通过 N 个节点旋转双向链表
给定一个双向链表,将链表逆时针旋转 N 个节点。这里 N 是一个给定的正整数,小于链表中的节点数。

N = 2
轮换名单:
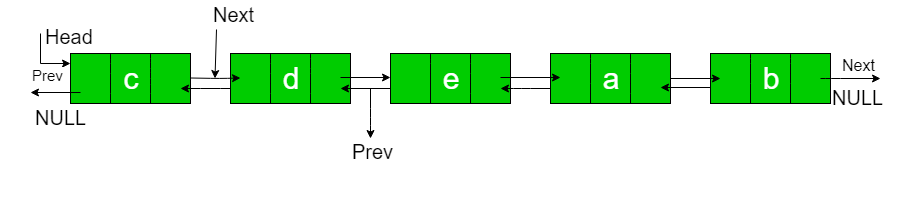
例子:
Input : a b c d e N = 2
Output : c d e a b
Input : a b c d e f g h N = 4
Output : e f g h a b c d 在亚马逊询问
1、要旋转双向链表,首先我们需要遍历链表,找到最后一个节点的地址。
2. 然后把它做成一个循环链表。
3. 然后将头部和临时节点移动 n 个节点。
4. 然后将链表设为非循环。
C++
#include
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
char data;
Node* next;
Node* pre;
Node(int data)
{
this->data=data;
pre=NULL;
next=NULL;
}
};
void insertAtHead(Node* &head, int data)
{
Node* n = new Node(data);
if(head==NULL)
{
head=n;
return;
}
n->next=head;
head->pre=n;
head=n;
return;
}
void insertAtTail(Node* &head, int data)
{
if(head==NULL)
{
insertAtHead(head,data);
return;
}
Node* temp=head;
while(temp->next!=NULL)
{
temp=temp->next;
}
Node* n=new Node(data);
temp->next=n;
n->pre=temp;
return;
}
void display(Node* head)
{
while(head!=NULL)
{
cout << head->data << "-->";
head=head->next;
}
cout << "NULL\n";
}
void rotateByN(Node* &head, int pos)
{
// return without any changes if positin is 0.
if(pos==0) return;
// Finding last node.
Node* temp=head;
while(temp->next!=NULL)
{
temp=temp->next;
}
// making the list circular.
temp->next=head;
head->pre=temp;
// move head and temp by the given position.
int count=1;
while(count<=pos)
{
head=head->next;
temp=temp->next;
count++;
}
// now again make list un-circular.
temp->next=NULL;
head->pre=NULL;
}
int main()
{
Node* head=NULL;
insertAtTail(head,'a');
insertAtTail(head,'b');
insertAtTail(head,'c');
insertAtTail(head,'d');
insertAtTail(head,'e');
int n=2;
cout << "\nBefore Rotation : \n";
display(head);
rotateByN(head,n);
cout << "\nAfter Rotation : \n";
display(head);
cout << "\n\n";
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to rotate a Doubly linked
// list counter clock wise by N times
class GfG {
/* Link list node */
static class Node
{
char data;
Node prev;
Node next;
}
static Node head = null;
// This function rotates a doubly linked
// list counter-clockwise and updates the
// head. The function assumes that N is
// smallerthan size of linked list. It
// doesn't modify the list if N is greater
// than or equal to size
static void rotate( int N)
{
if (N == 0)
return;
// Let us understand the below code
// for example N = 2 and
// list = a <-> b <-> c <-> d <-> e.
Node current = head;
// current will either point to Nth
// or NULL after this loop. Current
// will point to node 'b' in the
// above example
int count = 1;
while (count < N && current != null)
{
current = current.next;
count++;
}
// If current is NULL, N is greater
// than or equal to count of nodes
// in linked list. Don't change the
// list in this case
if (current == null)
return;
// current points to Nth node. Store
// it in a variable. NthNode points to
// node 'b' in the above example
Node NthNode = current;
// current will point to last node
// after this loop current will point
// to node 'e' in the above example
while (current.next != null)
current = current.next;
// Change next of last node to previous
// head. Next of 'e' is now changed to
// node 'a'
current.next = head;
// Change prev of Head node to current
// Prev of 'a' is now changed to node 'e'
(head).prev = current;
// Change head to (N+1)th node
// head is now changed to node 'c'
head = NthNode.next;
// Change prev of New Head node to NULL
// Because Prev of Head Node in Doubly
// linked list is NULL
(head).prev = null;
// change next of Nth node to NULL
// next of 'b' is now NULL
NthNode.next = null;
}
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of the Doubly Linked List
static void push(char new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.prev = null;
new_node.next = (head);
if ((head) != null)
(head).prev = new_node;
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
static void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null && node.next != null)
{
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
if(node != null)
System.out.print(node.data);
}
// Driver's Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list */
// Node head = null;
/* Let us create the doubly
linked list a<->b<->c<->d<->e */
push( 'e');
push( 'd');
push('c');
push('b');
push( 'a');
int N = 2;
System.out.println("Given linked list ");
printList(head);
rotate( N);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Rotated Linked list ");
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Prerna SainiPython3
# Node of a doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, next = None,
prev = None, data = None):
self.next = next # reference to next node in DLL
self.prev = prev # reference to previous node in DLL
self.data = data
def push(head, new_data):
new_node = Node(data = new_data)
new_node.next = head
new_node.prev = None
if head is not None:
head.prev = new_node
head = new_node
return head
def printList(head):
node = head
print("Given linked list")
while(node is not None):
print(node.data, end = " "),
last = node
node = node.next
def rotate(start, N):
if N == 0 :
