给定大小为n的排序数组arr []和要在其中搜索的元素x。如果x存在于数组中,则返回x的索引,否则返回-1。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {2, 3, 4, 10, 40}, x = 10
Output: 3
Element x is present at index 3.
Input: arr[] = {2, 3, 4, 10, 40}, x = 11
Output: -1
Element x is not present.斐波那契搜索是一种基于比较的技术,使用斐波那契数字来搜索排序数组中的元素。
与二分搜索的相似之处:
- 适用于排序数组
- 分而治之算法。
- 具有Log n时间复杂度。
二进制搜索的区别:
- 斐波那契搜索将给定数组分为不相等的部分
- 二进制搜索使用除法运算符对范围进行除法。斐波那契搜索不使用/,而是使用+和-。在某些CPU上,除法运算符可能会很昂贵。
- Fibonacci Search在后续步骤中检查相对较近的元素。因此,当输入数组很大而无法容纳在CPU缓存或RAM中时,斐波那契搜索将很有用。
背景:
斐波那契数递归定义为F(n)= F(n-1)+ F(n-2),F(0)= 0,F(1)=1。前几个斐波那契数为0、1、1、1。 2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89,144,…
观察结果:
下面的观察用于范围消除,因此用于O(log(n))复杂度。
F(n - 2) ≈ (1/3)*F(n) and
F(n - 1) ≈ (2/3)*F(n).算法:
令搜索到的元素为x。
这个想法是首先找到大于或等于给定数组长度的最小斐波那契数。令找到的斐波那契数为fib(第m个斐波那契数)。我们使用第(m-2)个斐波那契数作为索引(如果它是有效索引)。令第(m-2)个斐波那契数为i,我们将arr [i]与x进行比较,如果x相同,则返回i。否则,如果x更大,则在i之后重现子数组,否则在i之前重现子数组。
下面是完整的算法
令arr [0..n-1]为输入数组,要搜索的元素为x。
- 查找大于或等于n的最小斐波那契数。将此数字设为fibM [第m个斐波那契数]。设其前面的两个斐波那契数为fibMm1 [第(m-1)个斐波那契数]和fibMm2 [第(m-2)个斐波那契数]。
- 虽然数组具有要检查的元素:
- 将x与fibMm2覆盖范围的最后一个元素进行比较
- 如果x匹配,则返回索引
- 否则,如果x小于元素,则将三个Fibonacci变量向下移动两个Fibonacci,表示消除了剩余数组的大约后三分之二。
- 如果x大于元素,则将三个斐波那契变量向下移动一个斐波那契。将偏移量重置为索引。这些共同表明消除了其余阵列的大约三分之一。
- 由于可能还剩下一个要比较的元素,因此请检查fibMm1是否为1。如果是,则将x与该剩余元素进行比较。如果匹配,则返回索引。
C
// C program for Fibonacci Search
#include
// Utility function to find minimum of two elements
int min(int x, int y) { return (x <= y) ? x : y; }
/* Returns index of x if present, else returns -1 */
int fibMonaccianSearch(int arr[], int x, int n)
{
/* Initialize fibonacci numbers */
int fibMMm2 = 0; // (m-2)'th Fibonacci No.
int fibMMm1 = 1; // (m-1)'th Fibonacci No.
int fibM = fibMMm2 + fibMMm1; // m'th Fibonacci
/* fibM is going to store the smallest Fibonacci
Number greater than or equal to n */
while (fibM < n) {
fibMMm2 = fibMMm1;
fibMMm1 = fibM;
fibM = fibMMm2 + fibMMm1;
}
// Marks the eliminated range from front
int offset = -1;
/* while there are elements to be inspected. Note that
we compare arr[fibMm2] with x. When fibM becomes 1,
fibMm2 becomes 0 */
while (fibM > 1) {
// Check if fibMm2 is a valid location
int i = min(offset + fibMMm2, n - 1);
/* If x is greater than the value at index fibMm2,
cut the subarray array from offset to i */
if (arr[i] < x) {
fibM = fibMMm1;
fibMMm1 = fibMMm2;
fibMMm2 = fibM - fibMMm1;
offset = i;
}
/* If x is greater than the value at index fibMm2,
cut the subarray after i+1 */
else if (arr[i] > x) {
fibM = fibMMm2;
fibMMm1 = fibMMm1 - fibMMm2;
fibMMm2 = fibM - fibMMm1;
}
/* element found. return index */
else
return i;
}
/* comparing the last element with x */
if (fibMMm1 && arr[offset + 1] == x)
return offset + 1;
/*element not found. return -1 */
return -1;
}
/* driver function */
int main(void)
{
int arr[]
= { 10, 22, 35, 40, 45, 50, 80, 82, 85, 90, 100,235};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 235;
int ind = fibMonaccianSearch(arr, x, n);
if(ind>=0)
printf("Found at index: %d",ind);
else
printf("%d isn't present in the array",x);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for Fibonacci Search
import java.util.*;
class Fibonacci {
// Utility function to find minimum
// of two elements
public static int min(int x, int y)
{
return (x <= y) ? x : y;
}
/* Returns index of x if present, else returns -1 */
public static int fibMonaccianSearch(int arr[], int x,
int n)
{
/* Initialize fibonacci numbers */
int fibMMm2 = 0; // (m-2)'th Fibonacci No.
