对于基于摄像机监控的安全系统来说,识别车牌是一项非常重要的任务。我们可以使用某些计算机视觉技术从图像中提取车牌,然后使用光学字符识别来识别车牌号。在这里,我将指导您完成此任务的整个过程。
要求:
opencv-python 3.4.2
numpy 1.17.2
skimage 0.16.2
tensorflow 1.15.0
imutils 0.5.3
例子:
Input: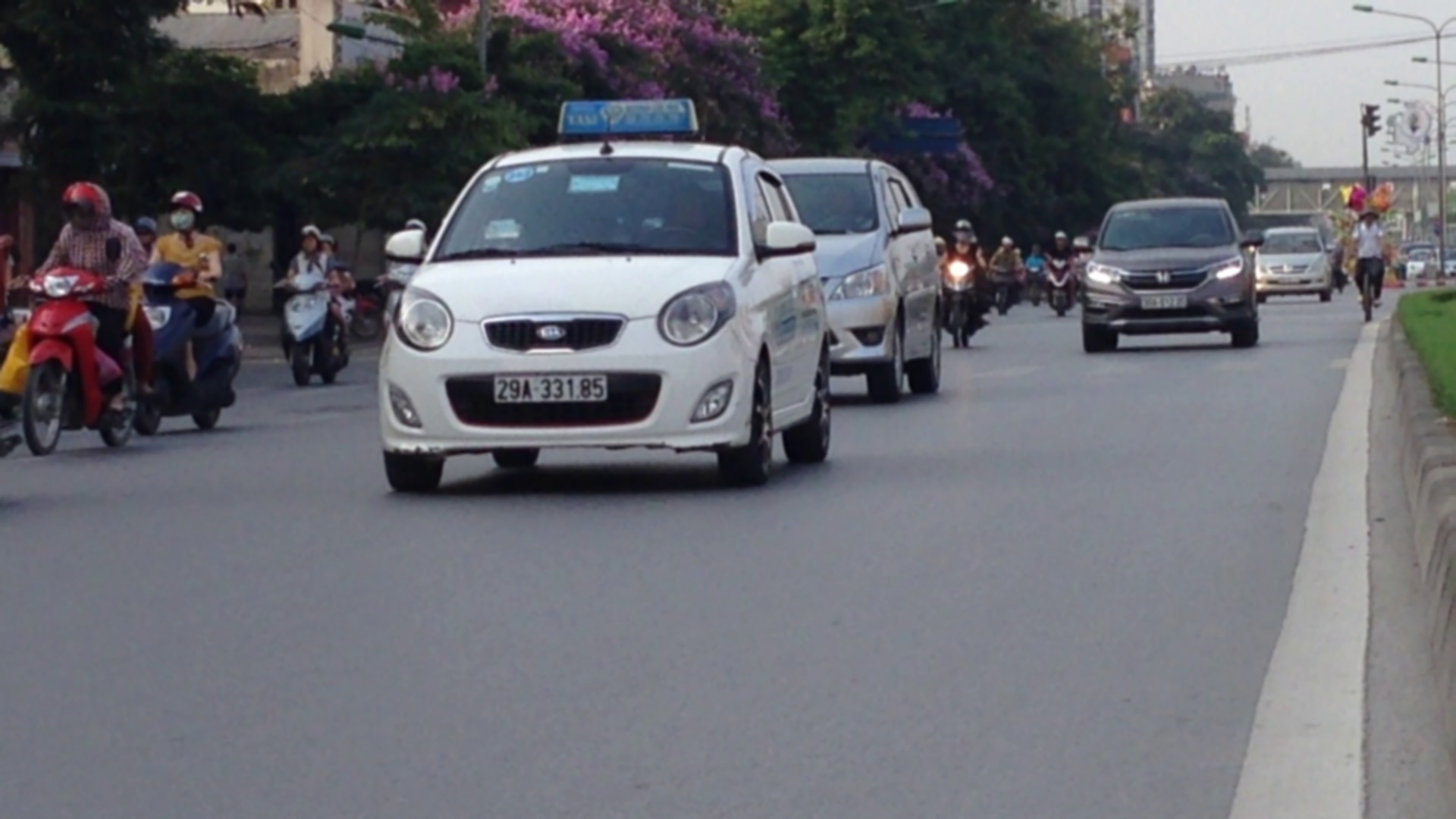
Output:
29A33185
方法:
- 找到图像中的所有轮廓。
- 找到每个轮廓的边界矩形。
- 用平均车牌比较并验证每个边界矩形的边长和面积。
- 在经过验证的轮廓内的图像中应用图像分割,以在其中找到字符。
- 使用OCR识别字符。
方法:
- 为了减少噪声,我们需要使用高斯模糊对输入图像进行模糊处理,然后将其转换为灰度。

- 查找图像中的垂直边缘。

- 要显示印版,我们必须对图像进行二值化处理。为此,在垂直边缘图像上应用Otsu的阈值。在其他阈值方法中,我们必须选择一个阈值以对图像进行二值化,但是Otsu的阈值自动确定该值。
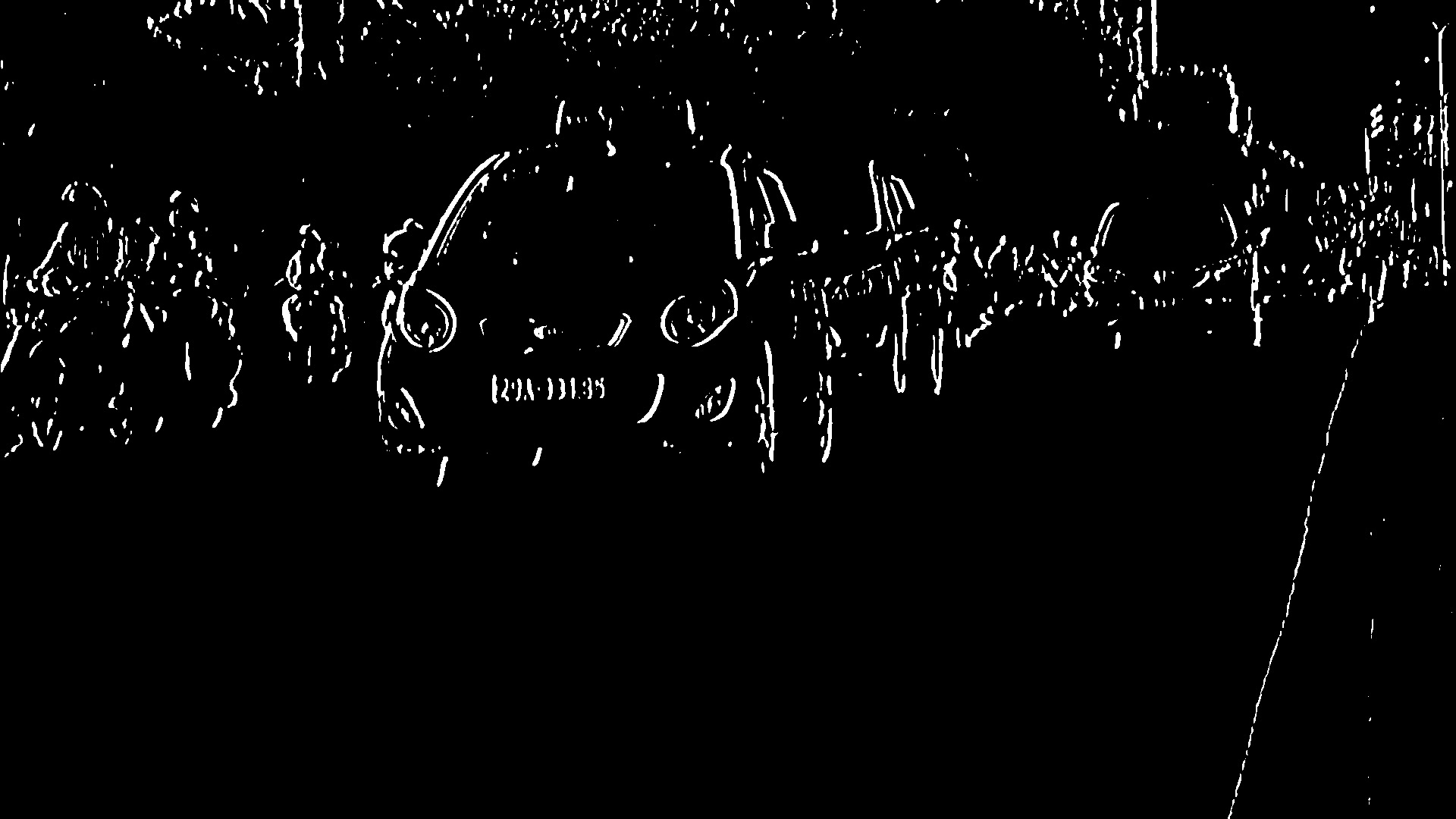
- 在阈值图像上应用闭合形态转换。关闭可用于填充阈值图像中白色区域之间的黑色小区域。它显示了牌照的矩形白色框。

以上四个步骤是通过PlateFinder类的预处理方法执行的
def preprocess(self, input_img): imgBlurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(input_img, (7, 7), 0) # convert to gray gray = cv2.cvtColor(imgBlurred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # sobelX to get the vertical edges sobelx = cv2.Sobel(gray, cv2.CV_8U, 1, 0, ksize = 3) # otsu's thresholding ret2, threshold_img = cv2.threshold(sobelx,0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU) element = self.element_structure morph_n_thresholded_img = threshold_img.copy() cv2.morphologyEx(src = threshold_img, op = cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel = element, dst = morph_n_thresholded_img) return morph_n_thresholded_img - 要检测印版,我们需要在图像中找到轮廓。重要的是在找到轮廓之前对图像进行二值化和变形处理,以便它可以在图像中找到更多相关且更少数量的轮廓。如果您在原始图像上绘制所有提取的轮廓,则将如下所示:

此步骤由PlateFinder类的extract_contours方法执行
def extract_contours(self, after_preprocess): _, contours, _ = cv2.findContours(after_preprocess, mode = cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, method = cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) return contours - 现在找到每个轮廓所包围的最小面积矩形,并验证其边长比和面积。我们将板的最小和最大面积分别定义为4500和30000。
代码:验证最小面积矩形的面积和边长比的方法是validateRatio和
PlateFinder类的preRatioCheck :def validateRatio(self, rect): (x, y), (width, height), rect_angle = rect if (width > height): angle = -rect_angle else: angle = 90 + rect_angle if angle > 15: return False if (height == 0 or width == 0): return False area = width * height if not self.preRatioCheck(area, width, height): return False else: return True def preRatioCheck(self, area, width, height): min = self.min_area max = self.max_area ratioMin = 2.5 ratioMax = 7 ratio = float(width) / float(height) if ratio < 1: ratio = 1 / ratio if (area < min or area > max) or (ratio < ratioMin or ratio > ratioMax): return False return True - 现在在经过验证的区域中找到轮廓,并验证该区域中最大轮廓的边长比和矩形区域。验证后,您将获得车牌的完美轮廓。现在从原始图像中提取轮廓。您将获得印版的图像:

- 代码:此步骤由PlateFinder类的clean_plate和ratioCheck方法执行。
