- rss 阅读器完整形式 (1)
- rss 阅读器完整形式 - 无论代码示例
- 演示 RSS 阅读器的 Shell 脚本
- 阅读器 - Java (1)
- 阅读器 - Java 代码示例
- Django-RSS
- Django-RSS(1)
- RSS教程(1)
- RSS教程
- 讨论RSS(1)
- 讨论RSS
- java 脚本阅读器 - Javascript (1)
- 配置阅读器 java (1)
- RSS-优势
- RSS-优势(1)
- RSS-摘要(1)
- RSS-摘要
- xml 阅读器属性 - C# (1)
- java 脚本阅读器 - Javascript 代码示例
- 配置阅读器 java 代码示例
- RSS-有用的资源(1)
- RSS-有用的资源
- xml 阅读器属性 - C# 代码示例
- 来自字符串 java 的阅读器(1)
- python csv阅读器 - Python(1)
- RSS-版本历史(1)
- RSS-版本历史
- 引导屏幕阅读器
- 来自字符串 java 代码示例的阅读器
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-05 05:29:39 🧑 作者: Mango
RSS代表Really Simple Syndication。 RSS是一种与用户共享您的网站更新和内容的简便方法,因此用户可能不必每天访问您的网站进行任何形式的更新。
RSS示例
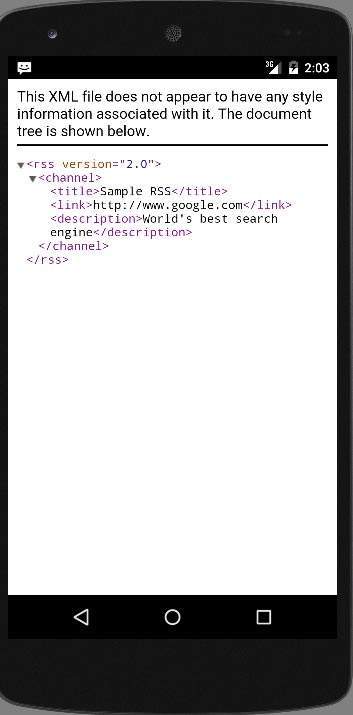
RSS是由网站创建的扩展名为.xml的文档。您可以轻松解析此文档,并将其显示给应用程序中的用户。 RSS文档如下所示。
Sample RSS
http://www.google.com
World's best search engine
RSS元素
如上所述的RSS文档具有以下元素。
| Sr.No | Component & description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
channel This element is used to describe the RSS feed |
| 2 |
title Defines the title of the channel |
| 3 |
link Defines the hyper link to the channel |
| 4 |
description Describes the channel |
解析RSS
解析RSS文档更像是解析XML。现在,让我们看看如何解析XML文档。
为此,我们将创建XMLPullParser对象,但为了创建该对象,我们将首先创建XmlPullParserFactory对象,然后调用其newPullParser()方法创建XMLPullParser。其语法如下-
private XmlPullParserFactory xmlFactoryObject = XmlPullParserFactory.newInstance();
private XmlPullParser myparser = xmlFactoryObject.newPullParser();
下一步涉及为XmlPullParser指定包含XML的文件。它可以是文件,也可以是流。在我们的例子中它是一个流,其语法如下-
myparser.setInput(stream, null);
最后一步是解析XML。 XML文件包含事件,Name,Text,AttributesValue等,因此XMLPullParser具有用于解析XML文件的每个组件的单独函数。其语法如下-
int event = myParser.getEventType();
while (event != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
String name=myParser.getName();
switch (event){
case XmlPullParser.START_TAG:
break;
case XmlPullParser.END_TAG:
if(name.equals("temperature")){
temperature = myParser.getAttributeValue(null,"value");
}
break;
}
event = myParser.next();
}
方法getEventType返回发生的事件的类型。例如:文档开始,标签开始等。getName方法返回标签的名称,并且由于我们仅对温度感兴趣,因此我们仅在条件语句中检查是否有温度标签,则调用getAttributeValue方法以返回给我们。温度标签的值。
除了这些方法之外,此类还提供了其他方法来更好地解析XML文件。这些方法在下面列出-
| Sr.No | Method & description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
getAttributeCount() This method just Returns the number of attributes of the current start tag. |
| 2 |
getAttributeName(int index) This method returns the name of the attribute specified by the index value. |
| 3 |
getColumnNumber() This method returns the Returns the current column number, starting from 0. |
| 4 |
getDepth() This method returns Returns the current depth of the element. |
| 5 |
getLineNumber() Returns the current line number, starting from 1. |
| 6 |
getNamespace() This method returns the name space URI of the current element. |
| 7 |
getPrefix() This method returns the prefix of the current element. |
| 8 |
getName() This method returns the name of the tag. |
| 9 |
getText() This method returns the text for that particular element. |
| 10 |
isWhitespace() This method checks whether the current TEXT event contains only white space characters. |
例
这是一个演示XMLPullParser类的用法的示例。它创建一个基本的解析应用程序,使您可以解析/android/sampleXML.xml中存在的RSS文档,然后显示结果。
要试验该示例,您可以在实际设备或仿真器上运行它。
| Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | You will use Android studio to create an Android application under a package com.example.sairamkrishna.myapplication. |
| 2 | Modify src/MainActivity.java file to add necessary code. |
| 3 | Modify the res/layout/activity_main to add respective XML components. |
| 4 | Create a new java file under src/HandleXML.java to fetch and parse XML data. |
| 5 | Create a new java file under src/second.java to display result of XML |
| 5 | Modify AndroidManifest.xml to add necessary internet permission. |
| 6 | Run the application and choose a running android device and install the application on it and verify the results. |
以下是修改后的主要活动文件src / MainActivity.java的内容。