int fibMMm1 = 1; // (m-1)'th Fibonacci No.
int fibM = fibMMm2 + fibMMm1; // m'th Fibonacci
/* fibM is going to store the smallest
Fibonacci Number greater than or equal to n */
while (fibM < n) {
fibMMm2 = fibMMm1;
fibMMm1 = fibM;
fibM = fibMMm2 + fibMMm1;
}
// Marks the eliminated range from front
int offset = -1;
/* while there are elements to be inspected.
Note that we compare arr[fibMm2] with x.
When fibM becomes 1, fibMm2 becomes 0 */
while (fibM > 1) {
// Check if fibMm2 is a valid location
int i = min(offset + fibMMm2, n - 1);
/* If x is greater than the value at
index fibMm2, cut the subarray array
from offset to i */
if (arr[i] < x) {
fibM = fibMMm1;
fibMMm1 = fibMMm2;
fibMMm2 = fibM - fibMMm1;
offset = i;
}
/* If x is less than the value at index
fibMm2, cut the subarray after i+1 */
else if (arr[i] > x) {
fibM = fibMMm2;
fibMMm1 = fibMMm1 - fibMMm2;
fibMMm2 = fibM - fibMMm1;
}
/* element found. return index */
else
return i;
}
/* comparing the last element with x */
if (fibMMm1 == 1 && arr[n-1] == x)
return n-1;
/*element not found. return -1 */
return -1;
}
// driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 10, 22, 35, 40, 45, 50,
80, 82, 85, 90, 100,235};
int n = 12;
int x = 235;
int ind = fibMonaccianSearch(arr, x, n);
if(ind>=0)
System.out.print("Found at index: "
+ind);
else
System.out.print(x+" isn't present in the array");
}
}
// This code is contributed by rishabh_jainPython3
# Python3 program for Fibonacci search.
from bisect import bisect_left
# Returns index of x if present, else
# returns -1
def fibMonaccianSearch(arr, x, n):
# Initialize fibonacci numbers
fibMMm2 = 0 # (m-2)'th Fibonacci No.
fibMMm1 = 1 # (m-1)'th Fibonacci No.
fibM = fibMMm2 + fibMMm1 # m'th Fibonacci
# fibM is going to store the smallest
# Fibonacci Number greater than or equal to n
while (fibM < n):
fibMMm2 = fibMMm1
fibMMm1 = fibM
fibM = fibMMm2 + fibMMm1
# Marks the eliminated range from front
offset = -1
# while there are elements to be inspected.
# Note that we compare arr[fibMm2] with x.
# When fibM becomes 1, fibMm2 becomes 0
while (fibM > 1):
# Check if fibMm2 is a valid location
i = min(offset+fibMMm2, n-1)
# If x is greater than the value at
# index fibMm2, cut the subarray array
# from offset to i
if (arr[i] < x):
fibM = fibMMm1
fibMMm1 = fibMMm2
fibMMm2 = fibM - fibMMm1
offset = i
# If x is less than the value at
# index fibMm2, cut the subarray
# after i+1
elif (arr[i] > x):
fibM = fibMMm2
fibMMm1 = fibMMm1 - fibMMm2
fibMMm2 = fibM - fibMMm1
# element found. return index
else:
return i
# comparing the last element with x */
if(fibMMm1 and arr[n-1] == x):
return n-1
# element not found. return -1
return -1
# Driver Code
arr = [10, 22, 35, 40, 45, 50,
80, 82, 85, 90, 100,235]
n = len(arr)
x = 235
ind = fibMonaccianSearch(arr, x, n)
if ind>=0:
print("Found at index:",ind)
else:
print(x,"isn't present in the array");
# This code is contributed by rishabh_jainC#
// C# program for Fibonacci Search
using System;
class GFG {
// Utility function to find minimum
// of two elements
public static int min(int x, int y)
{
return (x <= y) ? x : y;
}
/* Returns index of x if present, else returns -1 */
public static int fibMonaccianSearch(int[] arr, int x,
int n)
{
/* Initialize fibonacci numbers */
int fibMMm2 = 0; // (m-2)'th Fibonacci No.
