- SAS宏(1)
- SAS宏
- D编程-操作员(1)
- D编程-操作员
- SAS函数(1)
- SAS函数
- SAS字符串
- SAS字符串(1)
- SAS-SQL
- SAS-SQL(1)
- Powershell-操作员
- Powershell-操作员(1)
- sas - 任何代码示例
- C#|是操作员关键字(1)
- C#|是操作员关键字
- SAS数据集
- SAS数据集(1)
- 铲操作员打字稿代码示例
- Arduino-操作员(1)
- Arduino-操作员
- Tableau – 操作员
- Tableau – 操作员(1)
- SAS循环
- SAS循环(1)
- SAS变量
- SAS变量(1)
- SAS应用程序
- SAS应用程序(1)
- minecraft 操作员 (1)
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-08 14:26:44 🧑 作者: Mango
SAS运营商
在SAS中,运算符是符号,用于执行加,乘,减,除,比较等计算。这些符号是SAS编程语言的内置部分,因此我们可以将这些符号合并为一个表达式获得所需的输出。
SAS中有五种类型的运算符:
- 算术运算符
- 逻辑运算符
- 比较运算符
- 最小/最大运算符
- 优先运算符
算术运算符:
算术运算运算符用于执行数学计算,例如加法,乘法,减法,除法等。下表描述了算术运算运算符及其运算。
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | 12+2=14 |
| – | Subtraction | 24-4=10 |
| * | Multiplication | 6*3=32 |
| / | Division | 46/23=2 |
| ** | Exponentiation | 2**3=8 |
让我们通过一个示例来了解如何在SAS编程中使用算术运算运算符。
DATA Airthmatic_Operator;
input @1 A1 4.2@7 A2 3.1;
Add_result = A1+A2;
Sub_result = A1-A2;
Mult_result = A1*A2;
Div_result = A1/A2;
Expo_result = A1**A2;
datalines;
11.21 5.3
3.11 11
;
PROC PRINT DATA = Airthmatic_Operator;
RUN;
在SAS Studio中执行以上代码:

输出:
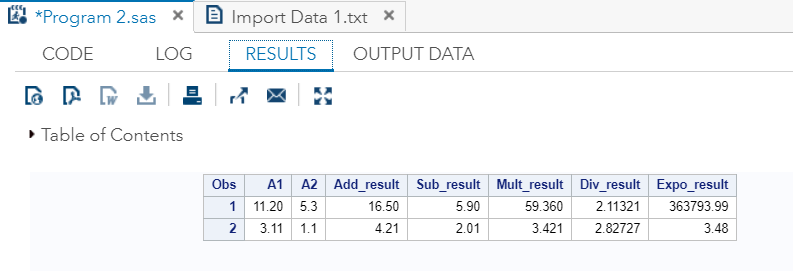
正如我们在输出中看到的,所有值都是根据算术运算运算符计算的。
逻辑运算符
逻辑运算符用于评估表达式的真或假值。逻辑运算符的结果始终为布尔值,即1或0。下表描述了逻辑运算符及其操作。
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| & | This symbol is calledthe AND Operator. If both data values evaluate true, then the result is 1 else it is 0. | (5>2 & 2> 3) gives 0 or false. |
| | | This symbol is calledthe OR Operator. If any one of the data values evaluates true, then the result is 1 else it is 0. | (10>9 & 5> 3) gives 1 or true. |
