使用 JDBC 在表中插入详细信息的Java程序
Java数据库连接基本上是Java编程语言与 Oracle、SQL、Postgress、SQL 等各种数据库之间的标准 API(应用程序接口)。它连接前端(用于与用户交互)和后端(用于存储数据) )。
算法:在JDBC中搜索/插入/删除/更新
为了处理 JDBC 标准,应该遵循 7 个步骤:
- 导入数据库
- 加载和注册驱动程序
- 创建连接
- 创建声明
- 执行查询
- 处理结果
- 关闭连接
程序:
- 创建数据库而不管SQL或NoSQL 。使用sqlyog创建数据库并在其中创建一些表并在其中填充数据以搜索表的内容。例如,数据库名为“hotelman”,表名为“cuslogin”和“adminlogin”。
- 创建连接:打开任何可以按照标准方法生成Java可执行文件的 IDE。创建一个包进一步创建一个类。在包内,打开一个新的Java文件并键入以下用于 JDBC 连接的代码并将文件名与 connection.json 一起保存。Java。
- 在输入示例图像中使用JDBC在表中插入详细信息,参数如下
- “cuslogin”表有列,即 -
- 姓名
- 密码
- 电子邮件
- 地址
- 电话
- ID
- 需要在“cuslogin”表中插入新的详细信息。
- “cuslogin”表有列,即 -
输入示例图像:
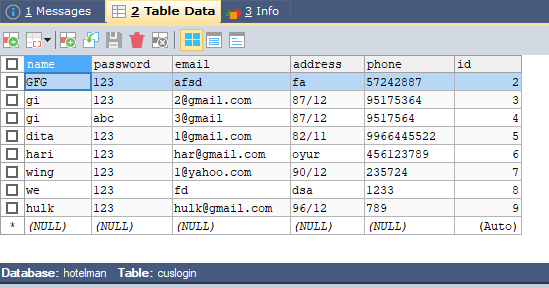
3.1:用SQL查询初始化一个字符串如下
String sql=”insert into cuslogin values(‘geeksforgeeks’,’gfg’,’geeks@email.com’,’flat 1′,’1239087474′,10)”;
3.2:初始化Connection类、PreparedStatement类(JDBC需要)的以下对象,连接数据库如下
Connection con=null;
PreparedStatement p=null;
con=connection.connectDB();3.3 :现在,在PrepareStatement里面添加步骤3.1的SQL查询,执行如下
p =con.prepareStatement(sql);
p.execute();3.4:在同一个包中打开一个新的Java文件(这里是它的结果Java)并输入完整的代码(如下所示)以在表“cuslogin”中插入客户的详细信息。
Note: Both the file’s viz result.java and connection.java should be inside the same package, else the program won’t give the desired output.
执行 :
- Example 1 是 JDBC 的 Connection 类
- 示例 2 是 App(Main) 类,其中连接类用作主类中 Connection 类的调用对象。
示例 1:连接类
Java
// Java Program to Insert Details in a Table using JDBC
// Connections class
// Importing all SQL classes
import java.sql.*;
public class connection {
// object of Connection class
// initially assigned NULL
Connection con = null;
public static Connection connectDB()
{
try {
// Step 2 is involved among 7 in Connection
// class i.e Load and register drivers
// 2(a) Loading drivers using forName() method
// name of database here is mysql
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2(b) Registering drivers using DriverManager
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hotelman",
"root", "1234");
// For DB here (custom sets)
// root is the username, and
// 1234 is the password
// returning the object of Connection class
// to be used in main class (Example2)
return con;
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions
catch (SQLException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
// Print the exceptions
System.out.println(e);
return null;
}
}
}Java
// Java Program to Insert Details in a Table using JDBC
// Main class
// Step 1: Importing DB classes
// DB is SQL here
import java.sql.*;
// Main/App class of above Connection class
public class GFG {
// MAin driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Step 2: Showing above Connection class i.e
// loading and registering drivers
// Initially assigning NULL parameters
// to object of Connection class
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
// Step 3: Establish the connection
con = connection.connectDB();
// Try block to check if exception/s occurs
try {
// Step 4: Create a statement
String sql = "insert into cuslogin values('geeksforgeeks','gfg','geeks@email.com','flat 1','1239087474',10)";
// Step 5: Execute the query
ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
// Step 6: Process the results
ps.execute();
}
// Optional but recommended
// Step 7: Close the connection
// Catch block to handle the exception/s
catch (Exception e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}示例2:程序编译运行的App/Main Class调用上述连接类对象
Java
// Java Program to Insert Details in a Table using JDBC
// Main class
// Step 1: Importing DB classes
// DB is SQL here
import java.sql.*;
// Main/App class of above Connection class
public class GFG {
// MAin driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Step 2: Showing above Connection class i.e
// loading and registering drivers
// Initially assigning NULL parameters
// to object of Connection class
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
// Step 3: Establish the connection
con = connection.connectDB();
// Try block to check if exception/s occurs
try {
// Step 4: Create a statement
String sql = "insert into cuslogin values('geeksforgeeks','gfg','geeks@email.com','flat 1','1239087474',10)";
// Step 5: Execute the query
ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
// Step 6: Process the results
ps.execute();
}
// Optional but recommended
// Step 7: Close the connection
// Catch block to handle the exception/s
catch (Exception e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
输出:
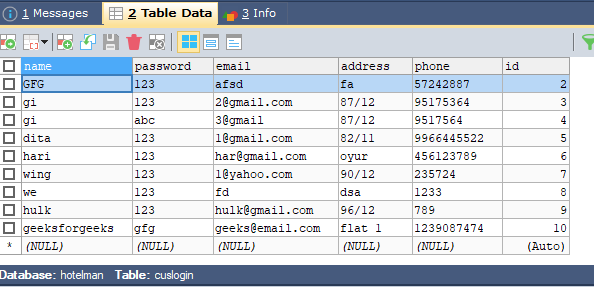
Details added here: “geeksforgeeks” named customer details have been added.