- TestNG (1)
- TestNG组
- TestNG组(1)
- 十大Pure.CSS面试问题
- 十大Pure.CSS面试问题(1)
- 十大敏捷开发面试问题
- 十大敏捷开发面试问题(1)
- 十大系统设计面试问题和答案
- 十大系统设计面试问题和答案(1)
- TestNG - 任何代码示例
- TestNG参数
- TestNG参数(1)
- TestNG教程
- TestNG教程(1)
- TestNG教程
- TestNG的功能(1)
- TestNG的功能
- Selenium-TestNG
- Selenium-TestNG(1)
- 讨论TestNG(1)
- 讨论TestNG
- TestNG-环境
- TestNG-环境(1)
- TestNG-概述(1)
- TestNG-概述
- TestNG注释(1)
- TestNG注释
- TestNG注释属性
- TestNG注释属性(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-11 12:11:09 🧑 作者: Mango
TestNG面试问题

下面列出了最常见的TestNG面试问题和答案。
1)什么是TestNG?
TestNG代表“测试下一代”。它是Credric beust开发的用于Java编程语言的自动化测试框架,它是从JUnit框架得到启发而来的。 TestNG包含JUnit框架的所有功能,但还包含一些其他功能,这些功能使TestNG更加强大。
2)TestNG的优点是什么?
以下是TestNG的优点:
- 它以适当的格式生成报告,其中包括以下信息:
- 执行的测试用例数。
- 通过的测试用例数。
- 测试用例数量失败。
- 跳过的测试用例数
- 通过将多个测试用例转换成一个testng.xml文件,可以轻松地将它们分组,在其中您可以设置每个测试用例的优先级,从而确定应该首先执行哪个测试用例。
- 借助TestNG,您可以在称为跨浏览器测试的多个浏览器上执行多个测试用例。
- TestNG框架可以轻松地与Maven等其他工具集成。Jenkins)等
- TestNG框架中使用的注释很容易理解,例如@ BeforeMethod,@ AfterMethod,@ BeforeTest,@ AfterTest。
- 当TestNG以可读格式生成报告时,WebDriver不会生成报告。
- TestNG简化了测试用例的编码方式。我们不必编写静态main方法。操作顺序仅由注释维护。
- TestNG允许您单独执行测试用例。例如,如果您有六个测试用例,则为每个测试用例编写一个方法。当我们运行程序时,成功执行了五个方法,而第六个方法失败了。要消除该错误,我们只需要运行第六种方法,而这只能通过TestNG来实现。因为TestNG在测试输出文件夹中生成testng-failed.xml文件,所以我们将仅运行该xml文件来执行失败的测试用例。
3)如何在TestNG中运行测试脚本?
您可以通过右键单击TestNG类,单击“运行方式”,然后选择“ TestNG测试”,在TestNG中运行测试脚本。
4)在TestNG中使用什么注释?
以下是TestNG中使用的注释:
- 前提条件注释前提条件注释在执行测试方法之前执行。前提条件注释是@ BeforeSuite,@ BeforeClass,@ BeforeTest,@ BeforeMethod。
- 测试注释测试注释是在定义测试方法之前指定的。它被指定为@Test。
- 后置条件注释后置条件注释在所有测试方法执行后执行。后置条件注释可以是@ AfterSuite,@ AfterClass,@ AfterTest,@ AfterMethod。
5)TestNG中所有注释的执行顺序是什么?
下面给出了TestNG中所有注释的执行顺序:
- @BeforeSuite
- @BeforeTest
- @课前
- @BeforeMethod
- @测试
- @AfterSuite
- @AfterTest
- @下课以后
- @AfterMethod
6)如何在TestNG中设置优先级?
如果我们不区分测试方法的优先级,则将按字母顺序选择测试方法并执行。如果我们希望按照所需的顺序执行测试方法,则需要提供优先级以及@Test批注。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Test_methods
{
@Test(priority=2)
public void test1()
{
System.out.println("Test1");
}
@Test(priority=1)
public void test2()
{
System.out.print("Test2");
}
}
7)在TestNG中定义分组?
该组是TestNG中的一个属性,它允许您执行多个测试用例。例如,如果我们有100个it_department测试用例和hr_department 10个测试用例,并且如果您要在一个套件中一起运行it_department的所有测试用例,则只能通过分组来实现。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Test_methods
{
@Test(groups="it_department")
public void java()
{
System.out.println("I am a java developer");
}
@Test(groups="it_department")
public void dot_net()
{
System.out.println("I am a .Net developer");
}
@Test(groups="it_department")
public void tester()
{
System.out.println("I am a software tester");
}
@Test (groups="hr")
public void hr()
{
System.out.print("I am hr");
}
}
testng.xml
?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
8)什么是TestNG中的依赖项?
