Java中的 For 循环 |要点
编程语言中的循环是一种有助于在某些条件评估为真时重复执行一组指令/函数的功能。在Java中,几乎不可能有任何编程语言提供四种执行循环的方法,即 while 循环、for 循环、for-each 循环、do-while 循环,或者我们可以在某些书籍中将其基本上称为三种类型的循环,因为 for-each 循环是被视为增强的 for 循环。让我们详细讨论for循环。
一般来说,我们倾向于使用 while 循环,因为如果我们进入学习循环,我们确实会更好地理解,但是在饱和之后,我们作为程序员倾向于倾向于 for 循环,因为它更干净并且基础是直接进行的我们必须仔细掌握语法如下:
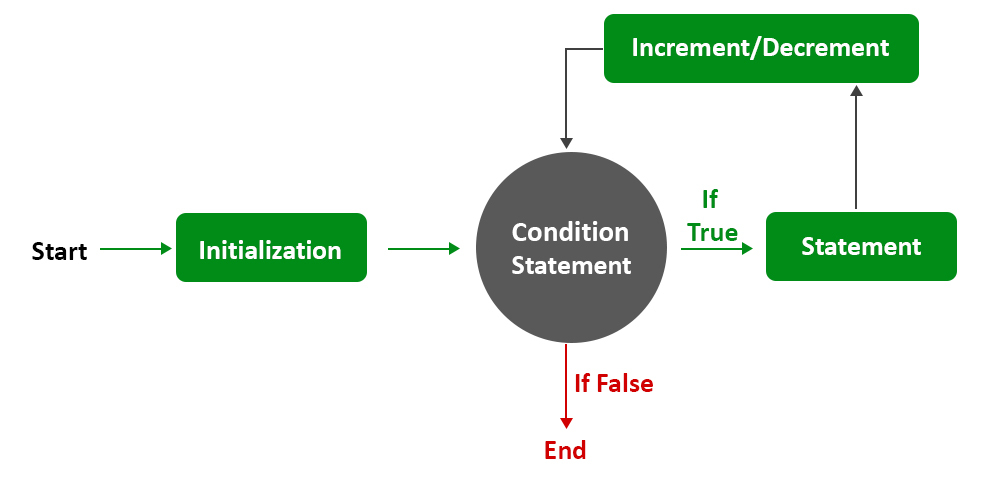
语法:它由三个部分组成,即列出:
- 变量的初始化
- 根据需要迭代这些定义的变量的要求的特定条件
- 一个终止部分,我们通常使用变量来达到终止条件状态。
for(initialization; boolean expression; update statement) {
// Body of for loop
} 这一般是for循环的基本朝圣结构。
让我们看一些使用 for 循环的基本示例以及使用 for 循环的常见陷阱,这使我们能够更好地了解内部工作,因为我们将在使用代码时进行描述。
用例 1:必须在 for 循环中提供表达式
For 循环必须包含循环语句中的有效表达式,失败可能导致无限循环。该声明
for ( ; ; )
is similar to
while(true)Note: This above said is crux of advanced programming as it is origin of logic building in programming.