def clean_plate(self, plate): gray = cv2.cvtColor(plate, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) thresh = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(gray, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 2) _, contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) if contours: areas = [cv2.contourArea(c) for c in contours] # index of the largest contour in the # areas array max_index = np.argmax(areas) max_cnt = contours[max_index] max_cntArea = areas[max_index] x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(max_cnt) if not self.ratioCheck(max_cntArea, plate.shape[1], plate.shape[0]): return plate, False, None return plate, True, [x, y, w, h] else: return plate, False, None def ratioCheck(self, area, width, height): min = self.min_area max = self.max_area ratioMin = 3 ratioMax = 6 ratio = float(width) / float(height) if ratio < 1: ratio = 1 / ratio if (area < min or area > max) or (ratio < ratioMin or ratio > ratioMax): return False return True - 为了准确识别车牌上的字符,我们必须应用图像分割。为此,第一步是从印版图像的HSV格式中提取值通道。它看起来像-

- 现在,在印版的价值通道图像上应用自适应阈值以将其二值化并显示字符。印版的图像在不同区域可能具有不同的闪电条件,在这种情况下,自适应阈值处理可能更适合于二值化,因为它会根据其周围区域中像素的亮度对不同区域使用不同的阈值。

- 二值化后,对图像应用按位非运算,以在图像中找到连接的组件,以便我们提取候选字符。

- 构造一个遮罩以显示所有字符组件,然后在遮罩中找到轮廓。提取等高线后,取最大的等高线,找到其边界矩形并验证边长比。
- 在验证了边长比之后,找到轮廓的凸包并将其绘制在候选字符蒙版上。面具看起来像-

- 现在,在字符候选遮罩中找到所有轮廓,并从车牌的阈值图像中提取这些轮廓区域,您将分别获得所有字符。

步骤8至13是由segment_chars函数执行的,您可以在下面的完整源代码中找到该函数。步骤6至13中使用的功能的驱动程序代码编写在PlateFinder类的check_plate方法中。 - 现在,使用OCR逐个识别字符。
完整的源代码及其工作原理:首先,创建PlateFinder类,该类可查找车牌并验证其尺寸比例和面积。
import cv2
import numpy as np
from skimage.filters import threshold_local
import tensorflow as tf
from skimage import measure
import imutils
def sort_cont(character_contours):
"""
To sort contours
"""
i = 0
boundingBoxes = [cv2.boundingRect(c) for c in character_contours]
(character_contours, boundingBoxes) = zip(*sorted(zip(character_contours,
boundingBoxes),
key = lambda b: b[1][i],
reverse = False))
return character_contours
def segment_chars(plate_img, fixed_width):
"""
extract Value channel from the HSV format
of image and apply adaptive thresholding
to reveal the characters on the license plate
"""
V = cv2.split(cv2.cvtColor(plate_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV))[2]
thresh = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(value, 255,
cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY,
11, 2)
thresh = cv2.bitwise_not(thresh)
# resize the license plate region to
# a canoncial size
plate_img = imutils.resize(plate_img, width = fixed_width)
