- C# 算术运算符 - C# (1)
- Python算术运算符
- python中的算术运算符(1)
- Python算术运算符(1)
- C# 算术运算符 - C# 代码示例
- JavaScript |算术运算符(1)
- JavaScript |算术运算符
- Bash 脚本 – 算术运算符(1)
- Bash 脚本 – 算术运算符
- python代码示例中的算术运算符
- Java算术运算符与示例(1)
- Java算术运算符与示例
- sql中的算术运算符(1)
- SQL |算术运算符
- SQL |算术运算符(1)
- 算术运算符 - 任何代码示例
- sql代码示例中的算术运算符
- C中的运算符|集合1(算术运算符)
- C中的运算符|集合1(算术运算符)(1)
- VBA算术运算符
- VBA算术运算符(1)
- PowerShell算术运算符(1)
- PowerShell算术运算符
- 算术数
- 谁是算术之父?
- 谁是算术之父?(1)
- LISP 中的算术运算符
- LISP 中的算术运算符(1)
- F#二元算术运算符
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-29 06:03:50 🧑 作者: Mango
Bash算术运算符
在本主题中,我们将了解如何在Bash中使用算术运算运算符。
根据我们希望通过脚本获得的结果类型,我们有时可能需要应用算术运算运算符。像变量一样,它们也很容易应用。在bash脚本中,我们可以对数值执行算术运算以获得所需的结果。
Bash Shell支持11种算术运算运算符。
查看下表,其中展示了每种算术运算运算符的语法,描述和示例:
| Operator | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition, measures addition of numbers (operands) |
$(( 10 + 3 )), result=13 |
| – | Substraction, measures subtraction of second operand from first |
$(( 10 - 3 )), result=7 |
| * | Multiplication, measures the multiplication of operands. |
$(( 10 * 3 )), result=30 |
| / | Division, measures the division of first operand by second operand and and return quotient. |
$(( 10 / 3 )), result=3 |
| ** | Exponentiation, measures the result of second operand raised to the power of first operand. |
$(( 10 ** 3 )), result=1000 |
| % | Modulo, measures remainder when the first operand is divided by second operand. |
$(( 10 % 3 )), result=1 |
| += | Increment Variable by Constant- used to increment the value of first operand by the constant provided. |
x=10 let "x += 3" echo $x result=13 |
| -= | Decrement Variable by Constant- used to decrement the value of first operand by the constant provided. |
x=10 let "x -= 3" echo $x result=7 |
| *= | Multiply Variable by Constant- used to multiply the value of the first operand by the constant provided. |
x=10 let "x *= 3" echo $x result=30 |
| /= | Divide Variable by Constant- used to calculate the value of (variable / constant) and store the result back to variable. |
x=10 let "10 /= 3" echo $x result=3 |
| %= | Remainder of Dividing Variable by Constant- used to calculate the value of (variable % constant) and store the result back to variable. |
x=10 let "10 %= 3" echo $x result=1 |
在Bash中执行算术运算
有很多选项可以在bash shell上执行算术运算。下面提供了一些我们可以用来执行算术运算的选项:
双括号
