自然语言处理(NLP)是计算机科学和人工智能的一个领域,与计算机和人类(自然)语言之间的相互作用有关,尤其是如何对计算机进行编程以处理和分析大量自然语言数据。这是机器学习的一个分支,它涉及分析任何文本并处理预测分析。
Scikit-learn是针对Python编程语言的免费软件机器学习库。 Scikit-learn主要是用Python编写的,一些核心算法是用Cython编写的,以实现性能。 Cython是Python编程语言的超集,旨在通过主要用Python编写的代码来提供类似于C的性能。
让我们了解文本处理和NLP流程所涉及的各个步骤。
该算法可以轻松地应用于任何其他类型的文本,例如将书籍分类为“浪漫”,“摩擦”,但现在,让我们使用餐厅评论数据集来评论负面或正面反馈。
涉及的步骤:
第1步:导入数据集,将定界符设置为“ \ t”,因为列被分隔为制表符空间。评论及其类别(0或1)没有用其他任何符号分隔,但带有制表符空格,因为大多数其他符号是评论(例如,价格为$,…。!等),算法可能会将它们用作定界符,这会在输出中导致奇怪的行为(例如错误,奇怪的输出)。
# Importing Libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Import dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv('Restaurant_Reviews.tsv', delimiter = '\t')
要下载使用的Restaurant_Reviews.tsv数据集,请单击此处。
步骤2:文本清理或预处理
- 删除标点,数字:标点,数字在处理给定的文本方面无济于事,如果包括在内,它们只会增加我们将在最后一步中创建的词袋的大小,并降低算法的效率。
- 词干:扎根词
- 将每个单词都转换成小写:例如,在不同情况下使用相同的单词(例如,“ good”和“ GOOD”)是无用的。
# library to clean data
import re
# Natural Language Tool Kit
import nltk
nltk.download('stopwords')
# to remove stopword
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
# for Stemming propose
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
# Initialize empty array
# to append clean text
corpus = []
# 1000 (reviews) rows to clean
for i in range(0, 1000):
# column : "Review", row ith
review = re.sub('[^a-zA-Z]', ' ', dataset['Review'][i])
# convert all cases to lower cases
review = review.lower()
# split to array(default delimiter is " ")
review = review.split()
# creating PorterStemmer object to
# take main stem of each word
ps = PorterStemmer()
# loop for stemming each word
# in string array at ith row
review = [ps.stem(word) for word in review
if not word in set(stopwords.words('english'))]
# rejoin all string array elements
# to create back into a string
review = ' '.join(review)
# append each string to create
# array of clean text
corpus.append(review)
示例:应用上述代码之前和之后(评论=>之前,语料库=>之后)
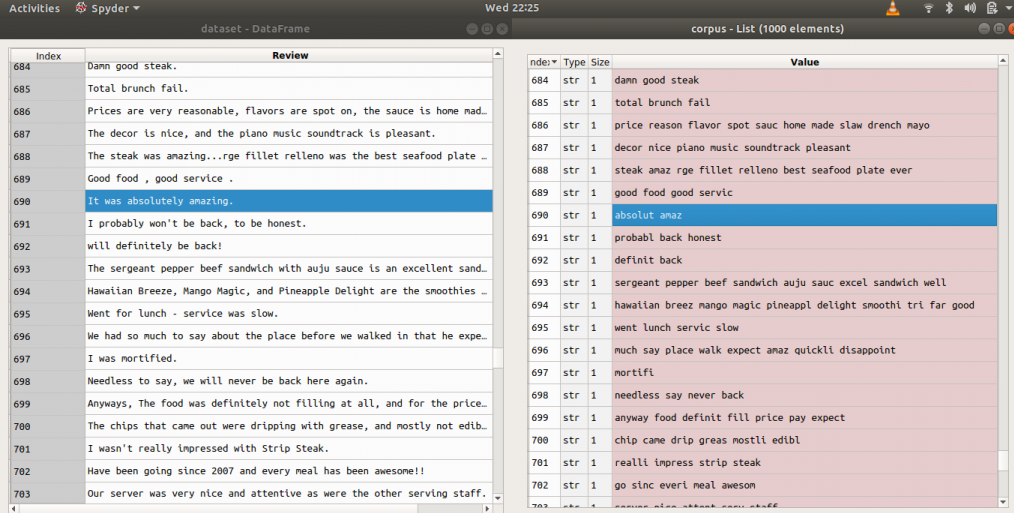
步骤3:标记化,涉及从文本主体中拆分句子和单词。
步骤4:通过稀疏矩阵制作单词袋
- 在数据集中获取评论中所有不同的词,而无需重复词。
- 每个单词一列,因此将有很多列。
- 行是评论
- 如果评论数据集中的行中有单词,则单词计数将在单词列下的单词袋行中存在。
示例:让我们仅获取两个评论的评论数据集
输入:“大坝好牛排”,“美食佳服务”输出: 
为此,我们需要CountVectorizer class 。
我们还可以设置最大数量的功能(通过属性“ max_features”提供最大帮助的最大数量的功能)。对语料库进行训练,然后对语料库“ .fit_transform(corpus)”应用相同的转换,然后将其转换为数组。如果评论为肯定或否定,则答案在数据集[:,1]的第二列中:所有行和第一列(从零开始索引)。
