给定正整数的数组Arr和值X。任务是找到大于或等于X的值的数量。
但是,问题在于数组的值在每次操作后都会保持变化。有两种可能性:
- 如果选择了当前值,则数组中所有剩余的值将减少1 。
- 如果未选择当前值,则数组中所有剩余值将增加1 。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {10, 5, 5, 4, 9}, X = 10
Output: 2Explanation:
Arr = {10, 5, 5, 4, 9}, pos = 0
10 is picked
Arr = {10, 4, 4, 3, 8}, pos = 1
4 is not picked
Arr = {10, 4, 5, 4, 9}, pos = 2
5 is not picked
Arr = {10, 4, 5, 5, 10}, pos = 3
5 is not picked
Arr = {10, 4, 5, 5, 11}, pos = 4
11 is picked
Hence two elements are picked.
Input: arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}, X = 4
Output: 1
天真的方法:想法是遍历数组中的每个值,并检查第i个值是否大于,小于或等于所需值X。如果第i个值小于要求值则通过1别的增加从第(i + 1)个以结束阵列的值。如果第i个值大于或等于比所需值X,则通过1从减小值( I + 1)到第结束阵列。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to count number
// of values greater or equal to x
int increaseDecreaseValue(int arr[],
int x, int n)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
// Current value is less
// than required value
// then we need to increase
// the value from i + 1 to
// len(arr) by 1
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
// Current value is greater
// or equal to required
// value then we need to
// decrease the value from
// (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int x = 4;
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x, n);
cout << countValue;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to count number
// of values greater or equal to x
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int []arr, int x)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
// Current value is less
// than required value
// then we need to increase
// the value from i + 1 to
// len(arr) by 1
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
// Current value is greater
// or equal to required
// value then we need to
// decrease the value from
// (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 4;
int[] arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
System.out.println(countValue);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiPython3
# Python3 implementation
# of the approach
# Function to count number
# of values greater or equal to x
def increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x):
TotalValue = 0
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] < x:
# Current value is less
# than required value
# then we need to increase
# the value from i + 1 to
# len(arr) by 1
for j in range(i + 1, len(arr)):
arr[j] += 1
else:
# Current value is greater
# or equal to required
# value then we need to
# decrease the value from
# (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1
for j in range(i + 1, len(arr)):
if arr[j] == 0:
continue
arr[j] -= 1
return TotalValue
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = 4
arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
countValue =\
increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x)
print(countValue)C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to count number
// of values greater or equal to x
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int []arr, int x)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
// Current value is less
// than required value
// then we need to increase
// the value from i + 1 to
// len(arr) by 1
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.Length; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
// Current value is greater
// or equal to required
// value then we need to
// decrease the value from
// (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.Length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int x = 4;
int[] arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
Console.WriteLine(countValue);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to count number
// of values greater or equal to x
int increaseDecreaseValue(int arr[],
int x, int n)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
// Current value is less
// than required value
// then we need to increase
// the value from i + 1 to
// len(arr) by 1
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
// Current value is greater
// or equal to required
// value then we need to
// decrease the value from
// (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int x = 4;
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x, n);
cout << countValue;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
// Function to count number
// of students got selected
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int arr[], int x)
{
int currentStatus = 0;
int totalValue = 0;
int i;
int len = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < len ; i++ )
{
// Adding currentStatus to the
// value of that index to get
// the original value
// if it is less than X
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else
{
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int x = 4;
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
System.out.println(countValue);
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01Python3
# Python3 implementation
# of the approach
# Function to count number
# of students got selected
def increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x):
currentStatus = 0
totalValue = 0
for i in arr:
# Adding currentStatus to the
# value of that index to get
# the original value
# if it is less than X
if i + currentStatus < x:
currentStatus += 1
else:
currentStatus -= 1
totalValue += 1
return totalValue
# Drivers Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = 4
arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x)
print(countValue)C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to count number
// of students got selected
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int []arr,
int x)
{
int currentStatus = 0;
int totalValue = 0;
int i;
int len = arr.Length;
for (i = 0; i < len ; i++ )
{
// Adding currentStatus to the
// value of that index to get
// the original value
// if it is less than X
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else
{
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main ()
{
int x = 4;
int []arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
Console.Write(countValue);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ajit.输出:
1
ime复杂度: ![]()
高效方法:
- 这个问题可以进一步优化为
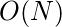 。
。 - 这里的主要思想是检查该索引值应更改多少。
- 这可以通过使用一个临时变量来完成,这里是currentStatus ,它将通过先前的决策保持对当前索引的净影响。
- 效果将添加到该索引的值,这将告诉我们数组的更新后的原始值。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to count number
// of values greater or equal to x
int increaseDecreaseValue(int arr[],
int x, int n)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
// Current value is less
// than required value
// then we need to increase
// the value from i + 1 to
// len(arr) by 1
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
// Current value is greater
// or equal to required
// value then we need to
// decrease the value from
// (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int x = 4;
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x, n);
cout << countValue;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
// Function to count number
// of students got selected
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int arr[], int x)
{
int currentStatus = 0;
int totalValue = 0;
int i;
int len = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < len ; i++ )
{
// Adding currentStatus to the
// value of that index to get
// the original value
// if it is less than X
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else
{
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int x = 4;
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
System.out.println(countValue);
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01
Python3
# Python3 implementation
# of the approach
# Function to count number
# of students got selected
def increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x):
currentStatus = 0
totalValue = 0
for i in arr:
# Adding currentStatus to the
# value of that index to get
# the original value
# if it is less than X
if i + currentStatus < x:
currentStatus += 1
else:
currentStatus -= 1
totalValue += 1
return totalValue
# Drivers Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = 4
arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x)
print(countValue)
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to count number
// of students got selected
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int []arr,
int x)
{
int currentStatus = 0;
int totalValue = 0;
int i;
int len = arr.Length;
for (i = 0; i < len ; i++ )
{
// Adding currentStatus to the
// value of that index to get
// the original value
// if it is less than X
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else
{
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main ()
{
int x = 4;
int []arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
Console.Write(countValue);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ajit.
输出:
1
时间复杂度: ![]()