. Bethe 和 V. Bleck 提出了晶体场理论 (CFT)。该理论更详细地描述了金属配合物的键合、特性、电子光谱和磁性。
Crystal field splitting is the conversion of five degenerate d-orbitals of a metal ion into different sets of orbitals with varying energies in the presence of a crystal field of ligands. Crystal field theory is founded on the splitting of crystal fields.
晶体场论的假设
- 根据晶体场理论,金属离子被配体产生的电场包围。
- 在配合物中,核心金属和配体之间的吸引力完全是静电的。金属离子被中性分子配体的偶极子的负端靶向。
- 过渡金属或离子是带有与氧化态相同电荷的正离子。
- 特定数量的配体围绕过渡金属原子或离子,可以是带有孤对电子的负离子或中性分子。
- 配体充当产生电场的点电荷。金属原子或离子上的轨道能量被该电场改变。
- 由于中心金属离子与配体之间的排斥吸引力,中心金属离子上的电子占据尽可能远离配体接近方向的d轨道。
- 金属轨道和配体轨道没有相互作用。
- 在一个孤立的金属原子或离子中,所有轨道都具有相同的能量,即所有五个 d 轨道(d xy 、d xz 、d yz 、d x 2 -y 2和d z 2 )都是简并的。
- 当核心金属原子或离子被球对称的负电荷场包围时,d-轨道保持简并。然而,场与金属原子或离子上的电子之间的排斥提高了轨道的能量。
- 在大多数过渡金属配合物中,d-轨道受到不同的影响,并且由于不对称配体产生的场,它们的简并性丧失。
光谱化学系列
配体的类型决定了晶场分裂。弱场配体是仅引起较小晶体场分裂的配体。强场配体是产生高晶体场分裂的配体。
The spectrochemical series is the grouping of common ligands in ascending order of crystal field splitting (Δ). In increasing order of crystal field splitting, the spectrochemical series is:
I–
NO–2
八面体配合物的晶体场理论
配体由八面体络合物离子中的适度负电荷表示,而金属离子由正变化表示。

- 当配体接近金属离子时,配体和 d 轨道之间的排斥发生在八面体配合物中,从而提高了它们相对于自由离子的能量。配体排斥 d x 2 –y 2和 d z 2轨道比其余三个 d 轨道 d xy 、d xz和 d yz 更强。
- 结果,d xy 、d xz和d yz轨道的能量低于d x 2 -y 2和d z 2轨道的能量。
- 低能 d xy 、 d xz和 d yz轨道被称为 t 2g轨道,而高能 d x 2 -y 2 、d z 2轨道被称为 e g轨道。
- 晶体场分裂能或晶体场稳定能是两组 d 轨道 (CFSE) 之间的能量差。它用字母 Δ O表示,代表八面体配合物。
- e g轨道的能级比平均值高 +0.6 Δ 0或 3/5 Δ 0 ,而 t 2g轨道的能级比平均值低 –0.4 Δ 0或 –2/5 Δ 0 。

- 强场配体具有高 Δ 0值并且是八面体配合物中的低自旋配合物。 [Fe(CN) 6 ] 4-和[Co(NH 3 ) 6 ] 3+是两个例子。
- 弱场配体是具有低 Δ 0值的高自旋配合物。
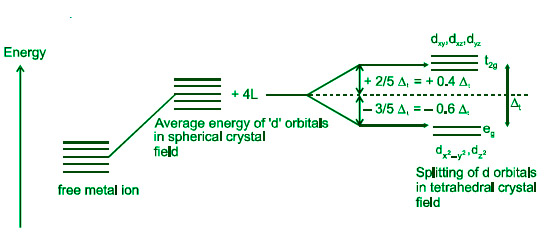
四面体配合物的晶体场理论
- 四面体配合物的分裂模式与八面体配合物的极性相反。四面体配合物中的 d x 2 –y 2和 d z 2轨道的能量低于 d xy 、d xz和 d yz轨道。
- Δt(Δt=49 Δ 0 )是两个能级之间的能量差。由于能隙窄,电子不会配对。因此,四面体配合物具有高自旋结构。
晶体场稳定能
Crystal field splitting energy or crystal field stabilisation energy is the difference in energy between the two sets of d-orbitals (CFSE). It is denoted by the symbol Δ.
影响轨道分裂能 (Δ) 大小的因素
- 轨道分裂能值越大,中心离子的氧化态越高。
- d块(过渡)元素的Δ值从3d增长到4d再到5d。因此,第二 (4d) 和第三 (5d) 过渡系列中的元素比第一 (3d) 过渡系列中的元素更容易形成低自旋配合物。
- 协调实体的 Δ 值有助于复合物的分类。四面体配合物的值大约是八面体配合物的一半。
晶体场论的局限性
晶体场理论能够令人满意地描述配位化合物的合成、结构、光学和磁性。然而,晶体场假说无法解释以下因素。
- 在一些过渡金属配合物中发现了共价键。
- 在光谱化学系列中,配体的顺序。因为配体是点电荷,阴离子配体应该有更强的分裂效应。另一方面,阴离子配体位于光谱化学系列的底部。
示例问题
问题一:什么是晶体场论?
回答:
Crystal field splitting is the conversion of five degenerate d-orbitals of a metal ion into different sets of orbitals with varying energies in the presence of a crystal field of ligands. Crystal field theory is founded on the splitting of crystal fields.
问题二:晶体场论的主要特点是什么?
回答:
According to the crystal field theory, the metal ion is surrounded by an electric field created by the ligands. In a complex, the attraction between the core metal and the ligand is solely electrostatic. The metal ion is targeted by the negative end of the dipole of the neutral molecule ligand. The transition metal or ion is a positive ion with the same charge as the oxidation state. A specified number of ligands surround the transition metal atom or ion, which can be negative ions or neutral molecules with lone pairs of electrons.
The ligands act as point charges that generate an electric field. The energy of the orbitals on the metal atom or ions is changed by this electric field. The electrons on the central metal ion occupy the d-orbitals as far away as possible from the direction of approach of the ligand due to the repulsive attraction between the central metal ion and the ligand.
问题3:影响晶场分裂的因素有哪些?
回答:
The crystal field splitting is affected by the type of the ligand and the oxidation state of the central atom. The larger the value of orbital splitting energy, the higher the oxidation state of the central ion. Various ligands have different splitting magnitudes for the same metal ion.
问题4:如何使用晶体场论?
回答:
The bonding characteristics, electronic spectra, and magnetism of metal complexes are all explained by crystal field theory. Strong field ligands have a high Δ0 value and are low spin complexes in octahedral complexes. The weak field ligands are high spin complexes with a low Δ0 value.
问题5:什么是晶场稳定能量?
回答:
The difference in energy between the two sets of d-orbitals is known as crystal field splitting energy or crystal field stabilisation energy (CFSE). It’s represented by the symbol Δ.
问题6:晶体场论的局限性是什么?
回答:
The synthesis, structure, optical, and magnetic properties of the coordination compound were all satisfactorily described by the crystal field theory. The crystal field hypothesis, on the other hand, failed to account for the following factors.
- Some transition metal compounds have covalent bonding.
- The order of the ligands in the spectrochemical series. Anionic ligands should have a higher splitting impact because they are point charges. The anionic ligands, on the other hand, are found at the bottom of the spectrochemical hierarchy.