| ~ | This symbol is called The NOT Operator. If the values evaluate false, then the result is 1 else, it is 0. | NOT(8> 3) is 1 or true. |
让我们通过一个示例来了解如何在SAS编程中使用逻辑运算符。
DATA Logical_Operator;
input @1 a1 5.2 @7 a2 4.1;
and_=(a1 > 10 & a2 > 5 );
or_ = (a1 > 12 | a2 > 15 );
not_ = ~( a2 > 7 );
datalines;
11.21 5.3
3.11 11.4
;
PROC PRINT DATA = Logical_Operator;
RUN;
在SAS Studio中执行以上代码:
输出:
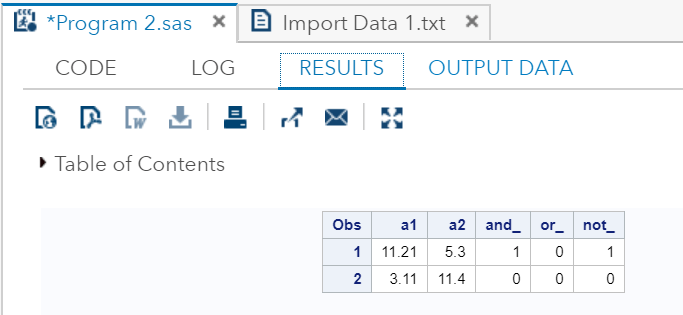
正如我们在输出中看到的那样,所有值都根据逻辑运算符的评估产生布尔结果。
比较运算符
运算符用于根据相等性比较值。运算符的结果始终是布尔值,即,1(对于真)或0(假)。下表描述了比较运算符及其操作。
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | This symbol is called the EQUAL Operator. If both values are equal, then the result is 1 else it is 0. | (8 =8) gives 1. (4=8) gives 0. |
| ^= | This symbol is called theNOT EQUAL Operator. If both values are unequal, then the result is 1 else it is 0. | (3 ^= 5) gives 1. (5^= 5) gives 0. |
| < | This symbol is called theLESS THAN Operator. | (2 < 9) gives 1. (12 < 9) gives 0. |
| <= | This symbol is called theLESS THAN or EQUAL TO Operator. | (3<= 4) gives 1. (4 <= 4) gives 1. (7 <= 4) gives 0. |
| > | This symbol is called theGREATER THAN Operator. | (22 > 20) gives 1. (10 > 20) gives 0. |
| >= | This symbol is called theGREATER THAN or EQUAL TO Operator. | (10 >=5) gives 1. (5 >=5) gives 1. (3 >=5) gives 0. |
| IN | If the value is equal to any of the value in a given list, then it returns 1 else returns 0. | 9 in (5,7,9,8) gives 1. 2 in (5,7,9,8) gives 0. |
我们先来了解通过一个例子,我们如何在SAS编程中使用的比较运算符。
DATA Comparison_Operator;
input @1 a1 5.2 @7 a2 4.1;
EQ_ = (a1 = 11.21);
