📌 相关文章
- PHP-决策制定
- PHP-决策制定(1)
- Swift-决策制定
- Swift-决策制定(1)
- Apex-决策制定(1)
- Apex-决策制定
- Groovy-决策制定(1)
- Groovy-决策制定
- TypeScript类
- 好的 - TypeScript (1)
- TypeScript集(1)
- 1, - TypeScript (1)
- TypeScript集
- TypeScript-类
- ++i 与 i++ - TypeScript (1)
- TypeScript类(1)
- TypeScript-类(1)
- TypeScript 中的类
- n*n 的前 k 位 - TypeScript (1)
- 示例 typescript 代码 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 数组 - TypeScript (1)
- 代码 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 可选属性 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 数组 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 使对象可选 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 可选属性 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 变量 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 转换为 javascript - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 使对象可选 - TypeScript 代码示例
📜 TypeScript决策制定
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-11 12:31:55 🧑 作者: Mango
做决定
编程语言中的决策类似于现实生活中的决策。在一种编程语言中,程序员使用决策程序来指定一个或多个要由程序评估的条件。决策总是将布尔结果返回true或false。
TypeScript中有多种类型的决策制定:
- 如果声明
- if-else语句
- if-else-if梯子
- 嵌套if语句
如果声明
这是决策的一种简单形式。它决定是否执行语句,即检查条件,如果满足给定条件,则返回true。
句法
if(condition) {
// code to be executed
}

例
let a = 10, b = 20;
if (a < b)
{
console.log('a is less than b.');
}
输出:
a is less than b.
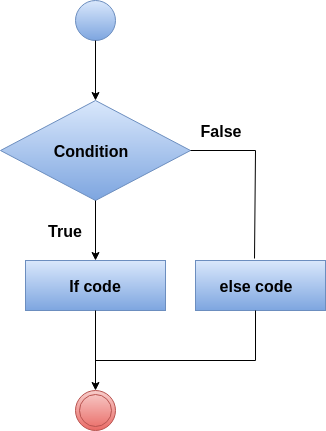
if-else语句
if语句仅在条件为true时返回结果。但是,如果我们想在条件为false时返回某些内容,则需要使用if-else语句。 if-else语句测试条件。如果条件为true,则执行if块,如果条件为false,则执行else块。
句法
if(condition) {
// code to be executed
} else {
// code to be executed
}
例
let n = 10
if (n > 0) {
console.log("The input value is positive Number: " +n);
} else {
console.log("The input value is negative Number: " +n);
}
输出:
The input value is positive Number: 10
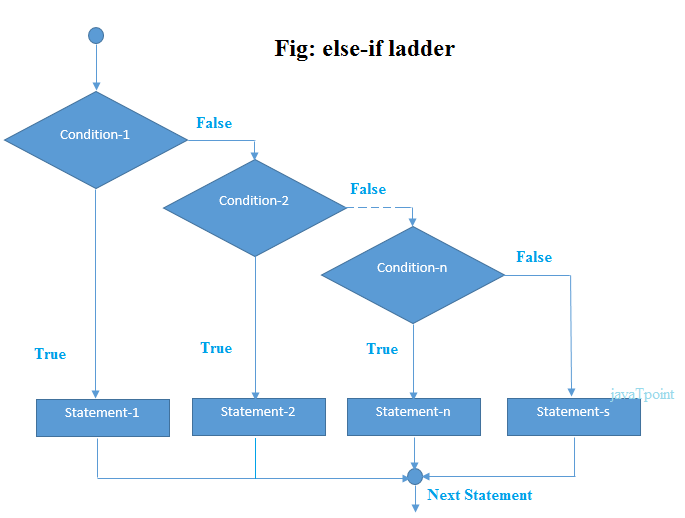
if-else-if梯子
在这里,用户可以在多个选项中做出决定。它以自上而下的方式开始执行。当条件为真时,它将执行关联的语句,其余条件将被绕过。如果找不到任何满足条件的条件,则返回最终的else语句。
句法
if(condition1){
//code to be executed if condition1 is true
}else if(condition2){
//code to be executed if condition2 is true
}
else if(condition3){
//code to be executed if condition3 is true
}
else{
//code to be executed if all the conditions are false
}
例
let marks = 95;
if(marks<50){
console.log("fail");
}
else if(marks>=50 && marks<60){
console.log("D grade");
}
else if(marks>=60 && marks<70){
console.log("C grade");
}
else if(marks>=70 && marks<80){
console.log("B grade");
}
else if(marks>=80 && marks<90){
console.log("A grade");
}else if(marks>=90 && marks<100){
console.log("A+ grade");
}else{
console.log("Invalid!");
}
输出:
A+ grade
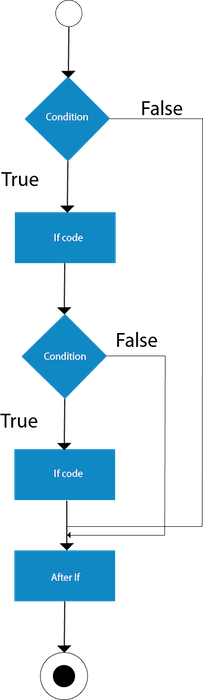
嵌套if语句
在此,if语句针对另一个if语句。嵌套的if语句意味着if语句位于另一个if or else语句的主体内。
句法
if(condition1) {
//Nested if else inside the body of "if"
if(condition2) {
//Code inside the body of nested "if"
}
else {
//Code inside the body of nested "else"
}
}
else {
//Code inside the body of "else."
}
例
let n1 = 10, n2 = 22, n3 = 25
if (n1 >= n2) {
if (n1 >= n3) {
console.log("The largest number is: " +n1)
}
else {
console.log("The largest number is: " +n3)
}
}
else {
if (n2 >= n3) {
console.log("The largest number is: " +n2)
}
else {
console.log("The largest number is: " +n3)
}
}
输出:
The largest number is: 25