Java中的自定义 ArrayList
在继续之前,让我们快速修改数组和ArrayList的概念。因此,在Java中,我们已经看到数组是线性数据结构,提供了在内存地址空间中以连续方式添加元素的功能,而 ArrayList 是属于 Collection 框架的类。作为一名优秀的程序员,尽管知道这两者之间的区别,但他已经意识到在数组上使用 ArrayList。现在继续前进,即使使用 ArrayList 也有一个功能可以传递应该存储在 ArrayList 中的元素的数据类型类型,可以是对象、字符串、整数、双精度、浮点数等。
句法:
Arraylist al = new ArrayList ; 注意: Java中的 ArrayList(相当于 C++ 中的向量)具有动态大小。它可以根据大小缩小或扩大。 ArrayList 是集合框架的一部分,存在于Java.util 包中。
句法:
ArrayList list = new ArrayList <> (); 这里重要的是,这里的 E 代表一个对象数据类型,想象一下这里的整数。 Integer 类将原始类型int的值包装在一个对象中。 Integer 类型的对象包含一个类型为 int 的字段。在继续之前,请先了解Java中包装类的概念,因为如果我们非常了解自动装箱和拆箱概念,它将在后端服务,从而使理解更加清晰。这是因为在对列表中的元素执行操作时,它们的语法会有所不同,因此对概念的掌握会耗尽,因为假设考虑将元素添加到自定义 ArrayList 的场景并注意它们之间的语法差异。
句法:
ArrayList al = new Arraylist() ;
al.add(1) ; 句法:
ArrayList alobj = new Arraylist() ;
alobj(new Integer(1)) ;让我们以一个示例说明来感知,如下所示:
插图:

在这里,我们拥有通常我们经常使用的相同类型的所有元素。现在让我们提出相同的图解流程 ArrayList 以该图像所示的方式简单地支持多个数据。
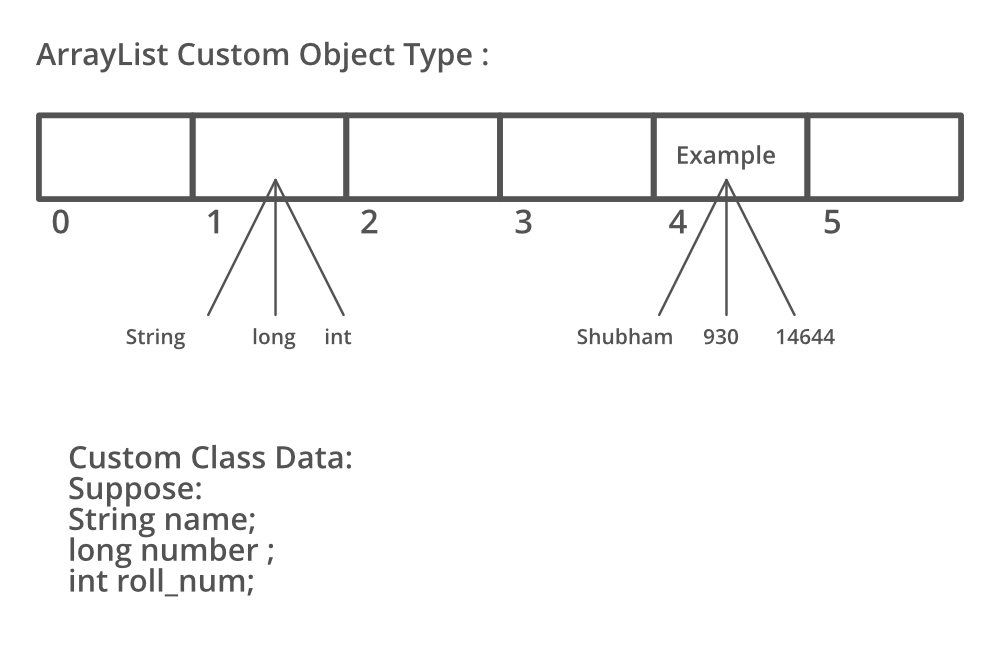
在上面的 ArrayList 中,我们可以清楚地看到存储的元素是不同类型的。所以它确实爆发了 限制。到一个单一的类型,不仅这个 List 可以让我们灵活地根据我们的类型创建 List,我们可以访问 ArrayList 中可以存在的数据类型之王。这个 List 在Java中被称为 Custom ArrayList 。自定义 ArrayList 具有基于用户要求的属性,并且可以具有多种类型的数据。此数据由自定义内部类提供,该内部类由各种原始对象数据类型组合而成。
实现:考虑一个案例,当我们必须将输入作为N个学生时,细节是:
- 卷号
- 姓名
- 分数
- 电话号码
假设如果我们不知道Java中自定义 Arraylist 的概念,那么我们将在下面列出单独的 ArrayList。当我们定义 4 个 ArrayList 并在每个数组中相应地保存数据时。
ArrayList roll = new ArrayList<>(); // roll number ArrayList name = new ArrayList<>(); // name ArrayList marks = new ArrayList<>(); // marks ArrayList phone = new ArrayList<>(); // phone number 现在我们将遍历它们中的每一个以获取学生数据,从而在更大程度上增加我们程序的时间复杂度,如下所示。
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Adding all the values to each arraylist
// each arraylist has primitive datatypes
roll.add(rollnum_i);
name.add(name_i);
marks.add(marks_i);
phone.add(phone_i);
}现在让我们在上面学到的概念的帮助下通过实现相同的方法来做同样的事情。因此,为了构造我们的自定义 ArrayList,请执行以下列出的步骤,如下所示:
过程:构造自定义ArrayList如下:
- 构建一个 ArrayList 对象并将其类型放置为 Class Data。
- 定义一个类并将所需的实体放入构造函数中。
- 将这些实体链接到全局变量。
- 从 ArrayList 接收的数据属于存储多个数据的类类型。
例子
Java
// Java program to illustrate Custom ArrayList
// Importing ArrayList class from java.util package
import java.util.ArrayList;
// Class 1
// Outer class
// Main class
// CustomArrayList
class GFG {
// Custom class which has data type class has