当我们要按特定顺序运行测试用例时,我们在TestNG中使用依赖的概念。
TestNG中使用两种类型的依赖项属性:
- dependsOnMethodsdependsOnMethods属性告诉TestNG该测试将依赖于哪些方法,以便那些方法将在此测试方法之前执行。
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Login
{
@Test
public void login()
{
System.out.println("Login page");
}
@Test(dependsOnMethods="login")
public void home()
{
System.out.println("Home page");
}
}
- dependsOnGroups它类似于dependsOnMethods属性。它允许测试方法依赖于测试方法组。它在相关测试方法之前执行测试方法组。
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Test_cases
{
@Test(groups="test")
public void testcase1()
{
System.out.println("testcase1");
}
@Test(groups="test")
public void testcase2()
{
System.out.println("testcase2");
}
@Test(dependsOnGroups="test")
public void testcase3()
{
System.out.println("testcase3");
}
}
9)什么是TestNG中的timeout?
在运行测试用例时,可能会出现某些测试用例比预期花费更多时间的情况。在这种情况下,我们可以使用timeOut将测试用例标记为失败的测试用例。
TestNG中的TimeOut允许您配置等待测试完全执行的时间段。可以分为两个级别进行配置:
- 在西服级别:所有测试方法均可用。
- 在每个方法级别:它可用于特定的测试方法。
可以如下所示指定timeOut属性:
@Test( timeOut = 700)
上面的@Test批注表明将给测试方法700毫秒以完成其执行,否则它将被标记为失败的测试用例。
10)什么是TestNG中的invocationCount?
TestNG中的invocationCount是我们想要执行相同测试的次数。
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Test_cases
{
@Test(invocationCount=5)
public void testcase1()
{
System.out.println("testcase1");
}
}
