什么是方法?
在数学中,我们可能已经研究过函数。例如, f(x) = x 2是一个函数 ,返回x的平方值。
If x = 2, then f(2) = 4
If x = 3, f(3) = 9
and so on.同样,在计算机编程中, 函数是执行特定任务的代码块。
在面向对象的编程中,该方法是用于函数的行话。方法绑定到类,并且它们定义类的行为。
在学习方法之前,请确保了解Java类和对象。
Java方法的类型
根据用户定义的方法还是标准库中可用的方法,Java中有两种类型的方法:
- 标准库方法
- 用户定义的方法
标准库方法
标准库方法是Java中的内置方法,可以随时使用。这些标准库与Java类库(JCL)一起提供在带有JVM和JRE的Java归档文件(* .jar)中。
例如,
-
print()是java.io.PrintSteam。print("...")方法将字符串打印在引号内。 -
sqrt()是Math类的一种方法。它返回数字的平方根。
这是一个工作示例:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// using the sqrt() method
System.out.print("Square root of 4 is: " + Math.sqrt(4));
}
}输出 :
Square root of 4 is: 2.0用户定义的方法
我们还可以创建自己选择的方法来执行某些任务。这种方法称为用户定义方法。
如何创建用户定义的方法?
这是我们可以用Java创建方法的方法:
public static void myMethod() {
System.out.println("My Function called");
}在这里,我们创建了一个名为myMethod()的方法。我们可以看到我们在方法名称之前使用了public , static和void 。
-
public访问修饰符。这意味着可以从任何地方访问该方法。要了解更多信息,请访问Java访问修饰符 -
static-意味着可以在没有任何对象的情况下访问该方法。要了解更多信息,请访问Java静态关键字。 -
void这意味着该方法不返回任何值。我们将在本教程的后面部分进一步了解这一点。
这是我们如何创建方法的简单示例。但是,Java中方法定义的完整语法为:
modifier static returnType nameOfMethod (parameters) {
// method body
}这里,
- 修饰符 -它定义访问类型,方法是公共的,私有的,等等。
- static-如果使用
static关键字,则无需创建对象即可对其进行访问。例如,标准Math类的
sqrt()方法是静态的。因此,我们可以直接调用Math.sqrt()而不创建Math类的实例。 - returnType-它指定方法返回的值的类型。例如,如果方法具有
int返回类型,则它返回一个整数值。方法可以返回本机数据类型(
int,float,double等),本机对象(String,Map,List等)或任何其他内置的和用户定义的对象。如果该方法未返回值,则其返回类型为
void。 - nameOfMethod-它是一个标识符,用于引用程序中的特定方法。
我们可以给方法起任何名字。但是,以其执行的任务命名是更常规的做法。例如,
calculateArea(),display()等。
- 参数(参数) -这些是传递给方法的值。我们可以将任意数量的参数传递给方法。
- 方法主体 -它包括用于执行某些任务的编程语句。方法主体包含在花括号
{ }。
如何调用Java方法?
现在我们知道如何定义方法,我们需要学习使用它们。为此,我们必须调用该方法。这是如何做
myMethod();该语句调用先前声明的myMethod()方法。
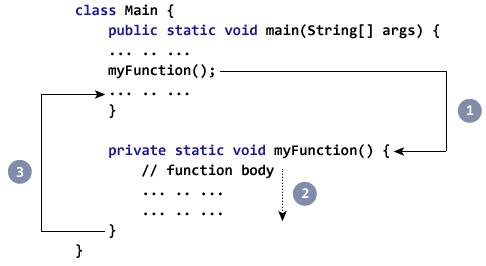
- 在执行程序代码时,它遇到
myFunction();在代码中。 - 然后,执行分支到
myFunction()方法,并在该方法主体内执行代码。 - 在执行方法主体之后,程序将返回到原始状态,并在方法调用之后执行下一条语句。
示例:Java方法
让我们看看如何在Java程序中使用方法。
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("About to encounter a method.");
// method call
myMethod();
System.out.println("Method was executed successfully!");
}
// method definition
private static void myMethod(){
System.out.println("Printing from inside myMethod()!");
}
}输出 :
About to encounter a method.
Printing from inside myMethod().