例子
Java
// Java program to illustrate Infinite For loop
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// For loop
for (;;) {
// Print statement everytime condition holds
// true making body to execute
System.out.println("This is an infinite loop");
}
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Initializing Multiple
// Variables in Initialization Block
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring an integer variable
int x = 2;
// For loop to iterate
for (long y = 0, z = 4; x < 10 && y < 10;
x++, y++) {
// Printing value/s stored in variable named y
// defined inside body of for loop
System.out.println(y + " ");
}
// Printing value/s stored in variable named x
// defined outside body of for loop
System.out.println(x);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Redeclaring a Variable
// in Initialization Block
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring an integer variable
int x = 0;
// Redeclaring above variable
// as long will not work
for (long y = 0, x = 1; x < 5; x++) {
// Printing the value inside the variable
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Redeclaring a Variable
// in Initialization Block
// Main class
public class GFG {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring and initializing variables
int x = 0;
long y = 10;
// For loop to iterate over till
// custom specified check
for (y = 0, x = 1; x < 5; x++) {
// Printing value contained in memory block
// of the variable
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}
}Java
// Java program to Illustrate Declaring a Variable
// in Initialization Block
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring integer variable
// int x;
// Note: This will cause error;
// Redeclaring x as long will not work
for (long y = 0, x = 1; x < 5; x++) {
// Printing the value stored
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Scope of Initializing
// Variables Within the oop
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// x and y scope is declared only
// within for loop
for (int x = 0, y = 0; x < 3 && y < 3; x++, y++) {
// Printing value stored in variable named y
System.out.println(y + " ");
}
// Printing value stored in variable named x
// after inner loop is over
System.out.println(x);
}
}输出:重复打印语句“这是一个无限循环”。
This is an infinite loop
This is an infinite loop
This is an infinite loop
This is an infinite loop
...
...
This is an infinite loop用例 2:初始化多个变量
在Java中,无论是否在循环中使用,都可以在 for 循环的初始化块中初始化多个变量。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Initializing Multiple
// Variables in Initialization Block
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring an integer variable
int x = 2;
// For loop to iterate
for (long y = 0, z = 4; x < 10 && y < 10;
x++, y++) {
// Printing value/s stored in variable named y
// defined inside body of for loop
System.out.println(y + " ");
}
// Printing value/s stored in variable named x
// defined outside body of for loop
System.out.println(x);
}
}
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
10在上面的代码中,for 循环有一个简单的变化。在初始化块中声明和初始化了两个变量。未使用变量“z”。此外,其他两个组件包含额外的变量。因此,可以看出这些块可能包含额外的变量,这些变量可能不会被彼此引用。
用例 3:在初始化块中重新声明变量
假设,一个初始化变量已经被声明为一个整数。这里我们不能在 for 循环中用另一种数据类型重新声明它,如下所示:
示例 1:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Redeclaring a Variable
// in Initialization Block
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring an integer variable
int x = 0;
// Redeclaring above variable
// as long will not work
for (long y = 0, x = 1; x < 5; x++) {
// Printing the value inside the variable
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}
}
输出:
Example3.java:12: error: variable x is already defined in method main(String[])
for(long y = 0, x = 1; x < 5; x++)在这里,x 已经作为整数初始化为零,并在循环中以 long 数据类型重新声明。但是这个问题可以通过稍微修改代码来解决。这里,变量 x 和 y 以不同的方式声明。
示例 2:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Redeclaring a Variable
// in Initialization Block
// Main class
public class GFG {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring and initializing variables
int x = 0;
long y = 10;
// For loop to iterate over till
// custom specified check
for (y = 0, x = 1; x < 5; x++) {
// Printing value contained in memory block
// of the variable
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}
}
输出:
1 2 3 4用例 4:在初始化块中声明的变量必须是相同的类型
当我们声明一个变量时,如下所示:
int x, y;这里两个变量属于同一类型。在 for 循环初始化块中也是如此。
例子:
Java
// Java program to Illustrate Declaring a Variable
// in Initialization Block
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring integer variable
// int x;
// Note: This will cause error;
// Redeclaring x as long will not work
for (long y = 0, x = 1; x < 5; x++) {
// Printing the value stored
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}
}
1 2 3 4 用例 5:循环中的变量只能在内部访问
在初始化块中声明的变量只能在循环中访问,就像我们根据变量范围的概念一样。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Scope of Initializing
// Variables Within the oop
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// x and y scope is declared only
// within for loop
for (int x = 0, y = 0; x < 3 && y < 3; x++, y++) {
// Printing value stored in variable named y
System.out.println(y + " ");
}
// Printing value stored in variable named x
// after inner loop is over
System.out.println(x);
}
}
错误:
Example5.java:13: error: cannot find symbol
System.out.println(x);In the above example, variable x is not accessible outside the loop. The statement which is commented gives a compiler error.