📌 相关文章
- 服务定位器模式(1)
- 定位器 (1)
- 服务定位器,Unity - 任何代码示例
- 设计模式-空对象模式
- 设计模式-空对象模式(1)
- 设计模式-命令模式(1)
- 设计模式-命令模式
- 定位器 - 任何代码示例
- 什么是定位器 (1)
- 设计模式-状态模式
- 定位器类型 (1)
- 设计模式-模板模式
- 设计模式-模板模式(1)
- 设计模式-迭代器模式
- 设计模式-迭代器模式(1)
- 设计模式-过滤器模式(1)
- 设计模式-过滤器模式
- 设计模式-生成器模式
- 设计模式-生成器模式(1)
- 设计模式-MVC模式(1)
- 设计模式-MVC模式
- 设计模式-策略模式(1)
- 设计模式-策略模式
- 设计模式-代理模式
- Selenium-定位器(1)
- selenium 中的定位器 (1)
- Selenium-定位器
- 设计模式 (1)
- Java的设计模式——迭代器模式(1)
📜 设计模式-服务定位器模式
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-21 02:09:14 🧑 作者: Mango
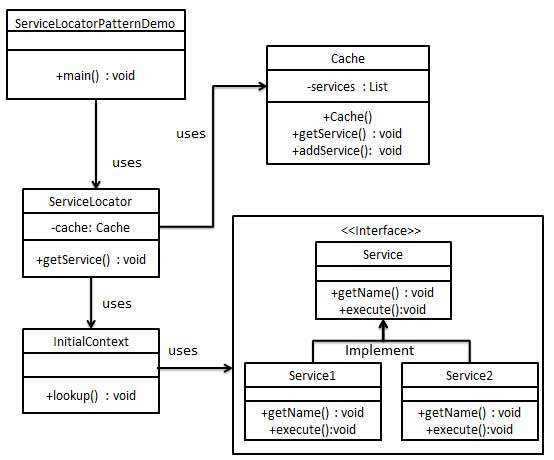
当我们想使用JNDI查找来定位各种服务时,将使用服务定位器设计模式。考虑到为服务查找JNDI的高昂成本,服务定位器模式利用了缓存技术。第一次需要服务时,服务定位器会在JNDI中查找并缓存服务对象。通过服务定位器进行的进一步查找或相同服务在其缓存中完成,这在很大程度上提高了应用程序的性能。以下是这种类型的设计模式的实体。
-
服务-将处理请求的实际服务。此类服务的参考将在JNDI服务器中查看。
-
上下文/初始上下文-JNDI上下文携带对用于查找目的服务的引用。
-
服务定位器-服务定位器是通过JNDI查找将服务缓存的服务来获取服务的单一联系点。
-
缓存-缓存以存储服务引用以重用它们
-
客户端-客户端是通过ServiceLocator调用服务的对象。
实作
我们将创建一个ServiceLocator , InitialContext , Cache , Service作为代表我们实体的各种对象。 Service1和Service2代表具体服务。
我们的演示类ServiceLocatorPatternDemo在这里充当客户端,并将使用ServiceLocator演示服务定位器设计模式。
第1步
创建服务界面。
Service.java
public interface Service {
public String getName();
public void execute();
}
第2步
创建具体服务。
服务1.java
public class Service1 implements Service {
public void execute(){
System.out.println("Executing Service1");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "Service1";
}
}
Service2.java
public class Service2 implements Service {
public void execute(){
System.out.println("Executing Service2");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "Service2";
}
}
第三步
创建用于JNDI查找的InitialContext
InitialContext.java
public class InitialContext {
public Object lookup(String jndiName){
if(jndiName.equalsIgnoreCase("SERVICE1")){
System.out.println("Looking up and creating a new Service1 object");
return new Service1();
}
else if (jndiName.equalsIgnoreCase("SERVICE2")){
System.out.println("Looking up and creating a new Service2 object");
return new Service2();
}
return null;
}
}
第4步
创建缓存
Cache.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Cache {
private List services;
public Cache(){
services = new ArrayList();
}
public Service getService(String serviceName){
for (Service service : services) {
if(service.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(serviceName)){
System.out.println("Returning cached " + serviceName + " object");
return service;
}
}
return null;
}
public void addService(Service newService){
boolean exists = false;
for (Service service : services) {
if(service.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(newService.getName())){
exists = true;
}
}
if(!exists){
services.add(newService);
}
}
}
第5步
创建服务定位器
ServiceLocator.java
public class ServiceLocator {
private static Cache cache;
static {
cache = new Cache();
}
public static Service getService(String jndiName){
Service service = cache.getService(jndiName);
if(service != null){
return service;
}
InitialContext context = new InitialContext();
Service service1 = (Service)context.lookup(jndiName);
cache.addService(service1);
return service1;
}
}
第6步
使用ServiceLocator演示服务定位器设计模式。
ServiceLocatorPatternDemo.java
public class ServiceLocatorPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Service service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service1");
service.execute();
service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service2");
service.execute();
service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service1");
service.execute();
service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service2");
service.execute();
}
}
步骤7
验证输出。
Looking up and creating a new Service1 object
Executing Service1
Looking up and creating a new Service2 object
Executing Service2
Returning cached Service1 object
Executing Service1
Returning cached Service2 object
Executing Service2