双向链表顺时针旋转 N 个位置
给定一个双向链表和一个整数N ,任务是将链表顺时针旋转N 个节点。
例子:
Input: N = 2
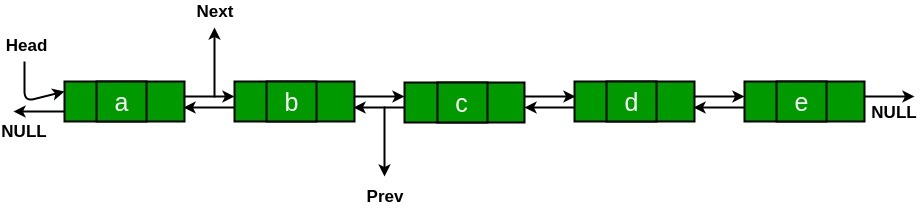
Output:
方法:要旋转双向链表,首先检查给定的 N 是否大于链表的长度。如果 N 大于列表的大小,则通过对列表的长度取模,在链表大小的范围内推导出它。之后从列表的长度中减去 N 的值。现在问题简化为双向链表逆时针旋转 N 个位置。
- 将最后一个节点的 next 更改为指向 Head 节点。
- 将 Head 节点的 prev 更改为指向最后一个节点。
- 将 Head_ref 的值更改为第 N 个节点的下一个。
- 将第 N 个节点的 next 值更改为 NULL。
- 最后,使 Head 节点的 prev 指向 NULL。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to rotate a Doubly linked
// list clock wise by N times
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
char data;
struct Node* prev;
struct Node* next;
};
// Utility function to find the size of
// Doubly Linked List
int size(struct Node* head_ref)
{
struct Node* curr = head_ref;
int sz = 0;
while (curr != NULL) {
curr = curr->next;
sz++;
}
return sz;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node->next != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " "
<< "<=>"
<< " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << node->data;
}
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of the Doubly Linked List
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->prev = NULL;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
// Function to rotate a doubly linked
// list clockwise and update the head
void rotate(struct Node** head_ref, int N, int sz)
{
/* If N is greater than the size of Doubly
Linked List, we have to deduce it in the range
of Doubly linked list size by taking modulo with the
length of the list.*/
N = N % sz;
/* We will update N by subtracting it's value length of
the list. After this the question will reduce to
counter clockwise rotation of linked list to N places*/
N = sz - N;
if (N == 0)
return;
struct Node* current = *head_ref;
// current will either point to Nth
// or NULL after this loop. Current
// will point to node 'b' in the
// above example
int count = 1;
while (count < N && current != NULL) {
current = current->next;
count++;
}
// If current is NULL, N is greater
// than or equal to count of nodes
// in linked list
// Don't change the list in this case
if (current == NULL)
return;
// current points to Nth node. Store
// it in a variable. NthNode points to
// node 'b' in the above example
struct Node* NthNode = current;
// current will point to last node
// after this loop current will point
// to node 'e' in the above example
while (current->next != NULL)
current = current->next;
// Change next of last node to previous
// head. Next of 'e' is now changed to
// node 'a'
current->next = *head_ref;
// Change prev of Head node to current
// Prev of 'a' is now changed to node 'e'
(*head_ref)->prev = current;
// Change head to (N+1)th node
// head is now changed to node 'c'
*head_ref = NthNode->next;
// Change prev of New Head node to NULL
// Because Prev of Head Node in Doubly
// linked list is NULL
(*head_ref)->prev = NULL;
// Change next of Nth node to NULL
// next of 'b' is now NULL
NthNode->next = NULL;
}
// Driver code
int main(void)
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
/* Create the doubly linked
list a<->b<->c<->d<->e */
push(&head, 'e');
push(&head, 'd');
push(&head, 'c');
push(&head, 'b');
push(&head, 'a');
int N = 2;
// Length of the list
int sz = size(head);
cout << "Given Doubly linked list \n";
printList(head);
rotate(&head, N, sz);
cout << "\nRotated Linked list clockwise \n";
printList(head);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to rotate a Doubly linked
// list clock wise by N times
class GFG
{
/* Link list node */
static class Node
{
char data;
Node prev;
Node next;
};
// Utility function to find the size of
// Doubly Linked List
static int size(Node head_ref)
{
Node curr = head_ref;
int sz = 0;
while (curr != null)
{
curr = curr.next;
sz++;
}
return sz;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
static void printList(Node node)
{
while (node.next != null)
{
System.out.print(
node.data + " " + "<=>" + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.print(node.data);
}
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of the Doubly Linked List
static Node push(Node head_ref,
char new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.prev = null;
new_node.next = head_ref;
if (head_ref != null)
head_ref.prev = new_node;
head_ref = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// Function to rotate a doubly linked
// list clockwise and update the head
static Node rotate(Node head_ref,
int N, int sz)
{
/* If N is greater than the size of
Doubly Linked List, we have to deduce it
in the range of Doubly linked list size
by taking modulo with the length of the list.*/
N = N % sz;
/* We will update N by subtracting
it's value length of the list.