thresh = imutils.resize(thresh, width = fixed_width)
bgr_thresh = cv2.cvtColor(thresh, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
# perform a connected components analysis
# and initialize the mask to store the locations
# of the character candidates
labels = measure.label(thresh, neighbors = 8, background = 0)
charCandidates = np.zeros(thresh.shape, dtype ='uint8')
# loop over the unique components
characters = []
for label in np.unique(labels):
# if this is the background label, ignore it
if label == 0:
continue
# otherwise, construct the label mask to display
# only connected components for the current label,
# then find contours in the label mask
labelMask = np.zeros(thresh.shape, dtype ='uint8')
labelMask[labels == label] = 255
cnts = cv2.findContours(labelMask,
cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[0] if imutils.is_cv2() else cnts[1]
# ensure at least one contour was found in the mask
if len(cnts) > 0:
# grab the largest contour which corresponds
# to the component in the mask, then grab the
# bounding box for the contour
c = max(cnts, key = cv2.contourArea)
(boxX, boxY, boxW, boxH) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
# compute the aspect ratio, solodity, and
# height ration for the component
aspectRatio = boxW / float(boxH)
solidity = cv2.contourArea(c) / float(boxW * boxH)
heightRatio = boxH / float(plate_img.shape[0])
# determine if the aspect ratio, solidity,
# and height of the contour pass the rules
# tests
keepAspectRatio = aspectRatio < 1.0
keepSolidity = solidity > 0.15
keepHeight = heightRatio > 0.5 and heightRatio < 0.95
# check to see if the component passes
# all the tests
if keepAspectRatio and keepSolidity and keepHeight and boxW > 14:
# compute the convex hull of the contour
# and draw it on the character candidates
# mask
hull = cv2.convexHull(c)
cv2.drawContours(charCandidates, [hull], -1, 255, -1)
_, contours, hier = cv2.findContours(charCandidates,
cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
if contours:
contours = sort_cont(contours)
# value to be added to each dimension
# of the character
addPixel = 4
for c in contours:
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
if y > addPixel:
y = y - addPixel
else:
y = 0
if x > addPixel:
x = x - addPixel
else:
x = 0
temp = bgr_thresh[y:y + h + (addPixel * 2),
x:x + w + (addPixel * 2)]
characters.append(temp)
return characters
else:
return None
class PlateFinder:
def __init__(self):
# minimum area of the plate
self.min_area = 4500
