阈值处理是最简单的图像分割方法,也是将灰度图像转换为二进制图像的最常用方法。
在阈值化过程中,我们选择一个阈值,然后将所有低于所选阈值的灰度值归为0(黑色即背景),并将所有等于或大于阈值的灰度值归为1。 (白色即前景)。
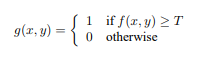
此处,g(x,y)表示(x,y)处的阈值图像像素,f(x,y)表示(x,y)处的灰度图像像素。
算法:
- 将目标图像读取到MATLAB环境中。
- 如果读取的图像是RGB图像,则将其转换为灰度图像。
- 计算阈值T
- 创建一个具有与原始图像数组相同的行数和列数的新图像数组(例如“ binary”),其中所有元素都为0(零)。
- 如果(i,j)处的灰度像素大于或等于阈值T,则将1分配给binary(i,j);否则将0分配给binary(i,j)。
对所有灰度像素执行相同的操作。
下面是上述算法的实现:
% Following MATLAB function will take a grayscale
% or an RGB image as input and will return a
% binary image as output
function [binary] = convert2binary(img)
[x, y, z]=size(img);
% if Read Image is an RGB Image then convert
% it to a Gray Scale Image For an RGB image
% the value of z will be 3 and for a Grayscale
% Image the value of z will be 1
if z==3
img=rgb2gray(img);
end
% change the class of image
% array from 'unit8' to 'double'
img=double(img);
% Calculate sum of all the gray level
% pixel's value of the GraySacle Image
sum=0;
for i=1:x
for j=1:y
sum=sum+img(i, j);
end
end
% Calculate Threshold value by dividing the
