- C++运算符重载(1)
- C#-运算符重载(1)
- C#-运算符重载
- C#|运算符重载(1)
- C++中的运算符重载(1)
- F#-运算符重载
- C++中的运算符重载
- F#-运算符重载(1)
- 运算符重载 - C++ (1)
- Python中的运算符重载(1)
- Python中的运算符重载
- Python中的运算符重载(1)
- Python中的运算符重载
- Python运算符重载(1)
- Python运算符重载
- Python运算符重载
- Python运算符重载(1)
- C++代码示例中的运算符重载
- 运算符重载 - C++ 代码示例
- java中的重载+运算符(1)
- C++重载(运算符和函数)
- C++重载(运算符和函数)(1)
- C ++ |运算符重载|问题9
- C ++ |运算符重载|问题7(1)
- C ++ |运算符重载|问题9(1)
- C ++ |运算符重载|问题4
- C++ |运算符重载|问题7(1)
- C++ |运算符重载|问题9(1)
- C ++ |运算符重载|问题3
📅 最后修改于: 2020-09-25 05:02:47 🧑 作者: Mango
在本教程中,我们将借助示例来学习运算符重载。
在C++中,我们可以更改运算符对用户定义类型(如对象和结构)的工作方式。这称为运算符重载 。例如,
假设我们已经创建了三个对象c1 , c2并来自名为Complex的类的result ,该类表示复数。
由于运算符重载允许我们更改运算符的工作方式,因此我们可以通过编写以下代码来重新定义+ 运算符的工作方式,并使用它来添加c1和c2的复数:
result = c1 + c2;而不是像
result = c1.addNumbers(c2);这使我们的代码直观易懂。
注意:我们不能对基本数据类型(例如int , float和char等)使用运算符重载。
C++运算符重载的语法
要使运算符重载,我们使用特殊的operator 函数。
class className {
... .. ...
public
returnType operator symbol (arguments) {
... .. ...
}
... .. ...
};这里,
一元运算符中的运算符重载
一元运算符只能对一个操作数进行运算。增量运算符 ++和减量运算符 --是一元运算运算符的示例。
示例1:++运算符(一元运算符)重载
// Overload ++ when used as prefix
#include
using namespace std;
class Count {
private:
int value;
public:
// Constructor to initialize count to 5
Count() : value(5) {}
// Overload ++ when used as prefix
void operator ++ () {
++value;
}
void display() {
cout << "Count: " << value << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Count count1;
// Call the "void operator ++ ()" function
++count1;
count1.display();
return 0;
} 输出
Count: 6在这里,当我们使用++count1; ,将调用void operator ++ () 。这会将对象count1的value属性增加1。
注意:当我们重载运算符,我们可以使用它以任何我们喜欢的方式工作。例如,我们可以使用++将value增加100。
但是,这使我们的代码混乱并且难以理解。作为程序员,我们的工作是以一致且直观的方式正确使用运算符重载。
上面的示例仅在将++用作前缀时才有效。为了使++作为后缀,我们使用此语法。
void operator ++ (int) {
// code
}注意括号内的int 。这是用于将一元运算运算符用作后缀的语法;它不是函数参数。
示例2:++运算符(一元运算符)重载
// Overload ++ when used as prefix and postfix
#include
using namespace std;
class Count {
private:
int value;
public:
// Constructor to initialize count to 5
Count() : value(5) {}
// Overload ++ when used as prefix
void operator ++ () {
++value;
}
// Overload ++ when used as postfix
void operator ++ (int) {
++value;
}
void display() {
cout << "Count: " << value << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Count count1;
// Call the "void operator ++ (int)" function
count1++;
count1.display();
// Call the "void operator ++ ()" function
++ count1;
count1.display();
return 0;
} 输出
Count: 6
Count: 7当++同时用作前缀和后缀时, 示例2可以工作。但是,如果我们尝试执行以下操作,则将无法正常工作:
Count count1, result;
// Error
result = ++count1;这是因为我们的运算符 函数的返回类型为void 。我们可以通过使解决这一问题Count的运算符 函数的返回类型。
// return Count when ++ used as prefix
Count operator ++ () {
// code
}
// return Count when ++ used as postfix
Count operator ++ (int) {