# maximum area of the plate
self.max_area = 30000
self.element_structure = cv2.getStructuringElement(
shape = cv2.MORPH_RECT, ksize =(22, 3))
def preprocess(self, input_img):
imgBlurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(input_img, (7, 7), 0)
# convert to gray
gray = cv2.cvtColor(imgBlurred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# sobelX to get the vertical edges
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(gray, cv2.CV_8U, 1, 0, ksize = 3)
# otsu's thresholding
ret2, threshold_img = cv2.threshold(sobelx, 0, 255,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
element = self.element_structure
morph_n_thresholded_img = threshold_img.copy()
cv2.morphologyEx(src = threshold_img,
op = cv2.MORPH_CLOSE,
kernel = element,
dst = morph_n_thresholded_img)
return morph_n_thresholded_img
def extract_contours(self, after_preprocess):
_, contours, _ = cv2.findContours(after_preprocess,
mode = cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,
method = cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
return contours
def clean_plate(self, plate):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(plate, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
thresh = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(gray,
255,
cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY,
11, 2)
_, contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(),
cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
if contours:
areas = [cv2.contourArea(c) for c in contours]
# index of the largest contour in the area
# array
max_index = np.argmax(areas)
max_cnt = contours[max_index]
max_cntArea = areas[max_index]
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(max_cnt)
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(max_cnt)
if not self.ratioCheck(max_cntArea, plate.shape[1],
plate.shape[0]):
return plate, False, None
return plate, True, [x, y, w, h]
else:
return plate, False, None
def check_plate(self, input_img, contour):
min_rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
if self.validateRatio(min_rect):
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour)
after_validation_img = input_img[y:y + h, x:x + w]
after_clean_plate_img, plateFound, coordinates = self.clean_plate(
after_validation_img)
if plateFound:
characters_on_plate = self.find_characters_on_plate(
after_clean_plate_img)
if (characters_on_plate is not None and len(characters_on_plate) == 8):
x1, y1, w1, h1 = coordinates
coordinates = x1 + x, y1 + y
after_check_plate_img = after_clean_plate_img
