我们得到了一个由连接在一起的六边形构成的无限二维平面。我们可以将该平面可视化为蜂窝。元素X存在于单元格/六边形之一上。
我们给了N步,任务是计算可能的六边形路径的数量,其中元素X必须执行N步走,然后返回到原来的六边形,其中![]()
例子:
Input : 1
Output : Number of walks possible is/are 0
Explanation :
0 because using just one step we can move to
any of the adjacent cells but we cannot trace
back to the original hexagon.
Input : 2
Output : Number of walks possible is/are 6
Input : 4
Output : Number of walks possible is/are 90
方法 :
- 六边形遍历可以定义为遍历相邻六边形并返回到原始单元格。我们知道一个六边形包含六个边的事实,即一个六边形被六个六边形包围。现在,我们必须计算采取N步并回到原始六边形的方式。
- 现在,让我们假设原始六边形(最初存在元素X)为原点。我们需要采取所有可能的方法来执行(Nk)个步骤,以便我们有一些步骤可以追溯到原始的六边形。我们可以从下面的图片中直观地看到这个六角形及其相关的坐标系。
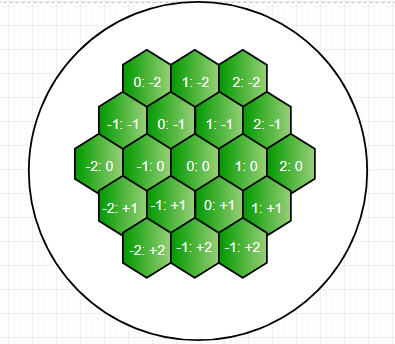
- 现在,让我们假设元素X出现在给定图片的0:0处。因此,我们可以从六边形沿六个可能的方向行进。现在,使用上面的说明,我们记住所有可能的移动,以便我们追溯到原始的0:0索引。为了记忆,我们使用3D数组,并针对给定数量的步骤对答案进行预处理,然后进行相应的查询。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of counting
// number of possible hexagonal walks
#include
using namespace std;
int depth = 16;
int ways[16][16][16];
int stepNum;
void preprocess(int list[])
{
// We initialize our origin with 1
ways[0][8][8] = 1;
// For each N = 1 to 14, we traverse in all possible
// direction. Using this 3D array we calculate the
// number of ways at each step and the total ways
// for a given step shall be found at
// ways[step number][8][8] because all the steps
// after that will be used to trace back to the
// original point index 0:0 according to the image.
for (int N = 1; N <= 14; N++)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= depth; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= depth; j++)
{
ways[N][i][j] = ways[N - 1][i][j + 1]
+ ways[N - 1][i][j - 1]
+ ways[N - 1][i + 1][j]
+ ways[N - 1][i - 1][j]
+ ways[N - 1][i + 1][j - 1]
+ ways[N - 1][i - 1][j + 1];
}
}
// This array stores the number of ways
// possible for a given step
list[N] = ways[N][8][8];
}
}
// Driver function
int main()
{
int list[15];
// Preprocessing all possible ways
preprocess(list);
int steps = 4;
cout << "Number of walks possible is/are "
<< list[steps] << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of counting
// number of possible hexagonal walks
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int depth = 14;
static int ways[][][] = new int[16][16][16];
static int stepNum;
static void preprocess(int list[])
{
// We initialize our origin with 1
ways[0][8][8] = 1;
// For each N = 1 to 14, we traverse in
// all possible direction. Using this 3D
// array we calculate the number of ways
// at each step and the total ways for a
// given step shall be found at ways[step
// number][8][8] because all the steps
// after that will be used to trace back
// to the original point index 0:0
// according to the image.
for (int N = 1; N <= 14; N++)
{
for (int i = 1; i < depth; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < depth; j++)
{
ways[N][i][j] =
ways[N - 1][i][j + 1]
+ ways[N - 1][i][j - 1]
+ ways[N - 1][i + 1][j]
+ ways[N - 1][i - 1][j]
+ ways[N - 1][i + 1][j - 1]
+ ways[N - 1][i - 1][j + 1];
}
}
// This array stores the number of
// ways possible for a given step
list[N] = ways[N][8][8];
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int list[] = new int[15];
// Preprocessing all possible ways
preprocess(list);
int steps = 4;
System.out.println( "Number of walks"
+ " possible is/are "+
list[steps] );
}
}Python3
# Python 3 implementation of counting
# number of possible hexagonal walks
depth = 16
ways = [[[0 for i in range(17)]
for i in range(17)]
for i in range(17)]
def preprocess(list, steps):
# We initialize our origin with 1
ways[0][8][8] = 1
# For each N = 1 to 14, we traverse in
# all possible direction. Using this 3D
# array we calculate the number of ways
# at each step and the total ways for a
# given step shall be found at ways[step
# number][8][8] because all the steps after
# that will be used to trace back to the
# original point index 0:0 according to the image.
for N in range(1, 16, 1):
for i in range(1, depth, 1):
for j in range(1, depth, 1):
ways[N][i][j] = (ways[N - 1][i][j + 1] +
ways[N - 1][i][j - 1] +
ways[N - 1][i + 1][j] +
ways[N - 1][i - 1][j] +
ways[N - 1][i + 1][j - 1] +
ways[N - 1][i - 1][j + 1])
# This array stores the number of ways
# possible for a given step
list[N] = ways[N][8][8]
print("Number of walks possible is/are",
list[steps])
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
list = [0 for i in range(16)]
steps = 4
# Preprocessing all possible ways
preprocess(list, steps)
# This code is contributed by
# Surendra_GangwarC#
// C# implementation of counting
// number of possible hexagonal walks
using System;
class GFG {
static int depth = 14;
static int [, ,]ways = new int[16,16,16];
// static int stepNum;
static void preprocess(int []list)
{
// We initialize our origin with 1
ways[0,8,8] = 1;
// For each N = 1 to 14, we traverse in
// all possible direction. Using this 3D
// array we calculate the number of ways
// at each step and the total ways for a
// given step shall be found at ways[step
// number][8][8] because all the steps
// after that will be used to trace back
// to the original point index 0:0
// according to the image.
for (int N = 1; N <= 14; N++)
{
for (int i = 1; i < depth; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < depth; j++)
{
ways[N,i,j] =
ways[N - 1,i,j + 1]
+ ways[N - 1,i,j - 1]
+ ways[N - 1,i + 1,j]
+ ways[N - 1,i - 1,j]
+ ways[N - 1,i + 1,j - 1]
+ ways[N - 1,i - 1,j + 1];
}
}
// This array stores the number of
// ways possible for a given step
list[N] = ways[N,8,8];
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void Main()
{
int []list = new int[15];
// Preprocessing all possible ways
preprocess(list);
int steps = 4;
Console.WriteLine( "Number of walks"
+ " possible is/are "+
list[steps] );
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.输出 :
Number of walks possible is/are 90
上面代码的时间复杂度是![]() 由于使用了3D阵列,因此空间复杂度也相似。
由于使用了3D阵列,因此空间复杂度也相似。