NEQ_= (a1 ^= 11.21);
GT_ = (a2 => 8);
LT_ = (a2 <= 12);
IN_ = a2 in( 6.2,5.3,12 );
datalines;
11.21 5.3
3.11 11.4
;
PROC PRINT DATA = Comparison_Operator;
RUN;
在SAS Studio中执行以上代码:
输出:
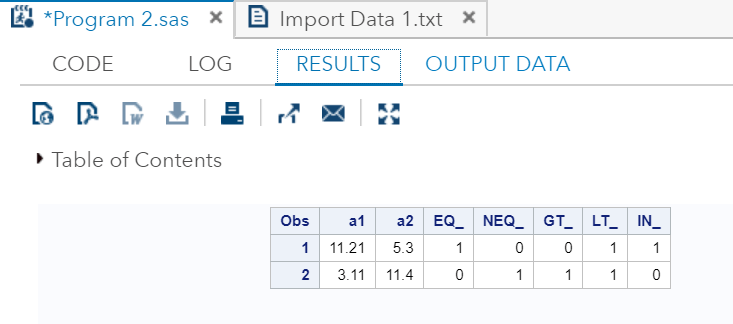
正如我们可以在输出看到,所有的值都根据比较运算符的计算产生布尔结果。
最小/最大运算符
这些运算符用于比较行中变量的值,以从该行的值列表中返回最大值或最小值。下表描述了Minimum / Maximum运算符及其操作。
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| MIN | This group of alphabets is called theMIN Operator. It returns the minimum value from the entire row. | MIN(45.2,11.6,15.41) gives 11.6 |
| MIN | This group of alphabets is called theMAX Operator. It returns the maximum value from the entire row. | MAX(46.3,11.6,15.41) gives 46.3 |
DATA MYDATA1;
input @1 A1 5.2 @7 A2 4.1 @12 A3 6.3;
min_ = MIN(A1 , A2 , A3);
max_ = MAX( A1, A2 , A3);
datalines;
10.21 5.3 29.12
3.11 11.4 18.12
;
PROC PRINT DATA = MYDATA1;
RUN;
在SAS Studio中执行以上代码:
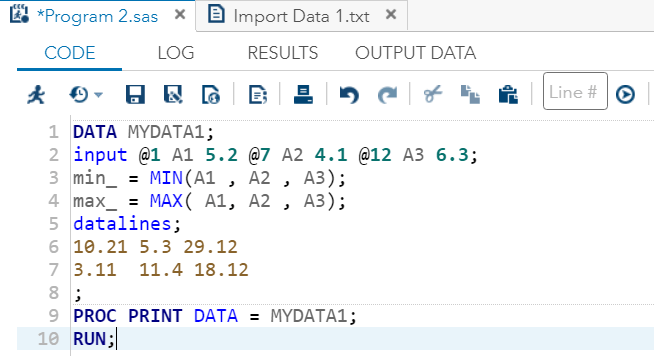
输出:

从输出中可以看到,最小值和最大值运算符已从两行的值列表中返回了最小值和最大值。
串联运算符
串联运算符用于串联两个或多个字符串值。下表描述了连接运算符及其操作。
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| || | This symbolis called theconcatenate Operator. It concatenates two or more string values. | ‘Hello’||’ SAS gives Hello SAS |
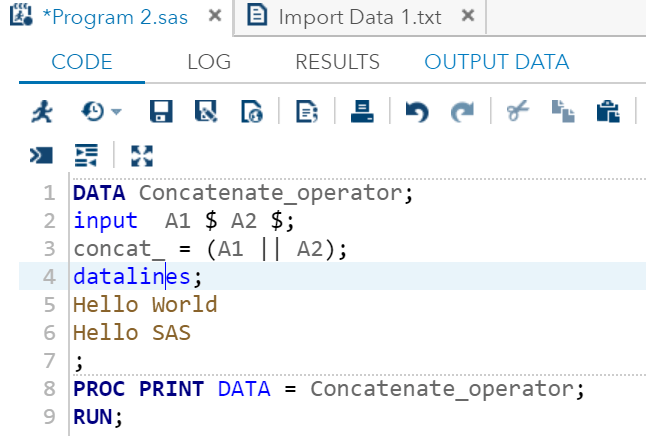
DATA Concatenate_operator;
input A1 $ A2 $;
concat_ = (A1 || A2);
datalines;
Hello World
Hello SAS
;
PROC PRINT DATA = Concatenate_operator;
RUN;
在SAS Studio中执行以上代码:
输出:
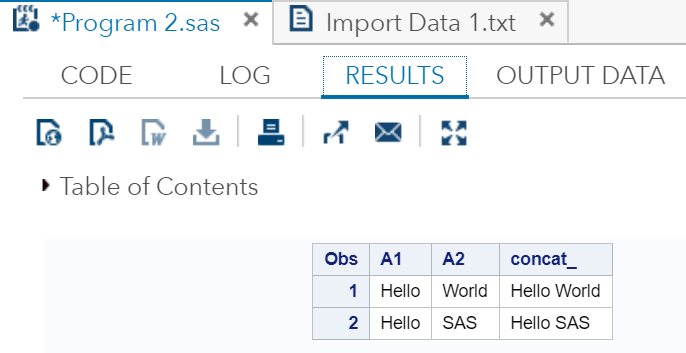
正如我们在输出中看到的,两个字符串变量都已连接在一起。
优先运算符:
优先运算符是一组运算符,用于指示复杂表达式中存在多个运算符时的求值顺序。下表介绍了优先运算符及其操作。
组顺序符号组I从右到左** +-非最小或最大值组II从左到右* /组III从左到右+-组IV从左到右||第五组从左到右<< = => =>