Method was executed successfully!在上面的程序中,我们有一个名为myMethod()的方法。该方法不接受任何参数。同样,该方法的返回类型为void (意味着不返回任何值)。
在这里,该方法是static 。因此,我们在不创建类的对象的情况下调用了该方法。
再来看一个例子
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create object of the Output class
Output obj = new Output();
System.out.println("About to encounter a method.");
// calling myMethod() of Output class
obj.myMethod();
System.out.println("Method was executed successfully!");
}
}
class Output {
// public: this method can be called from outside the class
public void myMethod() {
System.out.println("Printing from inside myMethod().");
}
}输出 :
About to encounter a method.
Printing from inside myMethod().
Method was executed successfully!在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个名为myMethod()的方法。该方法位于名为Output的类中。
由于该方法不是static ,因此使用类的对象obj进行调用。
obj.myMethod();方法参数和返回值
如前所述,Java方法可以具有零个或多个参数。并且,它也可能返回一些值。
示例:方法返回值
让我们以返回值的方法为例。
class SquareMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result;
// call the method and store returned value
result = square();
System.out.println("Squared value of 10 is: " + result);
}
public static int square() {
// return statement
return 10 * 10;
}
}输出 :
Squared value of 10 is: 100在上面的程序中,我们创建了一个名为square()的方法。此方法不接受任何参数,并返回值10 *10 。
在这里,我们将方法的返回类型称为int 。因此,该方法应始终返回整数值。
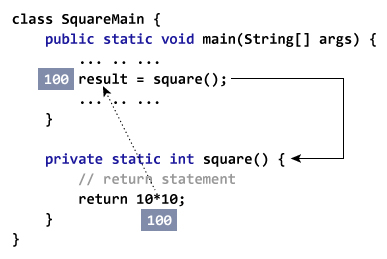
如我们所见,此方法的范围是有限的,因为它总是返回相同的值。现在,让我们修改上面的代码片段,以便它不总是返回平方值10,而是返回传递给该方法的任何整数的平方值。
示例:方法接受参数并返回值
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result, n;
n = 3;
result = square(n);
System.out.println("Square of 3 is: " + result);
n = 4;
result = square(n);
System.out.println("Square of 4 is: " + result);
}
// method
static int square(int i) {
return i * i;
}
}输出 :
Squared value of 3 is: 9
Squared value of 4 is: 16这里, square( )方法接受一个参数i和返回i的平方。返回的值存储在变量result中 。
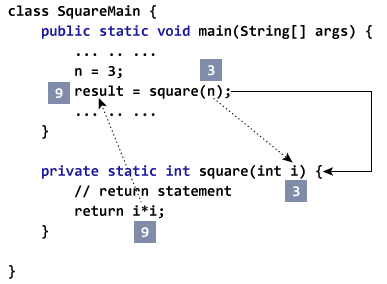
如果我们传递任何其他数据类型而不是int,则编译器将引发错误。这是因为Java是一种强类型语言。
在方法调用期间传递给getSquare()方法的参数n称为实际参数。
result = getSquare(n);我被方法定义接受的参数称为形式参数。形式参数的类型必须显式键入。
public static int square(int i) {...}我们还可以使用逗号将多个参数传递给Java方法。例如,
public class Main {
// method definition
public static int getIntegerSum (int i, int j) {
return i + j;
}
// method definition
public static int multiplyInteger (int x, int y) {
return x * y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// calling methods
System.out.println("10 + 20 = " + getIntegerSum(10, 20));
System.out.println("20 x 40 = " + multiplyInteger(20, 40));
}
}输出 :
10 + 20 = 30
20 x 40 = 800注意 :实际参数和形式参数的数据类型应匹配,即,第一个实际参数的数据类型应与第一个形式参数的类型匹配。同样,第二个实际参数的类型必须与第二个形式参数的类型相匹配,依此类推。
使用方法的优点是什么?
1.主要优点是代码可重用性 。我们可以编写一次方法,然后多次使用。我们不必每次都重写整个代码。可以将其视为“一次编写,多次重用”。例如,
public class Main {
// method defined
private static int getSquare(int x){
return x * x;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// method call
int result = getSquare(i);
System.out.println("Square of " + i + " is: " + result);
}
}
}输出 :
Square of 1 is: 1
Square of 2 is: 4
Square of 3 is: 9
Square of 4 is: 16
Square of 5 is: 25在上面的程序中,我们创建了名为getSquare()的方法来计算数字的平方。在这里,使用相同的方法来计算小于6的数字的平方。
因此,我们一次又一次地使用相同的方法。
2.方法使代码更具可读性且更易于调试。例如, getSquare()方法非常易读,以至于我们可以知道此方法将计算数字的平方。