return after_check_plate_img, characters_on_plate, coordinates
return None, None, None
def find_possible_plates(self, input_img):
"""
Finding all possible contours that can be plates
"""
plates = []
self.char_on_plate = []
self.corresponding_area = []
self.after_preprocess = self.preprocess(input_img)
possible_plate_contours = self.extract_contours(self.after_preprocess)
for cnts in possible_plate_contours:
plate, characters_on_plate, coordinates = self.check_plate(input_img, cnts)
if plate is not None:
plates.append(plate)
self.char_on_plate.append(characters_on_plate)
self.corresponding_area.append(coordinates)
if (len(plates) > 0):
return plates
else:
return None
def find_characters_on_plate(self, plate):
charactersFound = segment_chars(plate, 400)
if charactersFound:
return charactersFound
# PLATE FEATURES
def ratioCheck(self, area, width, height):
min = self.min_area
max = self.max_area
ratioMin = 3
ratioMax = 6
ratio = float(width) / float(height)
if ratio < 1:
ratio = 1 / ratio
if (area < min or area > max) or (ratio < ratioMin or ratio > ratioMax):
return False
return True
def preRatioCheck(self, area, width, height):
min = self.min_area
max = self.max_area
ratioMin = 2.5
ratioMax = 7
ratio = float(width) / float(height)
if ratio < 1:
ratio = 1 / ratio
if (area < min or area > max) or (ratio < ratioMin or ratio > ratioMax):
return False
return True
def validateRatio(self, rect):
(x, y), (width, height), rect_angle = rect
if (width > height):
angle = -rect_angle
else:
angle = 90 + rect_angle
if angle > 15:
return False
if (height == 0 or width == 0):
return False
area = width * height
if not self.preRatioCheck(area, width, height):
return False
else:
return True
这是PlateFinder类的每种方法的说明。
在预处理方法中,已完成以下步骤:
- 模糊影像
- 转换为灰度
- 查找垂直边缘
- 阈值垂直边缘图像。
- 关闭“变形阈值”图像。
方法extract_contours返回预处理图像中的所有外部轮廓。
方法find_possible_plates使用预处理方法对图像进行预处理,然后通过extract_contours方法提取轮廓,然后检查所有提取轮廓的边长比和面积,并使用check_plate和clean_plate方法清洁轮廓内部的图像。用clean_plate方法清洗轮廓图像后,它使用find_characters_on_plate方法在板上找到所有字符。
find_characters_on_plate方法使用segment_chars函数查找字符。它通过计算阈值的值的图像的轮廓的凸包和绘图它上的字符,揭示他们发现字符。
代码:创建另一个类来初始化神经网络,以预测提取的车牌上的字符。
class OCR:
def __init__(self):
self.model_file = "./model / binary_128_0.50_ver3.pb"
self.label_file = "./model / binary_128_0.50_labels_ver2.txt"
self.label = self.load_label(self.label_file)
self.graph = self.load_graph(self.model_file)
self.sess = tf.Session(graph = self.graph)
def load_graph(self, modelFile):
graph = tf.Graph()
graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