After this the question will
reduce to counter clockwise rotation
of linked list to N places*/
N = sz - N;
if (N == 0)
return null;
Node current = head_ref;
// current will either point to Nth
// or null after this loop. Current
// will point to node 'b' in the
// above example
int count = 1;
while (count < N && current != null)
{
current = current.next;
count++;
}
// If current is null, N is greater
// than or equal to count of nodes
// in linked list
// Don't change the list in this case
if (current == null)
return null;
// current points to Nth node. Store
// it in a variable. NthNode points to
// node 'b' in the above example
Node NthNode = current;
// current will point to last node
// after this loop current will point
// to node 'e' in the above example
while (current.next != null)
current = current.next;
// Change next of last node to previous
// head. Next of 'e' is now changed to
// node 'a'
current.next = head_ref;
// Change prev of Head node to current
// Prev of 'a' is now changed to node 'e'
head_ref.prev = current;
// Change head to (N+1)th node
// head is now changed to node 'c'
head_ref = NthNode.next;
// Change prev of New Head node to null
// Because Prev of Head Node in Doubly
// linked list is null
head_ref.prev = null;
// Change next of Nth node to null
// next of 'b' is now null
NthNode.next = null;
return head_ref;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String []args)
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node head = null;
/* Create the doubly linked
list a<->b<->c<->d<->e */
head = push(head, 'e');
head = push(head, 'd');
head = push(head, 'c');
head = push(head, 'b');
head = push(head, 'a');
int N = 2;
// Length of the list
int sz = size(head);
System.out.println("Given Doubly linked list ");
printList(head);
head = rotate(head, N, sz);
System.out.println("\nRotated Linked list clockwise ");
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Node of a doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, next = None,
prev = None, data = None):
self.next = next # reference to next node in DLL
self.prev = prev # reference to previous node in DLL
self.data = data
# Function to insert a node at the
# beginning of the Doubly Linked List
def push(head, new_data):
new_node = Node(data = new_data)
new_node.next = head
new_node.prev = None
if head is not None:
head.prev = new_node
head = new_node
return head
# Utility function to find the size of
# Doubly Linked List
def size(head):
node = head
sz = 0
while(node is not None):
sz+= 1
node = node.next
return sz
# Function to print linked list
def printList(head):
node = head
print("Given linked list")
while(node is not None):
print(node.data, end = " "),
last = node
node = node.next
# Function to rotate a doubly linked
# list clockwise and update the head
def rotate(start, N):
if N == 0 :
return
# Let us understand the below code
# for example N = 2 and
# list = a <-> b <-> c <-> d <-> e.
current = start
# current will either point to Nth
# or None after this loop. Current
# will point to node 'b' in the
# above example
count = 1
while count < N and current != None :
current = current.next
count += 1
# If current is None, N is greater
# than or equal to count of nodes
# in linked list. Don't change the
# list in this case
if current == None :
return
# current points to Nth node. Store
# it in a variable. NthNode points to
# node 'b' in the above example
NthNode = current
# current will point to last node
# after this loop current will point
# to node 'e' in the above example
while current.next != None :
current = current.next
# Change next of last node to previous
# head. Next of 'e' is now changed to
# node 'a'
current.next = start
# Change prev of Head node to current
# Prev of 'a' is now changed to node 'e'
start.prev = current
# Change head to (N + 1)th node
# head is now changed to node 'c'
start = NthNode.next
# Change prev of New Head node to None
# Because Prev of Head Node in Doubly
# linked list is None
start.prev = None
# change next of Nth node to None
# next of 'b' is now None
NthNode.next = None
return start
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
head = None
head = push(head, 'e')
head = push(head, 'd')
head = push(head, 'c')
head = push(head, 'b')
head = push(head, 'a')
printList(head)
print("\n")
N = 2
# Length of the list
sz = size(head)