输出量
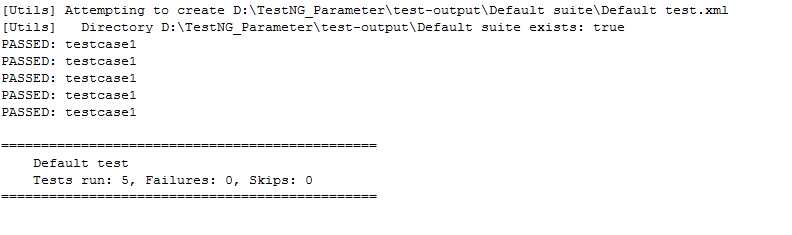
11)testng.xml文件的重要性是什么?
由于以下原因,testng.xml文件很重要:
- 它定义了所有测试用例的执行顺序。
- 它允许您对测试用例进行分组,并可以根据要求执行。
- 它执行所选的测试用例。
- 在TestNG中,可以在套件级别实现侦听器。
- 它允许您将TestNG框架与Jenkins的工具集成在一起。
12)如何通过testng.xml文件传递测试用例中的参数?
我们还可以在运行时将值传递给测试方法,我们可以通过通过testng.xml文件发送参数值来实现。我们可以使用@Parameter批注:
@Parameter("param-name");
让我们通过一个例子来理解:
package com.javatpoint;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import org.testng.annotations.Parameters;
public class Web {
@Parameters({"text"})
@Test
public void search()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "D:\\chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver=new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("http://www.google.com/");
driver.findElement(By.name("q")).sendKeys("javatpoint tutorial");
}
}
testng.xml文件
运行testng.xml文件时,我们得到如下所示的输出:
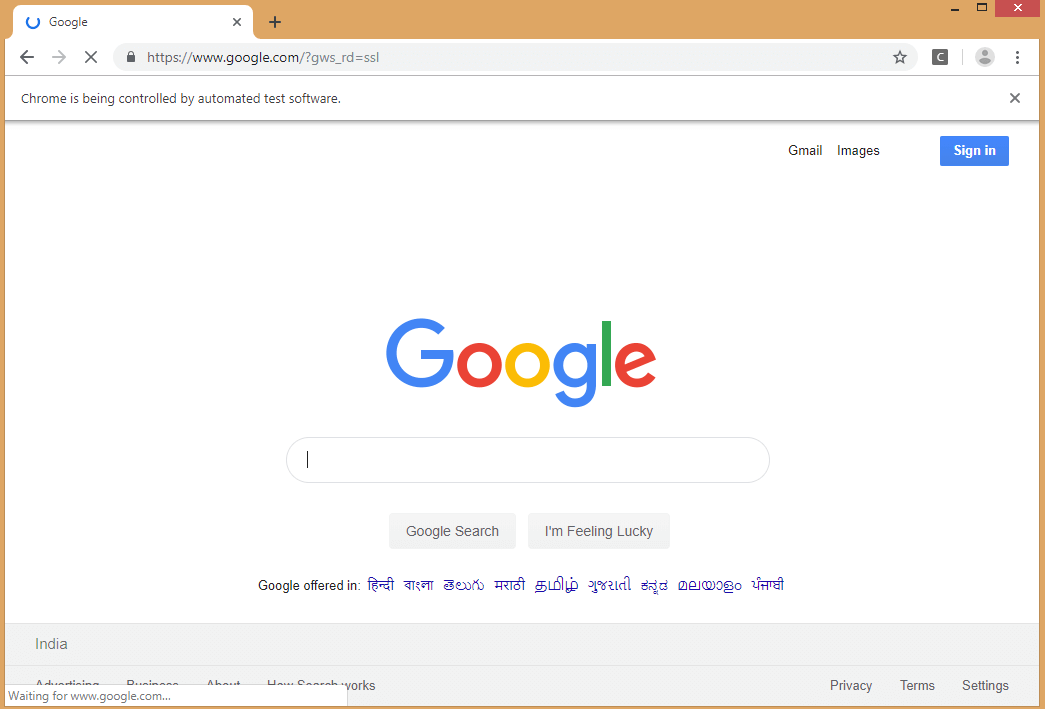
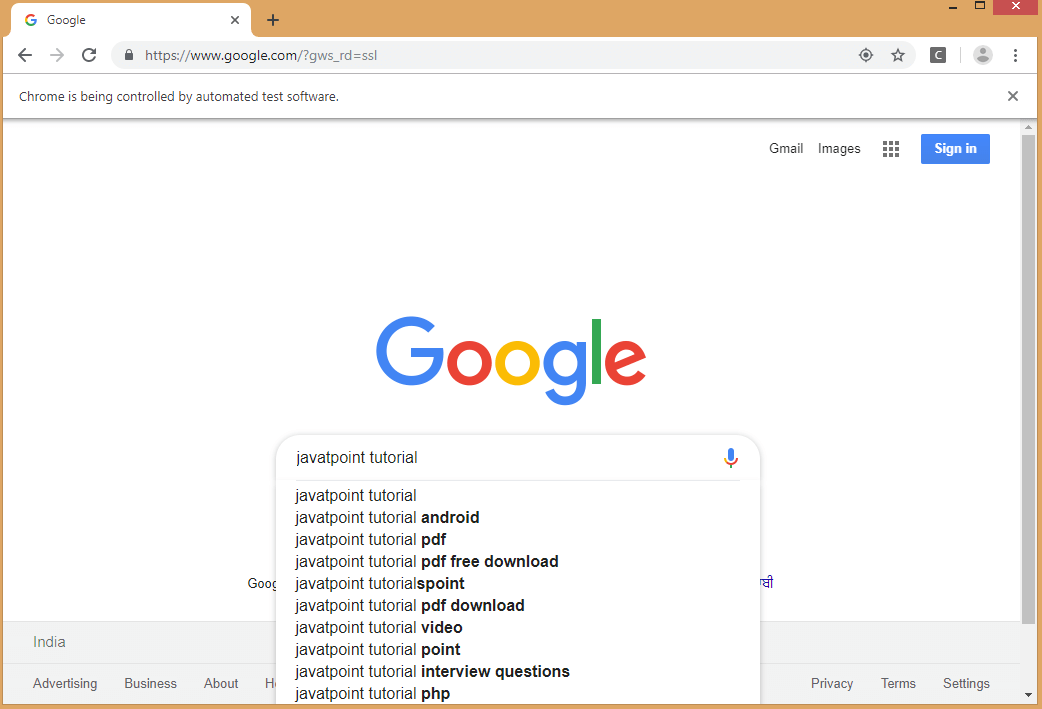
13)如何禁用测试用例?
我们可以使用enabled属性禁用测试用例的运行。我们可以将false值分配给enabled属性,这样就可以禁用测试用例。
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Test_cases
{
@Test(enabled=false)
public void testcase1()
{
System.out.println("testcase1");
}
@Test
public void testcase2()
{
System.out.println("testcase2");
}
}
14)软断言和硬断言有什么区别?