with open(modelFile, "rb") as f:
graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
with graph.as_default():
tf.import_graph_def(graph_def)
return graph
def load_label(self, labelFile):
label = []
proto_as_ascii_lines = tf.gfile.GFile(labelFile).readlines()
for l in proto_as_ascii_lines:
label.append(l.rstrip())
return label
def convert_tensor(self, image, imageSizeOuput):
"""
takes an image and tranform it in tensor
"""
image = cv2.resize(image,
dsize =(imageSizeOuput,
imageSizeOuput),
interpolation = cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
np_image_data = np.asarray(image)
np_image_data = cv2.normalize(np_image_data.astype('float'),
None, -0.5, .5,
cv2.NORM_MINMAX)
np_final = np.expand_dims(np_image_data, axis = 0)
return np_final
def label_image(self, tensor):
input_name = "import / input"
output_name = "import / final_result"
input_operation = self.graph.get_operation_by_name(input_name)
output_operation = self.graph.get_operation_by_name(output_name)
results = self.sess.run(output_operation.outputs[0],
{input_operation.outputs[0]: tensor})
results = np.squeeze(results)
labels = self.label
top = results.argsort()[-1:][::-1]
return labels[top[0]]
def label_image_list(self, listImages, imageSizeOuput):
plate = ""
for img in listImages:
if cv2.waitKey(25) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
plate = plate + self.label_image(self.convert_tensor(img, imageSizeOuput))
return plate, len(plate)
它将预训练的OCR模型及其标签文件加载到load_graph和load_label函数中。 label_image_list方法使用convert_tensor方法将图像转换为张量,然后使用label_image_list函数预测张量的标签并返回许可证号。
代码:创建一个主要函数来按顺序执行整个任务。
if __name__ == "__main__":
findPlate = PlateFinder()
model = OCR()
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('test_videos / video.MOV')
while (cap.isOpened()):
ret, img = cap.read()
if ret == True:
cv2.imshow('original video', img)
if cv2.waitKey(25) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
possible_plates = findPlate.find_possible_plates(img)
if possible_plates is not None:
for i, p in enumerate(possible_plates):
chars_on_plate = findPlate.char_on_plate[i]
recognized_plate, _ = model.label_image_list(
chars_on_plate, imageSizeOuput = 128)
print(recognized_plate)
cv2.imshow('plate', p)
if cv2.waitKey(25) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
else:
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
您可以从我的GitHub下载带有OCR模型的源代码和测试视频。
如何改进模型?
- 您可以在车架上设置一个特定的小区域以查找车内的车牌(确保所有车辆都必须通过该区域)。
- 您可以训练自己的机器学习模型来识别字符,因为给定的模型无法识别所有字母。
参考:
自动车牌识别系统(ANPR):Chirag Indravadanbhai Patel进行的调查。
OpenCV文档中的图像预处理技术。