# If N is greater than the size of Doubly
# Linked List, we have to deduce it in the range
# of Doubly linked list size by taking modulo with the
# length of the list.
N = N % sz;
# We will update N by subtracting it's value length of
# the list. After this the question will reduce to
# counter-clockwise rotation of linked list to N places
N = sz-N;
head = rotate(head, N)
printList(head)C#
// C# program to rotate a Doubly linked
// list clock wise by N times
using System;
class GFG
{
/* Link list node */
public class Node
{
public char data;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
};
// Utility function to find the size of
// Doubly Linked List
static int size(Node head_ref)
{
Node curr = head_ref;
int sz = 0;
while (curr != null)
{
curr = curr.next;
sz++;
}
return sz;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
static void printList(Node node)
{
while (node.next != null)
{
Console.Write(
node.data + " " + "<=>" + " ");
node = node.next;
}
Console.Write(node.data);
}
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of the Doubly Linked List
static Node push(Node head_ref,
char new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.prev = null;
new_node.next = head_ref;
if (head_ref != null)
head_ref.prev = new_node;
head_ref = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// Function to rotate a doubly linked
// list clockwise and update the head
static Node rotate(Node head_ref,
int N, int sz)
{
/* If N is greater than the size of
Doubly Linked List, we have to deduce it
in the range of Doubly linked list size
by taking modulo with the length of the list.*/
N = N % sz;
/* We will update N by subtracting
it's value length of the list.
After this the question will
reduce to counter clockwise rotation
of linked list to N places*/
N = sz - N;
if (N == 0)
return null;
Node current = head_ref;
// current will either point to Nth
// or null after this loop. Current
// will point to node 'b' in the
// above example
int count = 1;
while (count < N && current != null)
{
current = current.next;
count++;
}
// If current is null, N is greater
// than or equal to count of nodes
// in linked list
// Don't change the list in this case
if (current == null)
return null;
// current points to Nth node. Store
// it in a variable. NthNode points to
// node 'b' in the above example
Node NthNode = current;
// current will point to last node
// after this loop current will point
// to node 'e' in the above example
while (current.next != null)
current = current.next;
// Change next of last node to previous
// head. Next of 'e' is now changed to
// node 'a'
current.next = head_ref;
// Change prev of Head node to current
// Prev of 'a' is now changed to node 'e'
head_ref.prev = current;
// Change head to (N+1)th node
// head is now changed to node 'c'
head_ref = NthNode.next;
// Change prev of New Head node to null
// Because Prev of Head Node in Doubly
// linked list is null
head_ref.prev = null;
// Change next of Nth node to null
// next of 'b' is now null
NthNode.next = null;
return head_ref;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node head = null;
/* Create the doubly linked
list a<->b<->c<->d<->e */
head = push(head, 'e');
head = push(head, 'd');
head = push(head, 'c');
head = push(head, 'b');
head = push(head, 'a');
int N = 2;
// Length of the list
int sz = size(head);
Console.WriteLine("Given Doubly linked list ");
printList(head);
head = rotate(head, N, sz);
Console.WriteLine("\nRotated Linked list clockwise ");
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
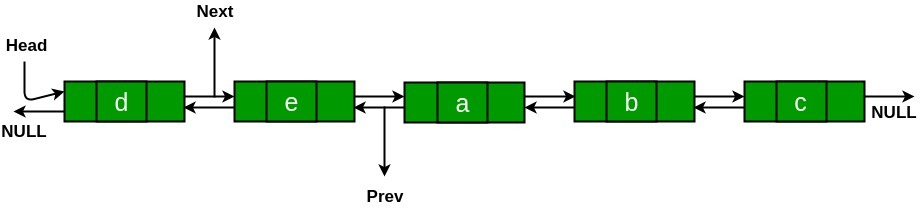
输出:
Given Doubly linked list
a <=> b <=> c <=> d <=> e
Rotated Linked list clockwise
d <=> e <=> a <=> b <=> c时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是链表中的节点数。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。