// code
}示例3:从运算符函数(++运算符)返回的值
#include
using namespace std;
class Count {
private:
int value;
public
:
// Constructor to initialize count to 5
Count() : value(5) {}
// Overload ++ when used as prefix
Count operator ++ () {
Count temp;
// Here, value is the value attribute of the calling object
temp.value = ++value;
return temp;
}
// Overload ++ when used as postfix
Count operator ++ (int) {
Count temp;
// Here, value is the value attribute of the calling object
temp.value = ++value;
return temp;
}
void display() {
cout << "Count: " << value << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Count count1, result;
// Call the "Count operator ++ ()" function
result = ++count1;
result.display();
// Call the "Count operator ++ (int)" function
result = count1++;
result.display();
return 0;
} 输出
Count: 6
Count: 7在这里,我们使用以下代码进行前缀运算符重载:
// Overload ++ when used as prefix
Count operator ++ () {
Count temp;
// Here, value is the value attribute of the calling object
temp.value = ++value;
return temp;
}后缀运算符重载的代码也相同。注意,我们已经创建了一个对象temp并将其值返回给运算符 函数。
另请注意代码
temp.value = ++value; 变量value属于main()的count1对象,因为count1正在调用函数,而temp.value属于temp对象。
二元运算符中的运算符重载
二进制运算符处理两个操作数。例如,
result = num + 9;在这里, +是对操作数num和9起作用的二进制运算符 。
当我们使用以下代码为用户定义类型重载二进制运算符 :
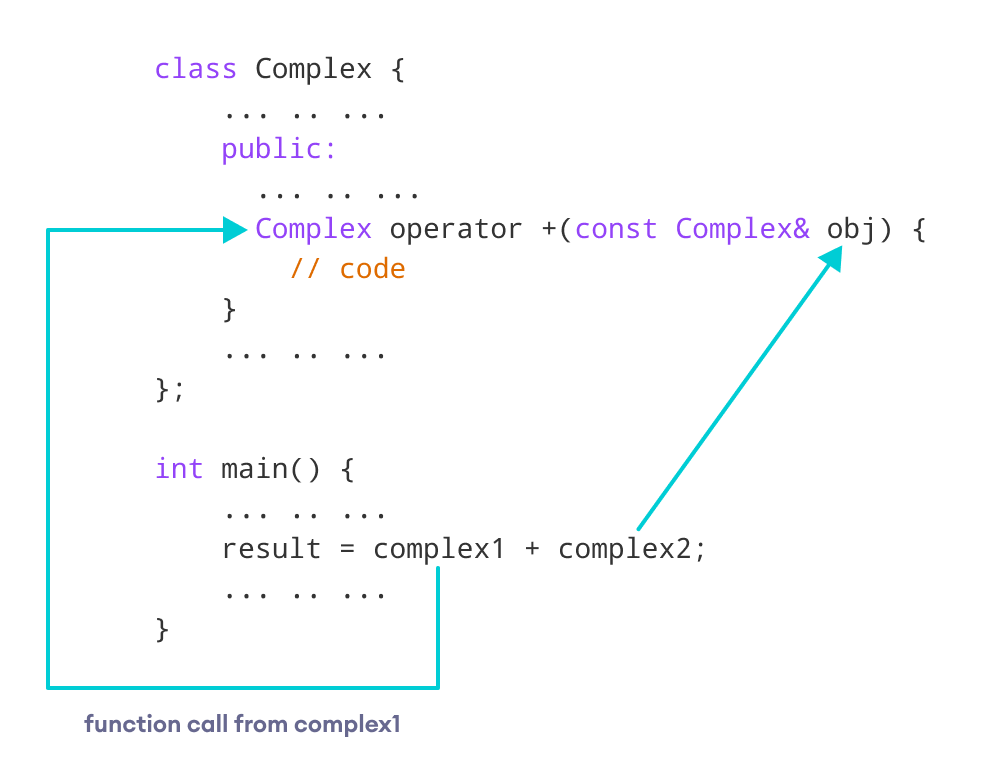
obj3 = obj1 + obj2;使用obj1对象调用运算符 函数,并将obj2作为参数传递给该函数。
示例4:C++二进制运算符重载
// C++ program to overload the binary operator +
// This program adds two complex numbers
#include
using namespace std;
class Complex {
private:
float real;
float imag;
public:
// Constructor to initialize real and imag to 0
Complex() : real(0), imag(0) {}
void input() {
cout << "Enter real and imaginary parts respectively: ";
cin >> real;
cin >> imag;
}
// Overload the + operator
Complex operator + (const Complex& obj) {
Complex temp;
temp.real = real + obj.real;
temp.imag = imag + obj.imag;
return temp;
}
void output() {
if (imag < 0)
cout << "Output Complex number: " << real << imag << "i";
else
cout << "Output Complex number: " << real << "+" << imag << "i";
}
};
int main() {
Complex complex1, complex2, result;
cout << "Enter first complex number:\n";
complex1.input();
cout << "Enter second complex number:\n";
complex2.input();
// complex1 calls the operator function
// complex2 is passed as an argument to the function
result = complex1 + complex2;
result.output();
return 0;
} 输出
Enter first complex number:
Enter real and imaginary parts respectively: 9 5
Enter second complex number:
Enter real and imaginary parts respectively: 7 6
Output Complex number: 16+11i在此程序中, 运算符 函数为:
Complex operator + (const Complex& obj) {
// code
}除此以外,我们还可以编写如下函数 :
Complex operator + (Complex obj) {
// code
}然而,
C++运算符重载中要记住的事情
访问这些页面以了解更多信息: