N 数组树中的第 K 个最大元素
给定一个由N个节点和一个整数K组成的 N-array Tree,任务是在给定的N-ary Tree中找到第K个最大的元素。
例子:
Input: K = 3
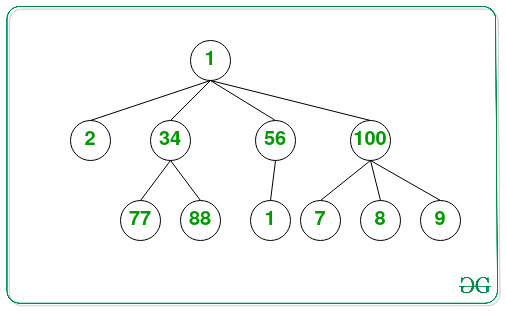
Output: 77
Explanation:
The 3rd largest element in the given N-array tree is 77.
Input: K = 4
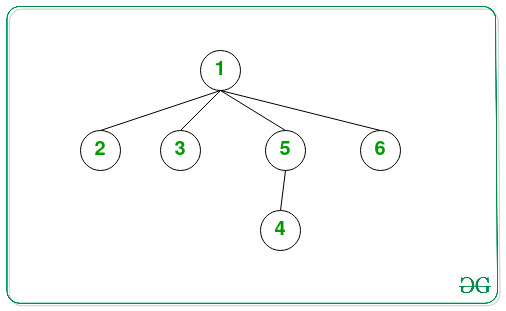
Output: 3
方法:给定问题可以通过在给定范围内查找最大元素K次来解决,并不断将范围的末尾更新为迄今为止找到的最大元素。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个变量,比如将最大ELE 初始化为 INT_MIN 。
- 定义一个函数,比如maximumEleUnderRange(root, data) ,然后执行以下步骤:
- 如果当前根的值小于数据,则将最大ELe的值更新为最大ELe和当前根的值的最大值。
- 遍历当前根的所有子节点并递归调用函数maximumEleUnderRange(child, data) 。
- 初始化一个变量,比如说, ans as INT_MAX来存储第K个最大的元素。
- 遍历范围[0, K – 1]递归调用函数maximumEleUnderRange(root, ans)并将ans的值更新为最大ELe ,将最大ELe 更新为INT_MIN 。
- 完成上述步骤后,将ans的值打印为得到的第K个最大值。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of N-array Tree
class Node {
public:
int data;
vector childs;
};
// Stores the minimum element
// in the recursive call
int largestELe = INT_MIN;
// Function to find the largest
// element under the range of key
void largestEleUnderRange(
Node* root, int data)
{
// If the current root's value
// is less than data
if (root->data < data) {
largestELe = max(root->data,
largestELe);
}
// Iterate over all the childrens
for (Node* child : root->childs) {
// Update under current range
largestEleUnderRange(child, data);
}
}
// Function to find the Kth Largest
// element in the given N-ary Tree
void KthLargestElement(Node* root,
int K)
{
// Stores the resultant
// Kth maximum element
int ans = INT_MAX;
// Iterate over the range [0, K]
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
// Recursively call for
// finding the maximum element
// from the given range
largestEleUnderRange(root, ans);
// Update the value of
// ans and largestEle
ans = largestELe;
largestELe = INT_MIN;
}
// Print the result
cout << ans;
}
// Function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node();
temp->data = data;
// Return the created node
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/* Create below the tree
* 10
* / / \ \
* 2 34 56 100
* / \ | / | \
* 77 88 1 7 8 9
*/
Node* root = newNode(10);
(root->childs).push_back(newNode(2));
(root->childs).push_back(newNode(34));
(root->childs).push_back(newNode(56));
(root->childs).push_back(newNode(100));
(root->childs[0]->childs).push_back(newNode(77));
(root->childs[0]->childs).push_back(newNode(88));
(root->childs[2]->childs).push_back(newNode(1));
(root->childs[3]->childs).push_back(newNode(7));
(root->childs[3]->childs).push_back(newNode(8));
(root->childs[3]->childs).push_back(newNode(9));
int K = 3;
KthLargestElement(root, K);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
// Structure of N-array Tree
static class Node {
public int data;
public Vector childs = new Vector();
}
// Function to create a new node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
return temp;
}
// Stores the minimum element
// in the recursive call
static int largestELe = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Function to find the largest
// element under the range of key
static void largestEleUnderRange(Node root, int data)
{
// If the current root's value
// is less than data
if (root.data < data) {
largestELe = Math.max(root.data, largestELe);
}
// Iterate over all the childrens
for (int child = 0; child < root.childs.size(); child++) {
// Update under current range
largestEleUnderRange(root.childs.get(child), data);
}
}
// Function to find the Kth Largest
// element in the given N-ary Tree
static void KthLargestElement(Node root, int K)
{
// Stores the resultant
// Kth maximum element
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Iterate over the range [0, K]
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
// Recursively call for
// finding the maximum element
// from the given range
largestEleUnderRange(root, ans);
// Update the value of
// ans and largestEle
ans = largestELe;
largestELe = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
// Print the result
System.out.print(ans);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* Create below the tree
* 10
* / / \ \
* 2 34 56 100
* / \ | / | \
* 77 88 1 7 8 9
*/
