Spring 和 JAXB 集成
术语 JAXB 代表用于 XML 绑定的Java体系结构。 Java程序员可以使用它将Java类转换为 XML 表示。可以使用 JAXB 将Java对象编组为 XML,反之亦然。 Sun 提供了一个 OXM(对象 XML 映射)或 O/M 框架。
Note: The biggest and only advantage of JAXB is as there’s no need to develop callback methods or create a SAX or DOM parser.
实现: Spring 和 JAXB 集成(将Java对象编组为 XML)
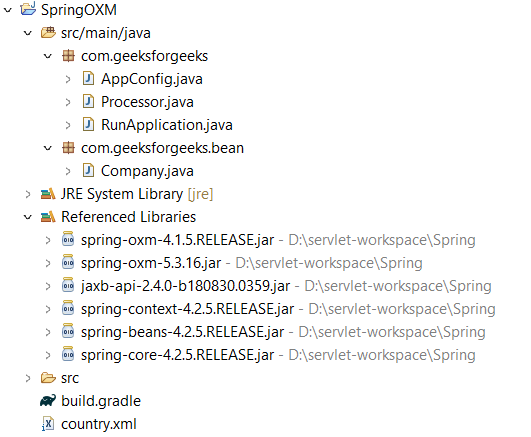
项目结构如下所示:
我们使用 Jaxb2Marshaller 实例构建 Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller 实例。在 Jaxb2Marshaller 中,将 jaxb.formatted.output 属性设置为 true 以获得良好的打印效果。要将 XML 标记和属性映射到Java对象,我们需要构造一个带有映射到 XML 标记和属性的属性的Java bean。使用 javax.xml.bind 注释属性。例如,XmlAttribute 和 XmlElement 是将 XML 属性和元素链接到Java bean 属性的注释。
Remember: To run the application, we need the following software as listed:
- Java 7
- Gradle
- Eclipse
- Spring-Oxm:4.1.5.RELEASE
Spring OXM 和 Spring Boot Starter 的 Gradle 文件
第 1 步:找到 spring OXM 和 spring Boot Starter 的 Gradle 文件。
文件:构建.xml
XML
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'eclipse'
archivesBaseName = 'geeksforgeeks'
version = '1'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
compile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter:1.2.2.RELEASE'
compile 'org.springframework:spring-oxm:4.1.5.RELEASE'
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Configuration Class
package com.geeksforgeeks;
// Importing required classes
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller;
// Annotation
@Configuration
// Class
public class AppConfig {
// Method
@Bean public Processor getHandler()
{
Processor handler = new Processor();
handler.setMarshaller(getCastorMarshaller());
handler.setUnmarshaller(getCastorMarshaller());
return handler;
}
// Method
@Bean public Jaxb2Marshaller getCastorMarshaller()
{
Jaxb2Marshaller jaxb2Marshaller
= new Jaxb2Marshaller();
jaxb2Marshaller.setPackagesToScan(
"com.geeksforgeeks.bean");
Map map
= new HashMap();
map.put("jaxb.formatted.output", true);
jaxb2Marshaller.setMarshallerProperties(map);
return jaxb2Marshaller;
}
} Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Bean for XML Mapping
package com.geeksforgeeks.bean;
// Importing required classes
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAttribute;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
// Annotation
@XmlRootElement(name = "company-info",
namespace = "com.geeksforgeeks")
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.NONE)
// Class
public class Company {
// Class data members
@XmlAttribute(name = "id") private Integer id;
@XmlElement(name = "company-name")
private String companyName;
@XmlElement(name = "ceo-name") private String ceoName;
@XmlElement(name = "no-emp") private Integer noEmp;
// Getters and setters
public Integer getId() { return id; }
public void setId(Integer id)
{
// this keyword refers to current itself
this.id = id;
}
// Getter and Setter
public String getCompanyName() { return companyName; }
public void setCompanyName(String companyName)
{
this.companyName = companyName;
}
// Getter and Setter
public String getCeoName() { return ceoName; }
public void setCeoName(String ceoName)
{
this.ceoName = ceoName;
}
// Getter and Setter
public Integer getNoEmp() { return noEmp; }
public void setNoEmp(Integer noEmp)
{
this.noEmp = noEmp;
}
}Java
// Java Program Defining Method for
// Marshaller and Unmarshaller
package com.geeksforgeeks;
// Importing required classes
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamResult;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamSource;
import org.springframework.oxm.Marshaller;
import org.springframework.oxm.Unmarshaller;
// Class
public class Processor {
// Class data members
private Marshaller marshaller;
private Unmarshaller unmarshaller;
// Setter