% calculated sum by total number of pixels
% total number of pixels = rows*columns (i.e x*y)
threshold=sum/(x*y);
% Create a image array having same number
% of rows and column as Original image
% with all elements as 0 (Zero).
binary=zeros(x, y);
% iterate over all the pixels of Grayscale
% Image and Assign 1 to binary(i, j), if gray
% level value is >= threshold value
% else assign 0 to binary(i, j) .
for i=1:x
for j=1:y
if img(i, j) >= threshold
binary(i, j) = 1;
else
binary(i, j)=0;
end
end
end
end
% driver function
% Read the target Image
img=imread('apple.png');
% Call convert2binary() function to convert
% Image to binary using thresholding
binary_image=convert2binary(img);
% Display result
imshow(binary_image);
输入: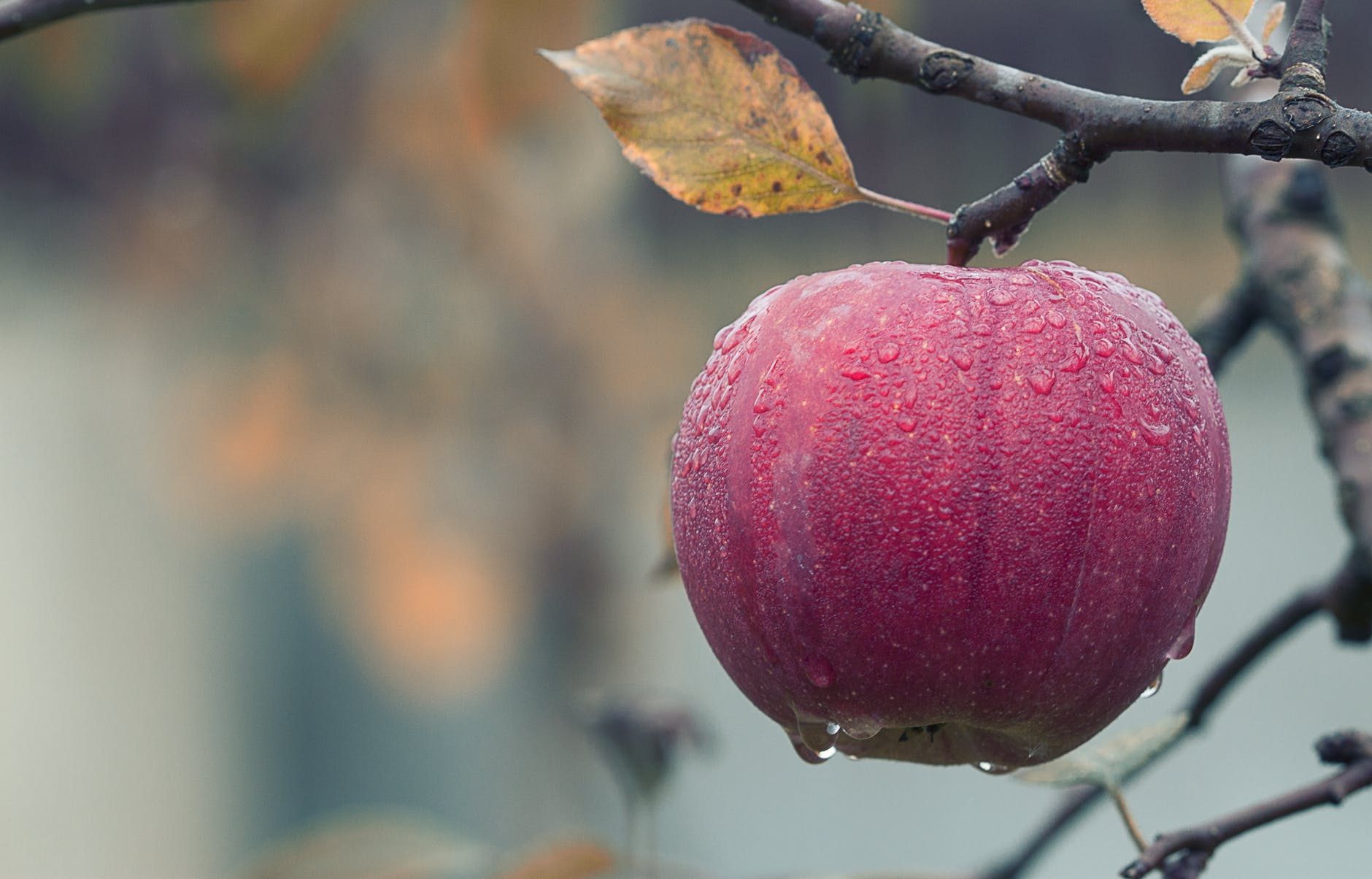 
输出: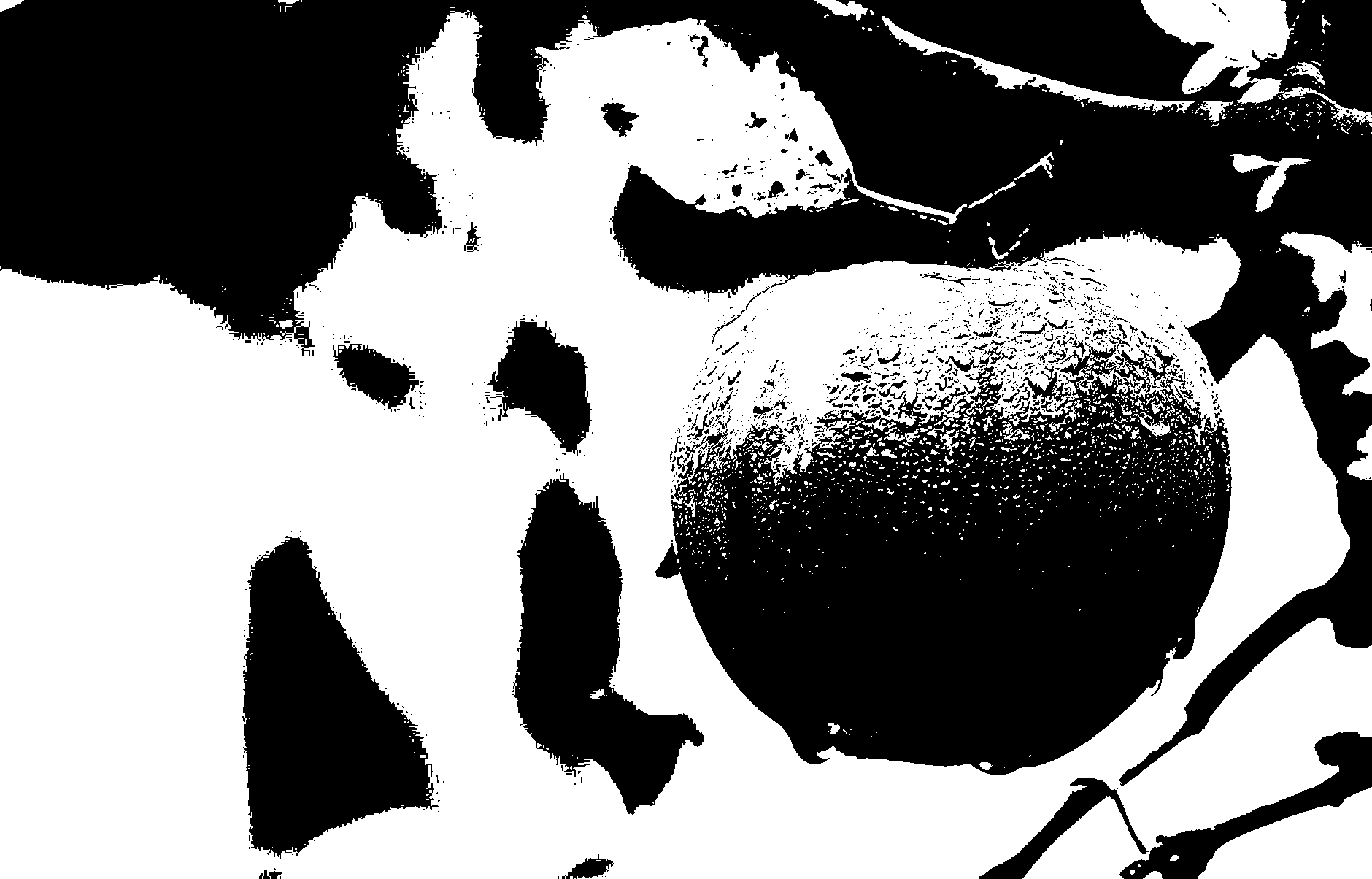 
阈值化的优点:
- 这种方法易于理解且易于实现。
- 它将灰度图像转换为二进制图像。
- 生成的二进制图像易于分析。
阈值的缺点:
- 我们仅考虑阈值处理的图像强度,而不考虑像素之间的任何关系。因此,通过阈值处理识别的像素可能不是连续的。
- 在进行阈值处理时,我们可以轻松地包含不属于所需区域的多余像素,并且可以轻松地错过属于所需区域的像素。
- 它还对图像中的噪点非常敏感。阈值处理的结果随着噪声的变差而变差。