给定一个唯一元素数组,我们必须使用该数组的元素找到长度L的所有排列。允许重复元素。
例子:
Input: arr = { 1, 2 }, L=3
Output:
111
211
121
221
112
212
122
222
Input: arr = { 1, 2, 3 }, L=2
Output:
11
21
31
12
22
32
13
23
33
方法:
- 为了形成具有N个元素的长度L的序列,已知该序列的第i个元素可以用N种方式填充。所以会有
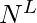 顺序
顺序 - 我们将运行一个从0到
 ,对于每一个i,我们都会将i从10以基数转换为N。转换后的数字将代表数组的索引
,对于每一个i,我们都会将i从10以基数转换为N。转换后的数字将代表数组的索引 - 我们可以打印所有
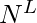 通过这种方式进行排序。
通过这种方式进行排序。
下面是该方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation
#include
using namespace std;
// Convert the number to Lth
// base and print the sequence
void convert_To_Len_th_base(int n,
int arr[],
int len,
int L)
{
// Sequence is of length L
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
// Print the ith element
// of sequence
cout << arr[n % len];
n /= len;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Print all the permuataions
void print(int arr[],
int len,
int L)
{
// There can be (len)^l
// permutations
for (int i = 0; i < (int)pow(len, L); i++) {
// Convert i to len th base
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int L = 2;
// function call
print(arr, len, L);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation for above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// Convert the number to Lth
// base and print the sequence
static void convert_To_Len_th_base(int n, int arr[],
int len, int L)
{
// Sequence is of length L
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
{
// Print the ith element
// of sequence
System.out.print(arr[n % len]);
n /= len;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Print all the permuataions
static void print(int arr[], int len, int L)
{
// There can be (len)^l
// permutations
for (int i = 0;
i < (int)Math.pow(len, L); i++)
{
// Convert i to len th base
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
int len = arr.length;
int L = 2;
// function call
print(arr, len, L);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ajit.Python3
# Python3 implementation for the above approach
# Convert the number to Lth
# base and print the sequence
def convert_To_Len_th_base(n, arr, Len, L):
# Sequence is of Length L
for i in range(L):
# Print the ith element
# of sequence
print(arr[n % Len], end = "")
n //= Len
print()
# Print all the permuataions
def printf(arr, Len, L):
# There can be (Len)^l permutations
for i in range(pow(Len, L)):
# Convert i to Len th base
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, Len, L)
# Driver code
arr = [1, 2, 3]
Len = len(arr)
L = 2
# function call
printf(arr, Len, L)
# This code is contributed by Mohit KumarC#
// C# implementation for above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Convert the number to Lth
// base and print the sequence
static void convert_To_Len_th_base(int n, int []arr,
int len, int L)
{
// Sequence is of length L
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
{
// Print the ith element
// of sequence
Console.Write(arr[n % len]);
n /= len;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Print all the permuataions
static void print(int []arr, int len, int L)
{
// There can be (len)^l
// permutations
for (int i = 0;
i < (int)Math.Pow(len, L); i++)
{
// Convert i to len th base
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main (String[] args)
{
int []arr = { 1, 2, 3 };
int len = arr.Length;
int L = 2;
// function call
print(arr, len, L);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji输出:
11
21
31
12
22
32
13
23
33