public void setMarshaller(Marshaller marshaller) {
this.marshaller = marshaller;
}
public void setUnmarshaller(Unmarshaller unmarshaller) {
this.unmarshaller = unmarshaller;
}
// Converting Object to XML file
public void objectToXML(String fileName, Object graph) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(fileName);
marshaller.marshal(graph, new StreamResult(fos));
}
// finally block that will execute for sure
finally {
// Closing the connections
fos.close();
}
}
// Method
// To Convert XML to Java Object
public Object xmlToObject(String fileName) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
return unmarshaller.unmarshal(new StreamSource(fis));
}
// finally block that will execute for sure
finally {
// Closing the connections
fis.close();
}
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Application Class
package com.geeksforgeeks;
// Importing required classes
import com.geeksforgeeks.bean.Company;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
// Application/Main Class
public class RunApplication {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Try block to check for exceptions
try (AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx
= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext()) {
ctx.register(AppConfig.class);
ctx.refresh();
Processor processor
= ctx.getBean(Processor.class);
// Perform Marshaling
Company company = new Company();
company.setId(1000);
company.setCompanyName("XYZ");
company.setCeoName("ABCD");
company.setNoEmp(100);
processor.objectToXML("country.xml", company);
// Display message only
System.out.println("Marshaling performed");
// Perform UnMarshaling
company = (Company)processor.xmlToObject(
"country.xml");
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"After UnMarshaling Data is: id:"
+ company.getId() + ", CountryName:"
+ company.getCompanyName());
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (BeansException | IllegalStateException e) {
// Display exceptions along with line number
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Jaxb2Marshaller 和 Pretty Print 的基于注释的配置文件
Spring OXM 中的 Jaxb2Marshaller 实例用于构造 Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller 实例。
第 2 步:在 Jaxb2Marshaller 中,我们可以配置漂亮的 XML 打印、编码等设置。要制作精美的印刷品,请按照以下说明进行操作。
map.put("jaxb.formatted.output", true);
jaxb2Marshaller.setMarshallerProperties(map); 文件:应用配置。Java
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Configuration Class
package com.geeksforgeeks;
// Importing required classes
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller;
// Annotation
@Configuration
// Class
public class AppConfig {
// Method
@Bean public Processor getHandler()
{
Processor handler = new Processor();
handler.setMarshaller(getCastorMarshaller());
handler.setUnmarshaller(getCastorMarshaller());
return handler;
}
// Method
@Bean public Jaxb2Marshaller getCastorMarshaller()
{
Jaxb2Marshaller jaxb2Marshaller
= new Jaxb2Marshaller();
jaxb2Marshaller.setPackagesToScan(
"com.geeksforgeeks.bean");
Map map
= new HashMap();
map.put("jaxb.formatted.output", true);
jaxb2Marshaller.setMarshallerProperties(map);
return jaxb2Marshaller;
}
}
Java支持许多用于 XML 和Java对象映射的注解,包括 @XmlRootElement、@XmlAccessorType、@XmlAttribute 和 @XmlElement。
第三步:使用@XmlAttribute 获取Java属性作为XML 属性,并在属性上使用@XmlElement 注解来检索XML 子标签。
档案:公司。Java
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Bean for XML Mapping
package com.geeksforgeeks.bean;
// Importing required classes
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAttribute;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
// Annotation
@XmlRootElement(name = "company-info",
namespace = "com.geeksforgeeks")
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.NONE)
// Class
