电子的发现
发现基本粒子的基本思想是由道尔顿原子论产生的。约翰道尔顿在 1808 年提出了第一个关于原子的科学理论,其中他指出原子是任何物质中最小的粒子。它们是不可分割和不可破坏的。根据道尔顿原子理论:
- 物质由称为原子的微小不可分割粒子组成。
- 原子既不能被创造也不能被摧毁。
- 相同元素的原子在所有方面都是相似的,但它们与不同元素的原子不同。
- 元素的原子以简单的整数比结合形成分子。
上述陈述被称为道尔顿原子论的假设。但是,后来这些假设被证明是错误的,因为亚原子粒子的第一个迹象来自法拉第对静电的研究,该研究表明电流是由带电粒子引起的。
JJ Thomson 爵士首先证明了在称为电子的原子中存在带负电的粒子。因此,电子是第一个被发现的亚原子粒子,这为发现所有其他亚原子粒子(即质子和中子)以及原子的实际结构铺平了道路。
在本文中,我们将讨论威廉克鲁克使用阴极射线管发现电子的过程,以及后来 JJ 汤姆森对电子的实际发现。
JJ汤姆森和电子的发现
科学家 JJ Thomson 在 1900 年代初开始研究阴极射线管。阴极射线管是真空密封的玻璃管,已去除大部分空气。在管子的一端,在两个电极之间放置高压,使粒子流从阴极(带负电的电极)流向阳极(带正电的电极)(带正电的电极)。
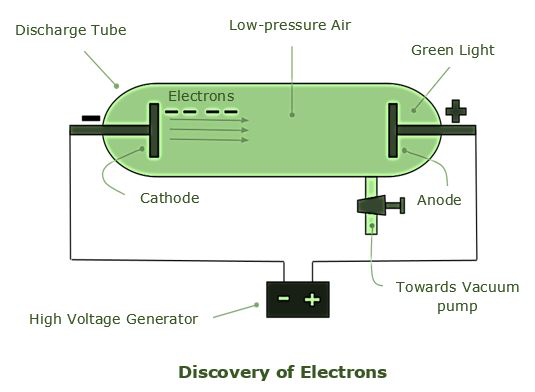
因为粒子束或阴极射线从阴极开始,所以管子被称为阴极射线管。可以通过在管的远端(阳极之外)涂上荧光粉来检测光束。当阴极射线撞击荧光粉时,它们会产生火花或发光。汤姆森用两个带相反电荷的电板包围阴极射线,以研究粒子的特性。阴极射线从带负电的电板重定向到带正电的板。据此,阴极射线由带负电的粒子组成。
汤姆森还在管子的两侧安装了两个磁铁,并注意到阴极射线被磁场转移了。汤姆森利用这些测试的结果来计算阴极射线粒子的质荷比,这导致了一个令人惊讶的发现:每个粒子的质量比任何已知原子都低得多。汤姆森继续用几种金属作为电极材料进行测试,发现无论阴极材料如何,阴极射线的特性都是一致的。
Thomson 根据证据得出以下结论:
- 带负电的粒子构成阴极射线。
- 因为每个粒子的质量约为氢原子的 1/2000,所以它们必须是原子的一部分。
- 在所有元素的原子中,都可以找到这些亚原子粒子。
汤姆森的发现最初是有争议的,但它们逐渐被科学家接受。他的阴极射线粒子最终被赋予了一个更通用的名称:电子。电子的发现与道尔顿的原子论关于原子不可分割的假设相矛盾。需要一个全新的原子模型来解释电子的存在。
What are Cathode Ray and Cathode ray tube?
J. J. Thomson built a glass tube that was partly evacuated, meaning that a significant amount of air was pushed out. He then used two electrodes at either end of the tube to apply a large electrical voltage. He saw a stream of particles (ray) travelling from the negatively charged electrode (cathode) to the positively charged electrode (anode) (anode). The ray is referred to as a cathode ray, and the entire structure is referred to as a cathode ray tube.
什么是电子?
The electron is a negatively charged, low-mass particle. As a result, passing close to other electrons or the positive nucleus of an atom might readily deflect it. The first basic particle identified was the electron.
JJ Thomson 通过在放电管中进行的测试发现了电子及其特性。基本电荷为 -1 的亚原子粒子称为电子。电子所持有的电荷与质子所持有的电荷相同(但符号相反)。
- 电子上的电荷:虽然质子和电子所拥有的电荷大小相同,但电子的大小和质量明显小于质子(电子的质量约为质子的 1/1836)。带负电的粒子是电子。负电荷的大小为 1.602 × 10 -19库仑。电子的质量是质子的 1/1837。
- 一个电子的质量:一个电子的质量为 9.10938356 × 10 -31千克。与质子的质量相比,电子的质量很小。
电子的特性
原子是物质组成的最小单位。原子核位于原子的核心,有一个或多个电子围绕它运行。质子和中子统称为核子,构成原子核。质子是质量为 1.00867 amu 的电中性粒子,而中子是质量为 1.00728 amu 的带正电粒子。
质量为 0.000549 amu 的电子是带负电的粒子。质子和中子的重量大约是电子的 1836 倍。电子的数量等于质子的数量,从而产生元素的中性原子。元素的化学特性由其电子排列决定,而核结构决定原子的稳定性和放射性跃迁。
示例问题
问题 1:JJ Thomson 在发现电子或阴极射线时使用的放电管内的情况是什么?
解决方案:
The conditions inside the discharged tube used by J.J. Thomson in the discovery of electrons are:
- It must have a very low pressure of 0.01 mm of Hg.
- It should have a vacuum inside it.
- Very high voltage must be applied across the terminals.
问题2:电场对阴极射线的影响是什么?
解决方案:
Cathode rays are deflected from their own straight-line path under the influence of the electric field. They are attracted towards the positive field due to their own negative charge and repelled away from the negative field.
问题 3:陈述阴极射线的两个性质。
解决方案:
The two properties of Cathode rays:
- They are negatively charged and always travel in straight lines.
- They can penetrate through matter and cause ionization of the particles of the gases through which they pass.
问题 4:X 射线是如何产生的?
解决方案:
X-rays are produced when a beam of the cathode ray is made to fall on hard metallic substances like tungsten.
问题5:法拉第对静电的研究如何为亚原子粒子的发现铺平道路?
解决方案:
Previously, Dalton proposed the atomic theory which says that the atoms are the most fundamental particles of matter and are indivisible but, Faraday while studying static electricity found that electricity flow through the matter due to the charged particles. This made many scientists believe that atoms are divisible into more fundamental particles. Thus, the study of static electricity by Faraday paved the way for the discovery of sub-atomic particles.