Node root = newNode(10);
(root.childs).add(newNode(2));
(root.childs).add(newNode(34));
(root.childs).add(newNode(56));
(root.childs).add(newNode(100));
(root.childs.get(0).childs).add(newNode(77));
(root.childs.get(0).childs).add(newNode(88));
(root.childs.get(2).childs).add(newNode(1));
(root.childs.get(3).childs).add(newNode(7));
(root.childs.get(3).childs).add(newNode(8));
(root.childs.get(3).childs).add(newNode(9));
int K = 3;
KthLargestElement(root, K);
}
}
// This code is contributed by suresh07. Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
import sys
# Structure of N-array Tree
class Node:
# Constructor to set the data of
# the newly created tree node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.childs = []
# Stores the minimum element
# in the recursive call
largestELe = -sys.maxsize
# Function to find the largest
# element under the range of key
def largestEleUnderRange(root, data):
global largestELe
# If the current root's value
# is less than data
if (root.data < data) :
largestELe = max(root.data, largestELe)
# Iterate over all the childrens
for child in range(len(root.childs)):
# Update under current range
largestEleUnderRange(root.childs[child], data)
# Function to find the Kth Largest
# element in the given N-ary Tree
def KthLargestElement(root, K):
global largestELe
# Stores the resultant
# Kth maximum element
ans = sys.maxsize
# Iterate over the range [0, K]
for i in range(K):
# Recursively call for
# finding the maximum element
# from the given range
largestEleUnderRange(root, ans)
# Update the value of
# ans and largestEle
ans = largestELe
largestELe = -sys.maxsize
# Print the result
print(ans)
""" Create below the tree
* 10
* / / \ \
* 2 34 56 100
* / \ | / | \
* 77 88 1 7 8 9
"""
root = Node(10)
(root.childs).append(Node(2));
(root.childs).append(Node(34));
(root.childs).append(Node(56));
(root.childs).append(Node(100));
(root.childs[0].childs).append(Node(77))
(root.childs[0].childs).append(Node(88))
(root.childs[2].childs).append(Node(1))
(root.childs[3].childs).append(Node(7))
(root.childs[3].childs).append(Node(8))
(root.childs[3].childs).append(Node(9))
K = 3
KthLargestElement(root, K)
# This code is contributed by rameshtravel07.C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Structure of N-array Tree
class Node
{
public int data;
public List childs = new List();
};
// Function to create a new node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
return temp;
}
// Stores the minimum element
// in the recursive call
static int largestELe = Int32.MinValue;
// Function to find the largest
// element under the range of key
static void largestEleUnderRange(Node root, int data)
{
// If the current root's value
// is less than data
if (root.data < data) {
largestELe = Math.Max(root.data, largestELe);
}
// Iterate over all the childrens
for (int child = 0; child < root.childs.Count; child++) {
// Update under current range
largestEleUnderRange(root.childs[child], data);
}
}
// Function to find the Kth Largest
// element in the given N-ary Tree
static void KthLargestElement(Node root, int K)
{
// Stores the resultant
// Kth maximum element
int ans = Int32.MaxValue;
// Iterate over the range [0, K]
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
// Recursively call for
// finding the maximum element
// from the given range
largestEleUnderRange(root, ans);
// Update the value of
// ans and largestEle
ans = largestELe;
largestELe = Int32.MinValue;
}
// Print the result
Console.Write(ans);
}
static void Main() {
/* Create below the tree
* 10
* / / \ \
* 2 34 56 100
* / \ | / | \
* 77 88 1 7 8 9
*/
Node root = newNode(10);
(root.childs).Add(newNode(2));
(root.childs).Add(newNode(34));
(root.childs).Add(newNode(56));
(root.childs).Add(newNode(100));
(root.childs[0].childs).Add(newNode(77));
(root.childs[0].childs).Add(newNode(88));
(root.childs[2].childs).Add(newNode(1));
(root.childs[3].childs).Add(newNode(7));
(root.childs[3].childs).Add(newNode(8));
(root.childs[3].childs).Add(newNode(9));
int K = 3;
KthLargestElement(root, K);
}
}
// This code is contributed by decode2207. Javascript
输出:
77时间复杂度: O(N*K)
辅助空间: O(1)