int fibMMm1 = 1; // (m-1)'th Fibonacci No.
int fibM = fibMMm2 + fibMMm1; // m'th Fibonacci
/* fibM is going to store the smallest
Fibonacci Number greater than or equal to n */
while (fibM < n) {
fibMMm2 = fibMMm1;
fibMMm1 = fibM;
fibM = fibMMm2 + fibMMm1;
}
// Marks the eliminated range from front
int offset = -1;
/* while there are elements to be inspected.
Note that we compare arr[fibMm2] with x.
When fibM becomes 1, fibMm2 becomes 0 */
while (fibM > 1) {
// Check if fibMm2 is a valid location
int i = min(offset + fibMMm2, n - 1);
/* If x is greater than the value at
index fibMm2, cut the subarray array
from offset to i */
if (arr[i] < x) {
fibM = fibMMm1;
fibMMm1 = fibMMm2;
fibMMm2 = fibM - fibMMm1;
offset = i;
}
/* If x is less than the value at index
fibMm2, cut the subarray after i+1 */
else if (arr[i] > x) {
fibM = fibMMm2;
fibMMm1 = fibMMm1 - fibMMm2;
fibMMm2 = fibM - fibMMm1;
}
/* element found. return index */
else
return i;
}
/* comparing the last element with x */
if (fibMMm1 == 1 && arr[n-1] == x)
return n-1;
/*element not found. return -1 */
return -1;
}
// driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 10, 22, 35, 40, 45, 50,
80, 82, 85, 90, 100,235 };
int n = 12;
int x = 235;
int ind = fibMonaccianSearch(arr, x, n);
if(ind>=0)
Console.Write("Found at index: "+ind);
else
Console.Write(x+" isn't present in the array");
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.PHP
1)
{
// Check if fibMm2 is a valid location