public class Company {
// Class data members
@XmlAttribute(name = "id") private Integer id;
@XmlElement(name = "company-name")
private String companyName;
@XmlElement(name = "ceo-name") private String ceoName;
@XmlElement(name = "no-emp") private Integer noEmp;
// Getters and setters
public Integer getId() { return id; }
public void setId(Integer id)
{
// this keyword refers to current itself
this.id = id;
}
// Getter and Setter
public String getCompanyName() { return companyName; }
public void setCompanyName(String companyName)
{
this.companyName = companyName;
}
// Getter and Setter
public String getCeoName() { return ceoName; }
public void setCeoName(String ceoName)
{
this.ceoName = ceoName;
}
// Getter and Setter
public Integer getNoEmp() { return noEmp; }
public void setNoEmp(Integer noEmp)
{
this.noEmp = noEmp;
}
}
为 Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller 定义方法
第 4 步:找到一个实用方法,我们在其中调用 Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller。
文件:处理器。Java
Java
// Java Program Defining Method for
// Marshaller and Unmarshaller
package com.geeksforgeeks;
// Importing required classes
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamResult;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamSource;
import org.springframework.oxm.Marshaller;
import org.springframework.oxm.Unmarshaller;
// Class
public class Processor {
// Class data members
private Marshaller marshaller;
private Unmarshaller unmarshaller;
// Setter
public void setMarshaller(Marshaller marshaller) {
this.marshaller = marshaller;
}
public void setUnmarshaller(Unmarshaller unmarshaller) {
this.unmarshaller = unmarshaller;
}
// Converting Object to XML file
public void objectToXML(String fileName, Object graph) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(fileName);
marshaller.marshal(graph, new StreamResult(fos));
}
// finally block that will execute for sure
finally {
// Closing the connections
fos.close();
}
}
// Method
// To Convert XML to Java Object
public Object xmlToObject(String fileName) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
return unmarshaller.unmarshal(new StreamSource(fis));
}
// finally block that will execute for sure
finally {
// Closing the connections
fis.close();
}
}
}
第 5 步:运行应用程序
现在为了测试程序,我们可以创建一个 bean 对象,将其转换为 XML,然后将该 XML 转换回Java对象。
文件:运行应用程序。Java
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Application Class
package com.geeksforgeeks;
// Importing required classes
import com.geeksforgeeks.bean.Company;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
// Application/Main Class
public class RunApplication {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Try block to check for exceptions
try (AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx
= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext()) {
ctx.register(AppConfig.class);
ctx.refresh();
Processor processor
= ctx.getBean(Processor.class);
// Perform Marshaling
Company company = new Company();
company.setId(1000);
company.setCompanyName("XYZ");
company.setCeoName("ABCD");
company.setNoEmp(100);
processor.objectToXML("country.xml", company);
// Display message only
System.out.println("Marshaling performed");
// Perform UnMarshaling
company = (Company)processor.xmlToObject(
"country.xml");
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"After UnMarshaling Data is: id:"
+ company.getId() + ", CountryName:"
+ company.getCompanyName());
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (BeansException | IllegalStateException e) {
// Display exceptions along with line number
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
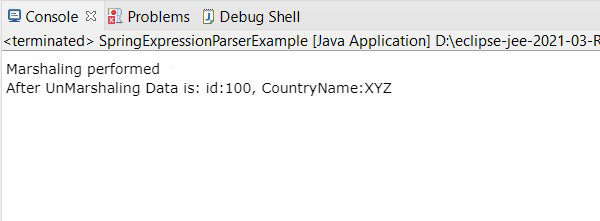
输出: Java对象转XML如下:
XYZ
ABCD
100
输出: XML 到Java对象如下: