偏斜堆(或自调整堆)是实现为二叉树的堆数据结构。倾斜堆是有利的,因为它们的合并能力比二进制堆更快。与二进制堆相比,没有结构约束,因此不能保证树的高度是对数的。仅需满足两个条件:
- 一般的堆顺序必须在那里(根是最小的,子树的递归也是如此),但是不需要平衡的属性(除了最后一个之外,所有级别都必须是完整的)。
- 歪斜堆的主要操作是合并。我们可以仅使用Merge来实现其他操作,例如insert,extractMin()等。
例子 :
1.考虑偏斜堆1为
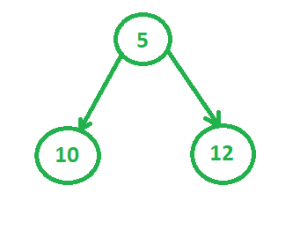
2.要考虑的第二个堆
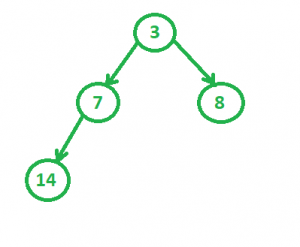
4.然后我们得到最终的合并树为
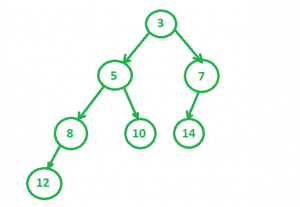
递归合并过程:
合并(h1,h2)
- 令h1和h2为要合并的两个最小歪斜堆。令h1的根小于h2的根(如果不小于,我们可以交换以获得相同的根)。
- 我们交换h1-> left和h1-> right。
- h1-> left = merge(h2,h1-> left)
例子 :
Let h1 be
10
/ \
20 30
/ /
40 50
Let h2 be
15
/ \
25 35
/ \
45 55
After swapping h1->left and h1->right, we get
10
/ \
30 20
/ /
50 40
Now we recursively Merge
30
/ AND
50
15
/ \
25 35
/ \
45 55
After recursive merge, we get (Please do it
using pen and paper).
15
/ \
30 25
/ \ / \
35 50 45 55
We make this merged tree as left of original
h1 and we get following result.
10
/ \
15 20
/ \ /
30 25 40
/ \ / \
35 40 45 55为了可视化:https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/JavascriptVisual/LeftistHeap.html
CPP
// CPP program to implement Skew Heap
// operations.
#include
using namespace std;
struct SkewHeap
{
int key;
SkewHeap* right;
SkewHeap* left;
// constructor to make a new
// node of heap
SkewHeap()
{
key = 0;
right = NULL;
left = NULL;
}
// the special merge function that's
// used in most of the other operations
// also
SkewHeap* merge(SkewHeap* h1, SkewHeap* h2)
{
// If one of the heaps is empty
if (h1 == NULL)
return h2;
if (h2 == NULL)
return h1;
// Make sure that h1 has smaller
// key.
if (h1->key > h2->key)
swap(h1, h2);
// Swap h1->left and h1->right
swap(h1->left, h1->right);
// Merge h2 and h1->left and make
// merged tree as left of h1.
h1->left = merge(h2, h1->left);
return h1;
}
// function to construct heap using
// values in the array
SkewHeap* construct(SkewHeap* root,
int heap[], int n)
{
SkewHeap* temp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
temp = new SkewHeap;
temp->key = heap[i];
root = merge(root, temp);
}
return root;
}
// function to print the Skew Heap,
// as it is in form of a tree so we use
// tree traversal algorithms
void inorder(SkewHeap* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
else {
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->key << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
return;
}
};
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Construct two heaps
SkewHeap heap, *temp1 = NULL,
*temp2 = NULL;
/*
5
/ \
/ \
10 12 */
int heap1[] = { 12, 5, 10 };
/*
3
/ \
/ \
7 8
/
/
14 */
int heap2[] = { 3, 7, 8, 14 };
int n1 = sizeof(heap1) / sizeof(heap1[0]);
int n2 = sizeof(heap2) / sizeof(heap2[0]);
temp1 = heap.construct(temp1, heap1, n1);
temp2 = heap.construct(temp2, heap2, n2);
// Merge two heaps
temp1 = heap.merge(temp1, temp2);
/*
3
/ \
/ \
5 7
/ \ /
8 10 14
/
12 */
cout << "Merged Heap is: " << endl;
heap.inorder(temp1);
} 输出:
The heap obtained after merging is:
12 8 5 10 3 14 7