// defined the type of data ArrayList
// size of input 4
int n = 4;
// Class 2
// Inner class
// The custom datatype class
class Data {
// Global variables of the class
int roll;
String name;
int marks;
long phone;
// Constructor has type of data that is required
Data(int roll, String name, int marks, long phone)
{
// Initialize the input variable from main
// function to the global variable of the class
// this keyword refers to current instance
this.roll = roll;
this.name = name;
this.marks = marks;
this.phone = phone;
}
}
// Method 1
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Custom input data
int roll[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
String name[]
= { "Shubham", "Atul", "Ayush", "Rupesh" };
int marks[] = { 100, 99, 93, 94 };
long phone[] = { 8762357381L, 8762357382L,
8762357383L, 8762357384L };
// Creating an object of the class
GFG custom = new GFG();
// Now calling function to add the values to the
// arraylist
custom.addValues(roll, name, marks, phone);
}
public void addValues(int roll[], String name[],
int marks[], long phone[])
{
// local custom arraylist of data type
// Data having (int, String, int, long) type
// from the class
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// create an object and send values to the
// constructor to be saved in the Data class
list.add(new Data(roll[i], name[i], marks[i],
phone[i]));
}
// after adding values printing the values to test
// the custom arraylist
printValues(list);
}
// Method 2
// To print the values
public void printValues(ArrayList list)
{
// list- the custom arraylist is sent from
// previous function
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Data received from arraylist is of Data type
// which is custom (int, String, int, long)
// based on class Data
Data data = list.get(i);
// Print and display custom ArrayList elements
// that holds for student attribute
// Data variable of type Data has four primitive
// datatypes roll -int name- String marks- int
// phone- long
System.out.println(data.roll + " " + data.name
+ " " + data.marks + " "
+ data.phone);
}
}
}1 Shubham 100 8762357381
2 Atul 99 8762357382
3 Ayush 93 8762357383
4 Rupesh 94 8762357384