双括号是在Bash shell中执行基本算术运算的最简单机制。我们可以使用带或不带前导$的双括号来使用此方法。
句法
((expression))
我们可以采用四种不同的方法来实现所需的目标。查看下面给出的方法,以了解如何使用双括号机制(假设我们想将数字10和3相加):
方法1
Sum=$((10+3))
echo "Sum = $Sum"
方法2
((Sum=10+3))
echo "Sum = $Sum"
方法3
Num1=10
Num2=3
((Sum=Num1+Num2))
echo "Sum = $Sum"
方法4
Num1=10
Num2=3
Sum=$((Num1+Num2))
echo "Sum = $Sum"
所有这些方法将提供与以下相同的输出:
Sum = 13
下面是一个示例,演示在Bash shell脚本中对运算符使用双括号的情况:
Bash脚本
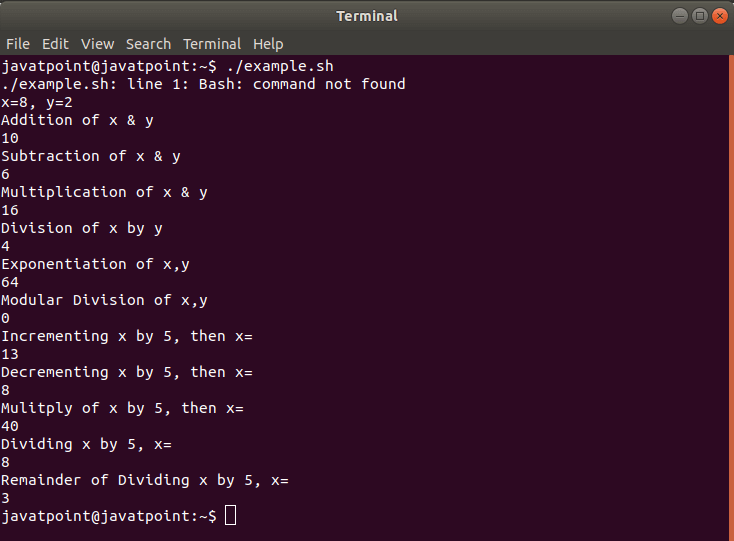
#!/bin/bash
x=8
y=2
echo "x=8, y=2"
echo "Addition of x & y"
echo $(( $x + $y ))
echo "Subtraction of x & y"
echo $(( $x - $y ))
echo "Multiplication of x & y"
echo $(( $x * $y ))
echo "Division of x by y"
echo $(( $x / $y ))
echo "Exponentiation of x,y"
echo $(( $x ** $y ))
echo "Modular Division of x,y"
echo $(( $x % $y ))
echo "Incrementing x by 5, then x= "
(( x += 5 ))
echo $x
echo "Decrementing x by 5, then x= "
(( x -= 5 ))
echo $x
echo "Multiply of x by 5, then x="
(( x *= 5 ))
echo $x
echo "Dividing x by 5, x= "
(( x /= 5 ))
echo $x
echo "Remainder of Dividing x by 5, x="
(( x %= 5 ))
echo $x
输出量
让建设
Let是Bash的内置命令,它允许我们执行算术运算。它遵循基本格式:
句法
let
下面给出一个示例,说明如何在Bash脚本中使用let命令:
Bash脚本
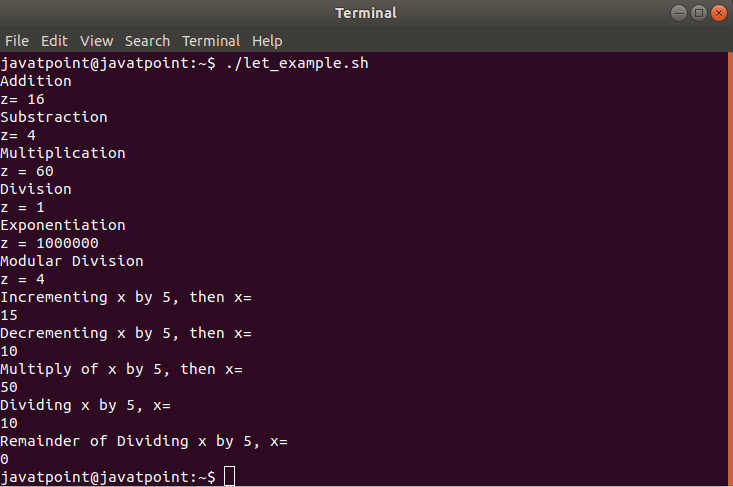
#!/bin/bash
x=10
y=6
z=0
echo "Addition"
let "z = $(( x + y ))"
echo "z= $z"
echo "Substraction"
let "z = $((x - y ))"
echo "z= $z"
echo "Multiplication"
let "z = $(( x * y ))"
echo "z = $z"
echo "Division"
let "z = $(( x / y ))"
echo "z = $z"
echo "Exponentiation"
let "z = $(( x ** y ))"
echo "z = $z"
echo "Modular Division"
let "z = $(( x % y ))"
echo "z = $z"
let "x += 5"
echo "Incrementing x by 5, then x= "
echo $x
let "x -= 5"
echo "Decrementing x by 5, then x= "
echo $x
let "x *=5"
echo "Multiply of x by 5, then x="
echo $x
let "x /= 5"
echo "Dividing x by 5, x= "
echo $x
let "x %= 5"
echo "Remainder of Dividing x by 5, x="
echo $x
输出量
反引号
在bash脚本中,还可以使用反引号和expr(称为通用表达式求值器)执行算术扩展。 “ expr”类似于“ let”,但是不会将结果保存到变量中。它直接打印结果。与let不同,我们不需要将表达式用引号引起来。我们需要在表达式的项目之间使用空格。重要的是要注意,我们应该在命令替换中使用'expr'将输出保存到变量中。
我们也可以不使用“反引号”而使用“ expr”。
句法
`expr item1 operator item2`
or
expr item1 operator item2
下面给出一个示例,说明如何在Bash脚本中使用反引号和expr:
Bash脚本程序
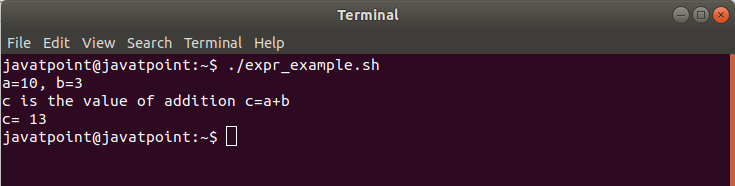
#!/bin/bash
#Basic arithmetic using expr
echo "a=10, b=3"
echo "c is the value of addition c=a+b"
a=10
b=3
echo "c= `expr $a + $b`"
输出量
结论
在本主题中,我们讨论了如何使用算术运算运算符执行算术运算。