Java.io.StringBufferInputStream Java中的类
Java.io.StringBufferInputStream类有助于创建一个输入流,可以从字符串中读取字节。如果我们使用这个类,我们只能读取字符串中每个字符的低 8 位。
但是如果我们使用 ByteArrayInputStream,则没有限制只能读取字符串中每个字符的低 8 位。
此类已被 Oracle 弃用,不应再使用。
宣言:
public class StringBufferInputStream
extends InputStream构造函数:
- StringBufferInputStream(String str) :创建一个字符串输入流以从指定的字符串中读取数据。
方法:
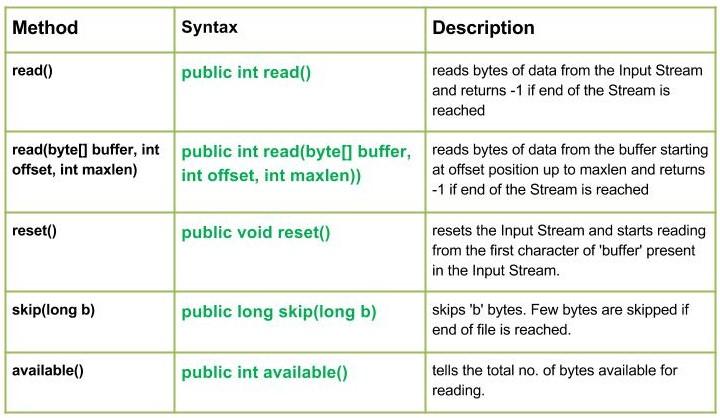
- read() : Java.io.StringBufferInputStream.read()从输入流中读取数据字节,如果到达流的末尾则返回-1。
句法 :public int read() Parameters : ----------- Return : Returns read character as an integer ranging from range 0 to 65535. -1 : when end of file is reached. - read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) : Java.io.StringBufferInputStream.read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen))从缓冲区中从偏移位置开始读取数据字节,直到 maxlen 并返回如果到达 Stream 的末尾,则为 -1。
句法 :public int read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen)) Parameters : buffer : destination buffer to be read into offset : starting position from where to store characters maxlen : maximum no. of characters to be read Return : Returns all the characters read -1 : when end of file is reached. - reset() : Java.io.StringBufferInputStream.reset()重置输入流并从输入流中存在的“缓冲区”的第一个字符开始读取。
句法 :public void reset() Parameters : ----------- Return : void - skip(long b) : Java.io.StringBufferInputStream.skip(long b)跳过“b”个字节。如果到达文件末尾,则跳过几个字节。
句法 :public long skip(long b) Parameters : b : no. of bytes to be skipped Return : no. of bytes skipped - available() : Java.io.StringBufferInputStream.available()告诉总数。可供读取的字节数。
句法 :public int available() Parameters : ---------------- Return : total no. of bytes that can be read
// Java program illustrating the working of StringBufferInputStream class methods
// read(), skip(), available(), reset()
// read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen)
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
String str1 = "Hello Geeks";
String str2 = "GeeksForGeeks";
StringBufferInputStream Geek_buffer1 = new StringBufferInputStream(str1);
StringBufferInputStream Geek_buffer2 = new StringBufferInputStream(str2);
// USe of available() : to count total bytes to be read
System.out.println("Use of available() 1 : "+ Geek_buffer1.available());
int a = 0;
System.out.print("Use of read() method : ");
// Use of read() method : reading each byte one by one
while((a = Geek_buffer1.read()) != -1)
{
// Converting byte to char
char c1 = (char)a;
System.out.println(c1);
// Use of skip() method
long char_no = Geek_buffer1.skip(1);
System.out.println("Characters Skipped : "+ (c1+1));
}
System.out.println("");
// USe of available() : to count total bytes to be read
System.out.println("Use of available() 2 : "+ Geek_buffer2.available());
byte[] buffer = new byte[15];
// Use of read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen):
// reading a part of array
Geek_buffer2.read(buffer, 1, 2);
int b = 0;
System.out.print("read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen): ");
while((b = Geek_buffer2.read()) != -1)
{
char c2 = (char)b;
System.out.print(c2);
}
System.out.println("");
// Use of reset() : to reset str1 for reading again
Geek_buffer1.reset();
int i = 0;
System.out.print("\nUse of read() method again after reset() : ");
// Use of read() method : reading each character one by one
while((i = Geek_buffer1.read()) != -1)
{
char c3 = (char)i;
System.out.print(c3);
}
}
}
输出 :
Use of available() 1 : 11
Use of read() method : H
Characters Skipped : 73
l
Characters Skipped : 109
o
Characters Skipped : 112
G
Characters Skipped : 72
e
Characters Skipped : 102
s
Characters Skipped : 116
Use of available() 2 : 13
Use of read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen) method : eksForGeeks
Use of read() method again after reset() : Hello Geeks