用Python将字典写入文件
字典用于以键:值对的形式存储数据值。在本文中,我们将看到如何将字典写入文件。实际上,我们只能将字符串写入文件。如果我们想编写一个字典对象,我们要么需要使用json将其转换为字符串,要么将其序列化。
方法:1使用 Json 存储带有对象的字典
方法:
- 导入Json
- 创建字典 按顺序将其传递到文本文件中。
- 以写模式打开文件。
- 将 json.dumps() 用于 json字符串
代码:
Python3
import json
details = {'Name': "Bob",
'Age' :28}
with open('convert.txt', 'w') as convert_file:
convert_file.write(json.dumps(details))Python3
details={'Name' : "Alice",
'Age' : 21,
'Degree' : "Bachelor Cse",
'University' : "Northeastern Univ"}
with open("myfile.txt", 'w') as f:
for key, value in details.items():
f.write('%s:%s\n' % (key, value))Python3
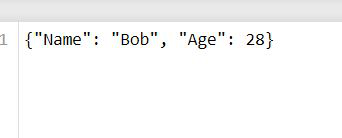
details = {'Name': "Bob", 'Age' :28}
with open('file.txt','w') as data:
data.write(str(details))输出:
方法二:使用循环
方法:
- 创建字典。
- 以写入模式打开文件。
- 这里我们使用带有键值对的 For 循环,其中“名称”是键,“爱丽丝”是值,因此 For 循环遍历每个键:每对的值对
- 然后 f.write()函数只写字符串“%s”形式的输出
代码:
蟒蛇3
details={'Name' : "Alice",
'Age' : 21,
'Degree' : "Bachelor Cse",
'University' : "Northeastern Univ"}
with open("myfile.txt", 'w') as f:
for key, value in details.items():
f.write('%s:%s\n' % (key, value))
输出:

方法:3 不使用loads(),dumps()。
这里的步骤遵循上述方法,但在 Write 中我们使用 Str() 方法将给定的字典转换为字符串
蟒蛇3
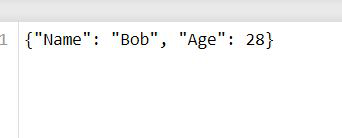
details = {'Name': "Bob", 'Age' :28}
with open('file.txt','w') as data:
data.write(str(details))
输出: