Fibonacci编码使用数字的Fibonacci表示形式将整数编码为二进制数。该想法基于Zeckendorf定理,该定理指出,每个正整数可以唯一地写为不同的非相邻斐波那契数之和(0、1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34、55, 89,141,……..)。
特定整数的斐波那契代码字正好是整数的Zeckendorf表示形式,其数字顺序相反,并且在末尾附加了附加的“ 1”。附加的1表示代码的末尾(请注意,根据Zeckendorf定理,该代码永远不会包含两个连续的1。表示形式使用的是从1(第二个Fibonacci数)开始的Fibonacci数。因此,所用的Fibonacci数为1、2 ,3、5、8、13、21、34、55、89、141,……。
给定数字n,请打印其斐波那契代码。
例子:
Input: n = 1
Output: 11
1 is first Fibonacci number in this representation
and an extra 1 is appended at the end.
Input: n = 11
Output: 001011
11 is sum of 8 and 3. The last 1 represents extra 1
that is always added. A 1 before it represents 8. The
third 1 (from beginning) represents 3.强烈建议您最小化浏览器,然后自己尝试。
以下算法将整数作为输入,并生成一个存储斐波那契编码的字符串。
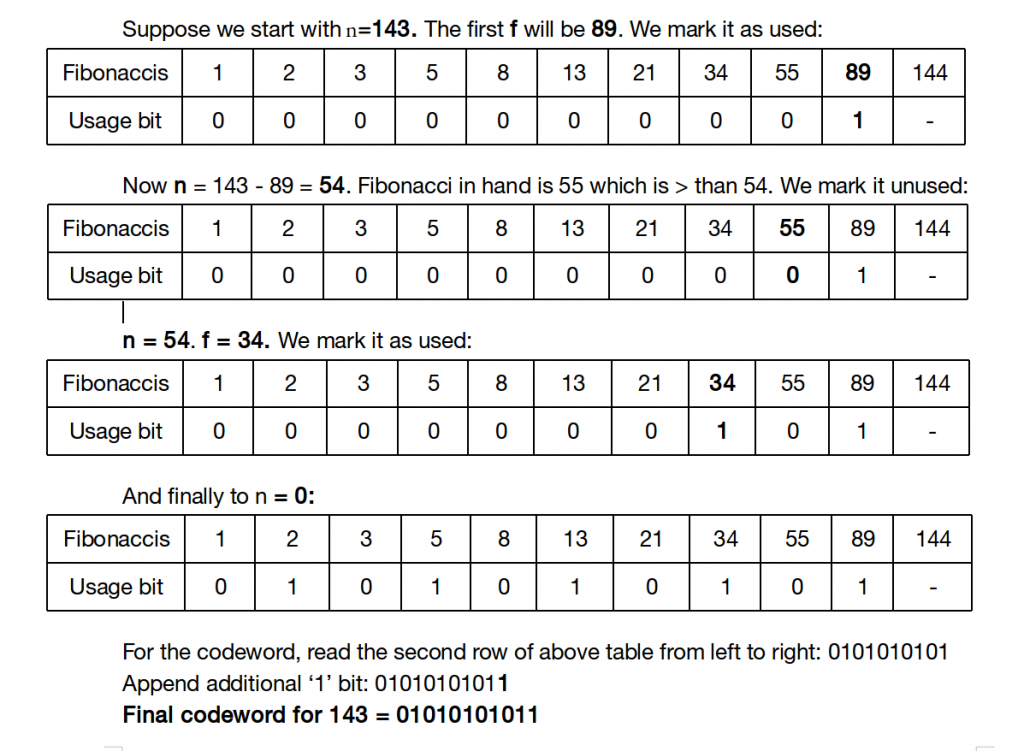
找到小于或等于n的最大斐波那契数f。说这是斐波那契数列中的第i个数字。 n的代码字长度将为i + 3个字符(一个用于末尾附加1个字符,一个因为i是索引,一个用于“ \ 0”字符)。假设斐波那契数列已存储:
- 令f为小于或等于n的最大斐波那契数,在二进制字符串中以’1’开头。这表示在表示n时使用f。从n减去f:n = n – f
- 否则,如果f大于n,则在二进制字符串加’0’。
- 移至正好小于f的斐波那契数。
- 重复直到剩余为零(n = 0)
- 在二进制字符串附加一个附加的“ 1”。我们获得一种编码,使得两个连续的1表示数字的结尾(以及下一个的开头)。
下面是上述算法的实现。
C
/* C program for Fibonacci Encoding of a positive integer n */
#include
#include
// To limit on the largest Fibonacci number to be used
#define N 30
/* Array to store fibonacci numbers. fib[i] is going
to store (i+2)'th Fibonacci number*/
int fib[N];
// Stores values in fib and returns index of the largest
// fibonacci number smaller than n.
int largestFiboLessOrEqual(int n)
{
fib[0] = 1; // Fib[0] stores 2nd Fibonacci No.
fib[1] = 2; // Fib[1] stores 3rd Fibonacci No.
// Keep Generating remaining numbers while previously
// generated number is smaller
int i;
for (i=2; fib[i-1]<=n; i++)
fib[i] = fib[i-1] + fib[i-2];
// Return index of the largest fibonacci number
// smaller than or equal to n. Note that the above
// loop stopped when fib[i-1] became larger.
return (i-2);
}
/* Returns pointer to the char string which corresponds to
code for n */
char* fibonacciEncoding(int n)
{
int index = largestFiboLessOrEqual(n);
//allocate memory for codeword
char *codeword = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*(index+3));
// index of the largest Fibonacci f <= n
int i = index;
while (n)
{
// Mark usage of Fibonacci f (1 bit)
codeword[i] = '1';
// Subtract f from n
n = n - fib[i];
// Move to Fibonacci just smaller than f
i = i - 1;
// Mark all Fibonacci > n as not used (0 bit),
// progress backwards
while (i>=0 && fib[i]>n)
{
codeword[i] = '0';
i = i - 1;
}
}
//additional '1' bit
codeword[index+1] = '1';
codeword[index+2] = '\0';
//return pointer to codeword
return codeword;
}
/* driver function */
int main()
{
int n = 143;
printf("Fibonacci code word for %d is %s\n", n, fibonacciEncoding(n));
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for Fibonacci Encoding
// of a positive integer n
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// To limit on the largest Fibonacci
// number to be used
public static int N = 30;
// Array to store fibonacci numbers.
// fib[i] is going to store (i+2)'th
// Fibonacci number
public static int[] fib = new int[N];
// Stores values in fib and returns index of
// the largest fibonacci number smaller than n.
public static int largestFiboLessOrEqual(int n)
{
// Fib[0] stores 2nd Fibonacci No.
fib[0] = 1;
// Fib[1] stores 3rd Fibonacci No.
fib[1] = 2;
// Keep Generating remaining numbers while
// previously generated number is smaller
int i;
for(i = 2; fib[i - 1] <= n; i++)
{
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];
}
// Return index of the largest fibonacci
// number smaller than or equal to n.
// Note that the above loop stopped when
// fib[i-1] became larger.
return(i - 2);
}
// Returns pointer to the char string which
// corresponds to code for n
public static String fibonacciEncoding(int n)
{
int index = largestFiboLessOrEqual(n);
// Allocate memory for codeword
char[] codeword = new char[index + 3];
// Index of the largest Fibonacci f <= n
int i = index;
while (n > 0)
{
// Mark usage of Fibonacci f(1 bit)
codeword[i] = '1';
// Subtract f from n
n = n - fib[i];
// Move to Fibonacci just smaller than f
i = i - 1;
// Mark all Fibonacci > n as not used
// (0 bit), progress backwards
while (i >= 0 && fib[i] > n)
{
codeword[i] = '0';
i = i - 1;
}
}
// Additional '1' bit
codeword[index + 1] = '1';
codeword[index + 2] = '\0';
String string = new String(codeword);
// Return pointer to codeword
return string;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 143;
System.out.println("Fibonacci code word for " +
n + " is " + fibonacciEncoding(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155Python3
# Python3 program for Fibonacci Encoding
# of a positive integer n
# To limit on the largest
# Fibonacci number to be used
N = 30
# Array to store fibonacci numbers.
# fib[i] is going to store
# (i+2)'th Fibonacci number
fib = [0 for i in range(N)]
# Stores values in fib and returns index of
# the largest fibonacci number smaller than n.
def largestFiboLessOrEqual(n):
fib[0] = 1 # Fib[0] stores 2nd Fibonacci No.
fib[1] = 2 # Fib[1] stores 3rd Fibonacci No.