return
# Let us understand the below code
# for example N = 2 and
# list = a <-> b <-> c <-> d <-> e.
current = start
# current will either point to Nth
# or None after this loop. Current
# will point to node 'b' in the
# above example
count = 1
while count < N and current != None :
current = current.next
count += 1
# If current is None, N is greater
# than or equal to count of nodes
# in linked list. Don't change the
# list in this case
if current == None :
return
# current points to Nth node. Store
# it in a variable. NthNode points to
# node 'b' in the above example
NthNode = current
# current will point to last node
# after this loop current will point
# to node 'e' in the above example
while current.next != None :
current = current.next
# Change next of last node to previous
# head. Next of 'e' is now changed to
# node 'a'
current.next = start
# Change prev of Head node to current
# Prev of 'a' is now changed to node 'e'
start.prev = current
# Change head to (N+1)th node
# head is now changed to node 'c'
start = NthNode.next
# Change prev of New Head node to None
# Because Prev of Head Node in Doubly
# linked list is None
start.prev = None
# change next of Nth node to None
# next of 'b' is now None
NthNode.next = None
return start
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
head = None
head = push(head, 'e')
head = push(head, 'd')
head = push(head, 'c')
head = push(head, 'b')
head = push(head, 'a')
printList(head)
print("\n")
N = 2
head = rotate(head, N)
printList(head)
# This code is contributed by vinayak sharmaC#
// C# program to rotate a Doubly linked
// list counter clock wise by N times
using System;
class GfG
{
/* Link list node */
public class Node
{
public char data;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
}
static Node head = null;
// This function rotates a doubly linked
// list counter-clockwise and updates the
// head. The function assumes that N is
// smallerthan size of linked list. It
// doesn't modify the list if N is greater
// than or equal to size
static void rotate( int N)
{
if (N == 0)
return;
// Let us understand the below code
// for example N = 2 and
// list = a <-> b <-> c <-> d <-> e.
Node current = head;
// current will either point to Nth
// or NULL after this loop. Current
// will point to node 'b' in the
// above example
int count = 1;
while (count < N && current != null)
{
current = current.next;
count++;
}
// If current is NULL, N is greater
// than or equal to count of nodes
// in linked list. Don't change the
// list in this case
if (current == null)
return;
// current points to Nth node. Store
// it in a variable. NthNode points to
// node 'b' in the above example
Node NthNode = current;
// current will point to last node
// after this loop current will point
// to node 'e' in the above example
while (current.next != null)
current = current.next;
// Change next of last node to previous
// head. Next of 'e' is now changed to
// node 'a'
current.next = head;
// Change prev of Head node to current
// Prev of 'a' is now changed to node 'e'
(head).prev = current;
// Change head to (N+1)th node
// head is now changed to node 'c'
head = NthNode.next;
// Change prev of New Head node to NULL
// Because Prev of Head Node in Doubly
// linked list is NULL
(head).prev = null;
// change next of Nth node to NULL
// next of 'b' is now NULL
NthNode.next = null;
}
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of the Doubly Linked List
static void push(char new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.prev = null;
new_node.next = (head);
if ((head) != null)
(head).prev = new_node;
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
static void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null && node.next != null)
{
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
if(node != null)
Console.Write(node.data);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
/* Start with the empty list */
// Node head = null;
/* Let us create the doubly
linked list a<->b<->c<->d<->e */
push( 'e');
push( 'd');
push( 'c');
push( 'b');
push( 'a');
int N = 2;
Console.WriteLine("Given linked list ");
printList(head);
rotate( N);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Rotated Linked list ");
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduJavascript
Output:
Before Rotation :
a-->b-->c-->d-->e-->NULL
After Rotation :
c-->d-->e-->a-->b-->NULL
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。