package com.example.sairamkrishna.myapplication;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
EditText title,link,description;
Button b1,b2;
private String finalUrl="http://tutorialspoint.com/android/sampleXML.xml";
private HandleXML obj;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
title = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText);
link = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText2);
description = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText3);
b1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
b2=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button2);
b1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
obj = new HandleXML(finalUrl);
obj.fetchXML();
while(obj.parsingComplete);
title.setText(obj.getTitle());
link.setText(obj.getLink());
description.setText(obj.getDescription());
}
});
b2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent in=new Intent(MainActivity.this,second.class);
startActivity(in);
}
});
}
}
以下是Java文件src / HandleXML.java的内容。
package com.example.rssreader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParser;
import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParserFactory;
import android.util.Log;
public class HandleXML {
private String title = "title";
private String link = "link";
private String description = "description";
private String urlString = null;
private XmlPullParserFactory xmlFactoryObject;
public volatile boolean parsingComplete = true;
public HandleXML(String url){
this.urlString = url;
}
public String getTitle(){
return title;
}
public String getLink(){
return link;
}
public String getDescription(){
return description;
}
public void parseXMLAndStoreIt(XmlPullParser myParser) {
int event;
String text=null;
try {
event = myParser.getEventType();
while (event != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
String name=myParser.getName();
switch (event){
case XmlPullParser.START_TAG:
break;
case XmlPullParser.TEXT:
text = myParser.getText();
break;
case XmlPullParser.END_TAG:
if(name.equals("title")){
title = text;
}
else if(name.equals("link")){
link = text;
}
else if(name.equals("description")){
description = text;
}
else{
}
break;
}
event = myParser.next();
}
parsingComplete = false;
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void fetchXML(){
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
URL url = new URL(urlString);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setReadTimeout(10000 /* milliseconds */);
conn.setConnectTimeout(15000 /* milliseconds */);
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setDoInput(true);
// Starts the query
conn.connect();
InputStream stream = conn.getInputStream();
xmlFactoryObject = XmlPullParserFactory.newInstance();
XmlPullParser myparser = xmlFactoryObject.newPullParser();
myparser.setFeature(XmlPullParser.FEATURE_PROCESS_NAMESPACES, false);
myparser.setInput(stream, null);
parseXMLAndStoreIt(myparser);
stream.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
}
}
});
thread.start();
}
}
在目录java / second.java下创建一个文件,并将其命名为second.java文件。
package com.example.sairamkrishna.myapplication;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.webkit.WebView;
public class second extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.second_activity);
WebView w1=(WebView)findViewById(R.id.webView);
w1.loadUrl("http://tutorialspoint.com/android/sampleXML.xml");
}
}
在res / layout / second_activity.xml中创建一个xml文件
将res / layout / activity_main.xml的内容修改为以下内容:
将res / values /字符串.xml修改为以下内容
My Application
这是默认的AndroidManifest.xml 。
让我们尝试运行您的应用程序。我假设您在进行环境设置时已创建了AVD 。要从Android Studio运行该应用,请打开您项目的活动文件之一,然后点击运行 工具栏中的图标。 Android studio将应用安装在您的AVD上并启动它,如果设置和应用程序一切正常,它将显示在“模拟器”窗口下方-
工具栏中的图标。 Android studio将应用安装在您的AVD上并启动它,如果设置和应用程序一切正常,它将显示在“模拟器”窗口下方-
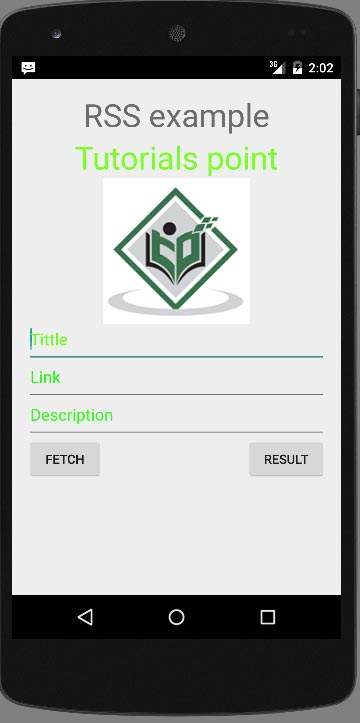
只需按Fetch Feed按钮即可获取RSS feed。按下后,将出现以下屏幕,其中将显示RSS数据。

只需按结果按钮即可查看XML,该XML位于http://tutorialspoint.com/android/sampleXML.xml