# Creating the Bag of Words model
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
# To extract max 1500 feature.
# "max_features" is attribute to
# experiment with to get better results
cv = CountVectorizer(max_features = 1500)
# X contains corpus (dependent variable)
X = cv.fit_transform(corpus).toarray()
# y contains answers if review
# is positive or negative
y = dataset.iloc[:, 1].values
Description of the dataset to be used:
- Columns seperated by \t (tab space)
- First column is about reviews of people
- In second column, 0 is for negative review and 1 is for positive review

步骤5:将语料库分为训练和测试集。为此,我们需要sklearn.cross_validation中的class train_test_split。可以拆分为70/30或80/20或85/15或75/25,这里我通过“ test_size”选择75/25。
X是单词袋,y是0或1(正数或负数)。
# Splitting the dataset into
# the Training set and Test set
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
# experiment with "test_size"
# to get better results
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25)
步骤6:拟合预测模型(此处为随机森林)
- 由于Random fored是sklearn.ensemble的集成模型(由许多树组成),因此请导入RandomForestClassifier类
- 使用501树或“ n_estimators”并将准则作为“熵”
- 通过.fit()方法使用属性X_train和y_train拟合模型
# Fitting Random Forest Classification
# to the Training set
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# n_estimators can be said as number of
# trees, experiment with n_estimators
# to get better results
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators = 501,
criterion = 'entropy')
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
步骤7:通过使用带有属性X_test的.predict()方法对最终结果进行定价
# Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
y_pred

注意:随机森林的准确度为72%。(使用不同的测试大小进行的实验可能会有所不同,此处= 0.25)。
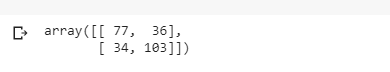
步骤8:要知道准确度,需要使用混淆矩阵。
混淆矩阵是2X2矩阵。
TRUE POSITIVE : measures the proportion of actual positives that are correctly identified.
TRUE NEGATIVE : measures the proportion of actual positives that are not correctly identified.
FALSE POSITIVE : measures the proportion of actual negatives that are correctly identified.
FALSE NEGATIVE : measures the proportion of actual negatives that are not correctly identified.
注意: True或False表示分配的类别是正确或不正确,而Positive或Negative表示分配给Positive或Negative类别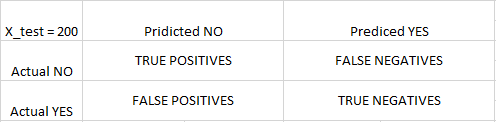
# Making the Confusion Matrix
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
cm