# Keep Generating remaining numbers while
# previously generated number is smaller
i = 2
while fib[i - 1] <= n:
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2]
i += 1
# Return index of the largest fibonacci number
# smaller than or equal to n. Note that the above
# loop stopped when fib[i-1] became larger.
return (i - 2)
# Returns pointer to the char string which
# corresponds to code for n
def fibonacciEncoding(n):
index = largestFiboLessOrEqual(n)
# allocate memory for codeword
codeword = ['a' for i in range(index + 2)]
# index of the largest Fibonacci f <= n
i = index
while (n):
# Mark usage of Fibonacci f (1 bit)
codeword[i] = '1'
# Subtract f from n
n = n - fib[i]
# Move to Fibonacci just smaller than f
i = i - 1
# Mark all Fibonacci > n as not used (0 bit),
# progress backwards
while (i >= 0 and fib[i] > n):
codeword[i] = '0'
i = i - 1
# additional '1' bit
codeword[index + 1] = '1'
# return pointer to codeword
return "".join(codeword)
# Driver Code
n = 143
print("Fibonacci code word for", n,
"is", fibonacciEncoding(n))
# This code is contributed by Mohit KumarC#
// C# program for Fibonacci Encoding
// of a positive integer n
using System;
class GFG{
// To limit on the largest Fibonacci
// number to be used
public static int N = 30;
// Array to store fibonacci numbers.
// fib[i] is going to store (i+2)'th
// Fibonacci number
public static int[] fib = new int[N];
// Stores values in fib and returns index of
// the largest fibonacci number smaller than n.
public static int largestFiboLessOrEqual(int n)
{
// Fib[0] stores 2nd Fibonacci No.
fib[0] = 1;
// Fib[1] stores 3rd Fibonacci No.
fib[1] = 2;
// Keep Generating remaining numbers while
// previously generated number is smaller
int i;
for(i = 2; fib[i - 1] <= n; i++)
{
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];
}
// Return index of the largest fibonacci
// number smaller than or equal to n.
// Note that the above loop stopped when
// fib[i-1] became larger.
return(i - 2);
}
// Returns pointer to the char string which
// corresponds to code for n
public static String fibonacciEncoding(int n)
{
int index = largestFiboLessOrEqual(n);
// Allocate memory for codeword
char[] codeword = new char[index + 3];
// Index of the largest Fibonacci f <= n
int i = index;
while (n > 0)
{
// Mark usage of Fibonacci f(1 bit)
codeword[i] = '1';
// Subtract f from n
n = n - fib[i];
// Move to Fibonacci just smaller than f
i = i - 1;
// Mark all Fibonacci > n as not used
// (0 bit), progress backwards
while (i >= 0 && fib[i] > n)
{
codeword[i] = '0';
i = i - 1;
}
}
// Additional '1' bit
codeword[index + 1] = '1';
codeword[index + 2] = '\0';
string str = new string(codeword);
// Return pointer to codeword
return str;
}
// Driver code
static public void Main()
{
int n = 143;
Console.WriteLine("Fibonacci code word for " +
n + " is " + fibonacciEncoding(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127输出:
Fibonacci code word for 143 is 01010101011插图
应用领域:
数据处理和压缩–表示数据(可以是文本,图像,视频等),其方式是存储或传输数据所需的空间小于输入数据的大小。统计方法使用可变长度代码,将较短的代码分配给出现概率较高的符号或符号组。如果要在嘈杂的通信信道上使用这些代码,则它们对于位插入,删除和位翻转的适应性非常重要。
在此处阅读有关该应用程序的更多信息。