SQLAlchemy Core – 执行表达式
在本文中,我们将了解如何使用Python执行 SQLAlchemy 核心表达式。
创建演示表:
从 SQLAlchemy 包中导入必要的函数。使用 create_engine()函数与 PostgreSQL 数据库建立连接,如下所示,创建一个名为 books 的表,其中包含 book_id 和 book_price 列。如图所示,使用 insert() 和 values()函数将记录插入表中。
Python3
# import necessary packages
import sqlalchemy
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, MetaData,
Table, Column, Numeric,insert, Integer,
VARCHAR, update, text, delete
from sqlalchemy.engine import result
# establish connections
engine = create_engine(
"database+dialect://username:password@hostname:port/database_name")
# initialize the Metadata Object
meta = MetaData(bind=engine)
MetaData.reflect(meta)
# create a table schema
books = Table(
'books', meta,
Column('book_id', Integer, primary_key=True),
Column('book_price', Numeric),
Column('genre', VARCHAR),
Column('book_name', VARCHAR)
)
meta.create_all(engine)
# insert records into the table
statement1 = books.insert().values(book_id=1,
book_price=12.2,
genre='fiction',
book_name='Old age')
statement2 = books.insert().values(book_id=2,
book_price=13.2,
genre='non-fiction',
book_name='Saturn rings')
statement3 = books.insert().values(book_id=3,
book_price=121.6,
genre='fiction',
book_name='Supernova')
statement4 = books.insert().values(book_id=4,
book_price=100,
genre='non-fiction',
book_name='History of the world')
statement5 = books.insert().values(book_id=5,
book_price=1112.2,
genre='fiction',
book_name='Sun city')
# execute the insert records statement
engine.execute(statement1)
engine.execute(statement2)
engine.execute(statement3)
engine.execute(statement4)
engine.execute(statement5)Python3
# write the SQL query inside the text() block
sql = text('SELECT * from BOOKS WHERE BOOKS.book_price > 100')
results = engine.execute(sql)
# Fetch all the records
result = engine.execute(sql).fetchall()
# View the records
for record in result:
print("\n", record)Python3
# write the SQL query inside the text() block
sql = text("SELECT * from BOOKS WHERE BOOKS.book_price/10 =10")
# Fetch all the records
result = engine.execute(sql).fetchall()
# View the records
for record in result:
print("\n", record)Python3
# Get the `books` table from the Metadata object
BOOKS = meta.tables['books']
from sqlalchemy import insert
# write the insert statement
stmt1 = insert(BOOKS).values(book_id=6,
book_price=400,
genre="fiction",
book_name="yoga is science")
stmt2 = insert(BOOKS).values(book_id=7,
book_price=800,
genre="non-fiction",
book_name="alchemy tutorials")
# execute
engine.execute(stmt1)
engine.execute(stmt2)
# write the SQL query to check
# whether the records are inserted
sql = text("SELECT * FROM BOOKS ")
results = engine.execute(sql)
# View the records
for record in results:
print("\n", record)Python3
# Get the `books` table from the Metadata object
BOOKS = meta.tables['books']
# update
stmt = BOOKS.update().where(BOOKS.c.genre == 'non-fiction'
).values(genre='sci-fi')
engine.execute(stmt)
# write the SQL query inside the
# text() block to fetch all records
sql = text("SELECT * from BOOKS")
# Fetch all the records
result = engine.execute(sql).fetchall()
# View the records
for record in result:
print("\n", record)输出:

样品表
查询以在 SQLAlchemy Core 中执行表达式
在这篇文章中,我们可以讨论 如何使用执行函数来执行SQLAlchemy 核心表达式和常规 SQL 查询。
示例 1:
SQLAlchemy 提供了一个名为 text() 的函数。我们可以在用“”括起来的文本函数中编写任何常规的 SQL 查询。现在,将此 SQL 查询传递给执行函数会将此查询转换为 SQLAlchemy 兼容格式并返回结果。
from sqlalchemy import text
text("YOUR SQL QUERY")将 SQL 查询传递给 execute()函数并使用 fetchall()函数获取所有结果。使用 for 循环遍历结果。下面代码中显示的 SQLAlchemy 查询选择了书价大于 Rs 的所有行。 100。
Python3
# write the SQL query inside the text() block
sql = text('SELECT * from BOOKS WHERE BOOKS.book_price > 100')
results = engine.execute(sql)
# Fetch all the records
result = engine.execute(sql).fetchall()
# View the records
for record in result:
print("\n", record)
输出:
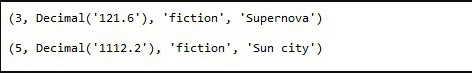
图书查询的输出
示例 2:
下面的查询返回的 book_price 完全等于可被 10 整除
Python3
# write the SQL query inside the text() block
sql = text("SELECT * from BOOKS WHERE BOOKS.book_price/10 =10")
# Fetch all the records
result = engine.execute(sql).fetchall()
# View the records
for record in result:
print("\n", record)
输出:
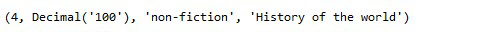
book_price 的输出完全等于可被 10 整除
示例 3:
下面的 SQL 表达式将使用 SQLAlchemy 核心在创建的表中插入额外的记录。
from sqlalchemy import insert
insert(table_name).values(column_name="value")从连接到数据库时初始化的元数据对象获取书籍表。将插入查询传递给 execute()函数并使用 fetchall()函数获取所有结果。使用 for 循环遍历结果。
下面代码中显示的 SQLAlchemy 查询使用 SQLAlchemy 核心在创建的表中插入附加记录。然后,我们可以编写一个常规的 SQL 查询并使用 fetchall() 打印结果来检查表是否正确更新。
Python3
# Get the `books` table from the Metadata object
BOOKS = meta.tables['books']
from sqlalchemy import insert
# write the insert statement
stmt1 = insert(BOOKS).values(book_id=6,
book_price=400,
genre="fiction",
book_name="yoga is science")
stmt2 = insert(BOOKS).values(book_id=7,
book_price=800,
genre="non-fiction",
book_name="alchemy tutorials")
# execute
engine.execute(stmt1)
engine.execute(stmt2)
# write the SQL query to check
# whether the records are inserted
sql = text("SELECT * FROM BOOKS ")
results = engine.execute(sql)
# View the records
for record in results:
print("\n", record)
输出:

插入附加记录的输出
示例 4:
让我们看另一个与更新查询相关的示例。
Tablename.update().where(Tablename.c.column_name == ‘value’).values(column_name = ‘value’)
从连接到数据库时初始化的元数据对象获取书籍表。将删除查询传递给 execute()函数并使用 fetchall()函数获取所有结果。使用 for 循环遍历结果。
下面代码中显示的 SQLAlchemy 查询将类型“非小说”更新为“科幻”,这将有效地一次更新多行。然后,我们可以编写一个常规的 SQL 查询并使用 fetchall() 打印结果来检查表是否正确更新。
Python3
# Get the `books` table from the Metadata object
BOOKS = meta.tables['books']
# update
stmt = BOOKS.update().where(BOOKS.c.genre == 'non-fiction'
).values(genre='sci-fi')
engine.execute(stmt)
# write the SQL query inside the
# text() block to fetch all records
sql = text("SELECT * from BOOKS")
# Fetch all the records
result = engine.execute(sql).fetchall()
# View the records
for record in result:
print("\n", record)
输出:

更新查询的输出