软断言:在软断言的情况下,如果TestNG在@Test期间出错,则断言失败时将抛出异常,并在assert语句之后继续下一个语句。
硬断言:在硬断言的情况下,如果TestNG在@Test期间出错,则断言失败时将立即引发AssertException,并在assert语句后停止执行。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import org.testng.asserts.SoftAssert;
public class Assertion {
SoftAssert soft_assert=new SoftAssert();
@Test
public void Soft_Assert()
{
soft_assert.assertTrue(false);
System.out.println("soft assertion");
}
@Test
public void Hard_Assert()
{
Assert.assertTrue(false);
System.out.println("hard assertion");
}
}
输出量
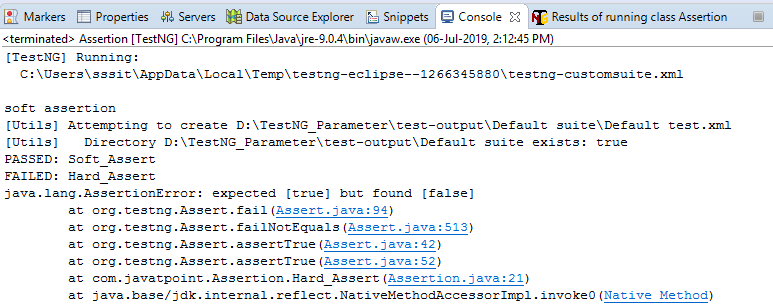
15)在TestNG中@Listener注释有什么用?
TestNG提供了不同种类的侦听器,每当事件触发时,它们便可以执行不同的操作。 TestNG中使用最广泛的侦听器是ITestListener接口。 ITestListener接口包含诸如onTestSuccess,onTestfailure,onTestSkipped等方法。
以下是可以实现的方案:
- 如果测试用例失败,那么侦听器应执行什么操作。
- 如果测试用例通过,则侦听器应执行什么操作。
- 如果跳过测试用例,那么侦听器应执行什么操作。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Listeners;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
@Listeners(com.javatpoint.Listener.class)
public class Test_cases
{
@Test
public void test_to_success()
{
Assert.assertTrue(true);
}
@Test
public void test_to_fail()
{
Assert.assertTrue(false);
}
}
侦听器
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.ITestContext;
import org.testng.ITestListener;
import org.testng.ITestResult;
public class Listener implements ITestListener
{
@Override
public void onTestStart(ITestResult result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void onTestSuccess(ITestResult result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Success of test cases and its details are : "+result.getName());
}
@Override
public void onTestFailure(ITestResult result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Failure of test cases and its details are : "+result.getName());
}
@Override
public void onTestSkipped(ITestResult result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Skip of test cases and its details are : "+result.getName());
}
@Override
public void onTestFailedButWithinSuccessPercentage(ITestResult result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Failure of test cases and its details are : "+result.getName());
}
@Override
public void onStart(ITestContext context) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void onFinish(ITestContext context) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}}
输出量
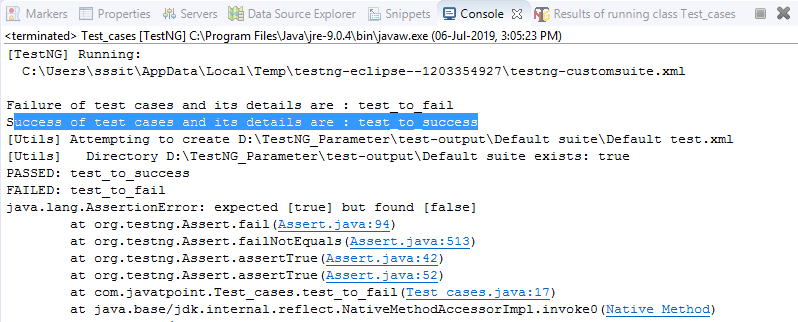
16)@Factory注释有什么用?
当我们要通过一个测试类运行多个测试用例时,@ Factory批注很有用。它主要用于测试用例的动态执行。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
testcase1.java
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Testcase1
{
@Test
public void test1()
{
System.out.println("testcase 1");
}
}
testcase2.java
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Testcase2
{
@Test
public void test1()
{
System.out.println("testcase 2");
}
}
工厂.java
import org.testng.annotations.Factory;
public class Factory1
{
@Factory
public Object[] getTestClasses()
{
Object tests[]=new Object[2];
tests[0]=new Testcase1();
tests[1]=new Testcase2();
return tests;
}
}
17)@Factory和@DataProvider批注有什么区别?
@DataProvider: TestNG使用它的注解,基于DataProvider提供的数据多次执行测试方法。
@Factory: TestNG使用它的注释,以使用相应类的不同实例来执行同一测试类中存在的测试方法。