$i = min($offset+$fibMMm2, $n-1);
/* If x is greater than the value at index fibMm2,
cut the subarray array from offset to i */
if ($arr[$i] < $x)
{
$fibM = $fibMMm1;
$fibMMm1 = $fibMMm2;
$fibMMm2 = $fibM - $fibMMm1;
$offset = $i;
}
/* If x is less than the value at index fibMm2,
cut the subarray after i+1 */
else if ($arr[$i] > $x)
{
$fibM = $fibMMm2;
$fibMMm1 = $fibMMm1 - $fibMMm2;
$fibMMm2 = $fibM - $fibMMm1;
}
/* element found. return index */
else return $i;
}
/* comparing the last element with x */
if($fibMMm1 && $arr[$n-1] == $x)return $n-1;
/*element not found. return -1 */
return -1;
}
/* driver code */
$arr = array(10, 22, 35, 40, 45, 50, 80, 82,85, 90, 100,235);
$n = count($arr);
$x = 235;
$ind = fibMonaccianSearch($arr, $x, $n);
if($ind>=0)
printf("Found at index: ".$ind);
else
printf($x." isn't present in the array");
// This code is contributed by mits
?>Javascript
Found at index: 11插图:
让我们通过以下示例了解算法:
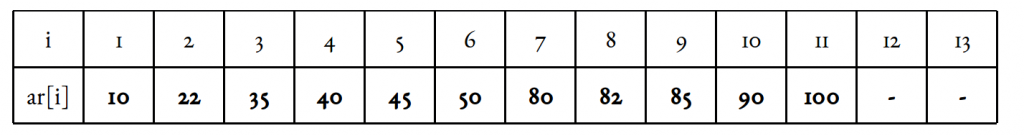
插图假设:基于1的索引。目标元素x为85。数组n的长度= 11。
大于或等于11的最小斐波那契数为13。根据我们的说明,fibMm2 = 5,fibMm1 = 8,fibM = 13。
另一个实现细节是偏移变量(零初始化)。它标志着从前面开始已消除的范围。我们会不时更新。
现在,由于偏移值是一个索引,并且已删除了包括它及其以下的所有索引,因此仅在其上添加内容是有意义的。由于fibMm2标记了数组的大约三分之一以及它所标记的索引肯定是有效的,因此我们可以将fibMm2添加到offset并检查索引为i = min(offset + fibMm2,n)的元素。
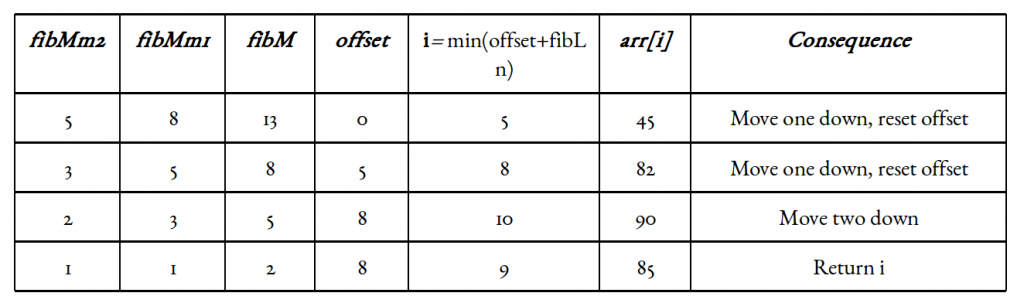
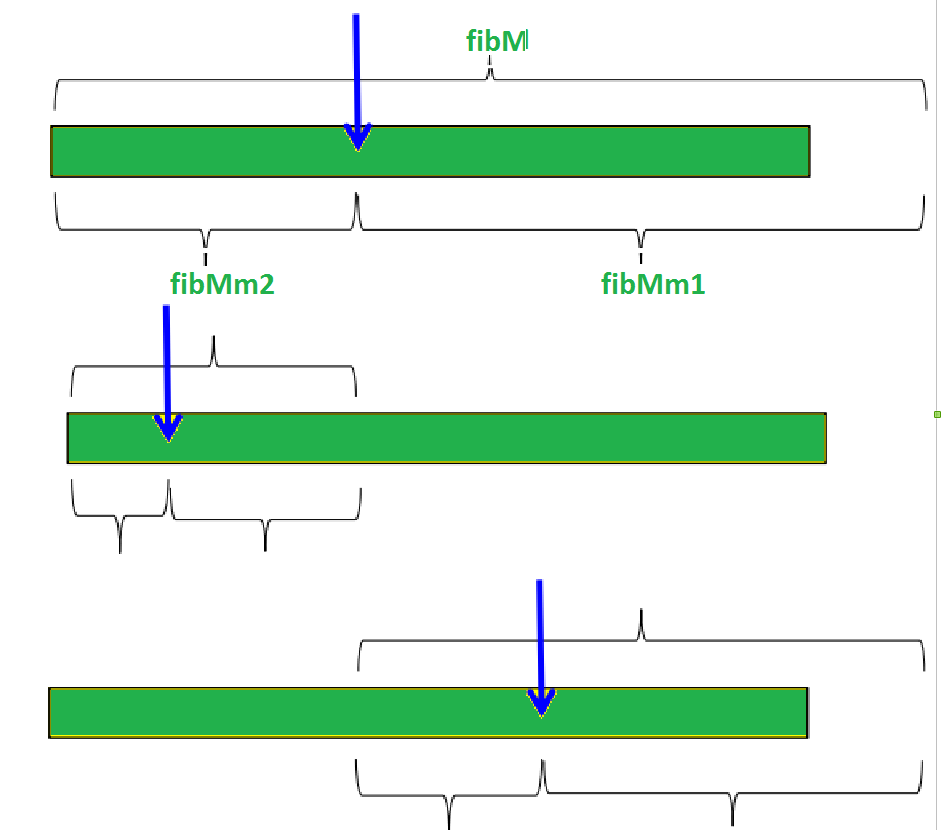
可视化:
时间复杂度分析:
当我们将目标放在数组的较大(2/3)分数中时,就会发生最坏的情况,因为我们继续找到它。换句话说,我们每次都消除了数组的较小部分(1/3)。我们一次调用n,然后调用(2/3)n,然后调用(4/9)n,此后。
考虑到:
