给定一个数字数组![]() 和的价值
和的价值![]() ,检查每个数字是否
,检查每个数字是否![]() 可以表示为确切的乘积
可以表示为确切的乘积![]() 质数。如果满足条件,则对数组的每个元素打印“是”,否则打印“否”。
质数。如果满足条件,则对数组的每个元素打印“是”,否则打印“否”。
注意:也可以考虑重复质数。例如,如果k = 2,则n = 4(= 2 * 2)是有效输入。
让我们考虑数字36。36可以分解为2 * 2 * 3 * 3。因此,它是4个质数的乘积。如果k值为4,则输出应为YES 。对于其他k值,输出应为NO 。
更多示例:
Input: arr[] = {30, 8, 12}, K = 3
Output: YES, YES, YES
30 = 2*3*5
8 = 2*2*2
12 = 2*3*2
Input: arr[] = {30, 16, 32}, k = 5
Output: NO, NO, YES
Only 32 can be represented as product of
5 prime numbers.
在本文中,我们将检查给定的数字是否可以表示为正好是k个素数的乘积。我们将要使用的基本概念仅仅是Eratosthenes筛网的一种变体。
推荐:如何构建Eratosthenes筛
Key Difference: In the Sieve, instead of storing binary values (0 if number not prime, 1 if the number is prime), we can store how many (repeating) prime factors make up that that number instead. This modification is done during its construction.
创建此修改过的筛网的一般过程如下:
- 创建一个全为0的数组,以存储连续整数(2、3、4…10 ^ 6)的列表。
- 最初将i的值设置为2。这是我们的第一个素数。
- 通过将i的值存储为j,遍历i的所有倍数(2 * i,3 * i…直到10 ^ 6)。继续执行步骤3和4。
- 使用i计算j可以分解的次数,并将结果存储到变量计数中。
- 当无法使用i进一步分解数量j时,将Sieve [j]的值增加计数值。
- 最后,在整数列表中找到大于i的下一个质数。如果没有这样的号码,则终止该过程。否则,再次从步骤2开始。
举例说明:
步骤1:
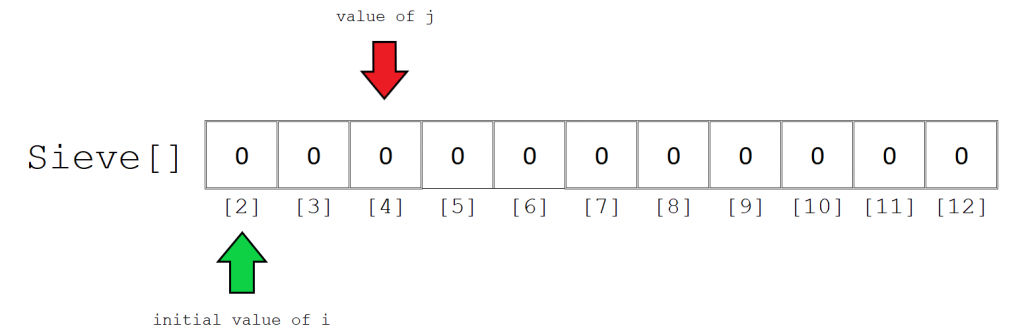
初始化的空筛阵列如下图所示。为简单起见,我们仅关注索引2到12。对于所有索引,最初存储的值为0。
现在,我们将采用的第一个质数是2。这是i的值。

第2步:
初始化变量j来保存i的每个后续倍数的值,从2 * i开始,在这种情况下为4。
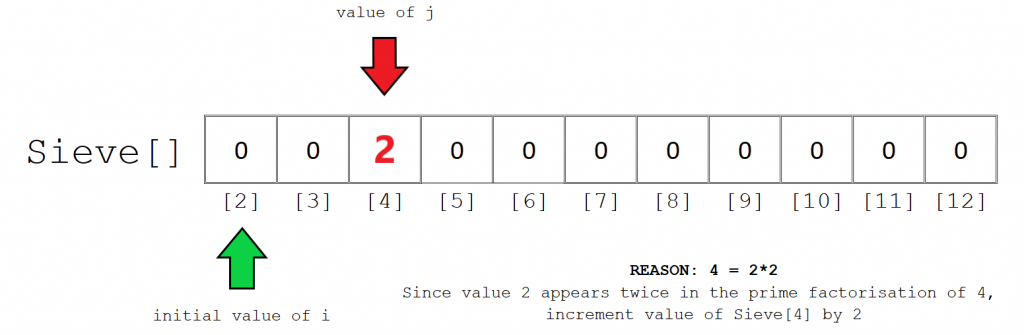
步骤3:
第三步涉及j的素因式分解的计算。更具体地说,当您分解j时,我们只想计算i的出现次数。
计算过程很简单。只需将j的值除以i,直到得到一个不能被i整除的数字。在这里,可以将4除以2两次。 4/2产生2,2 / 2产生1,它不能被2整除,并且循环停止。因此,我们用count变量的值2来更新Sieve [4]的值。
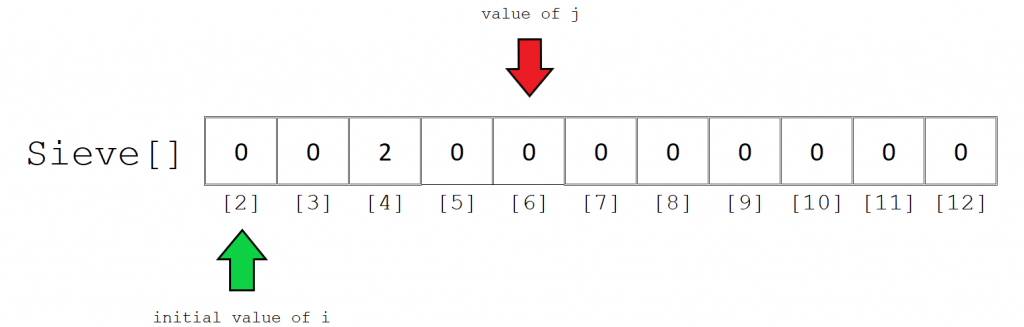
第四步:
我们可以类似的方式处理其他元素。接下来,j的值为6。6只能除以2一次。因此,Sieve [6]的值为1。
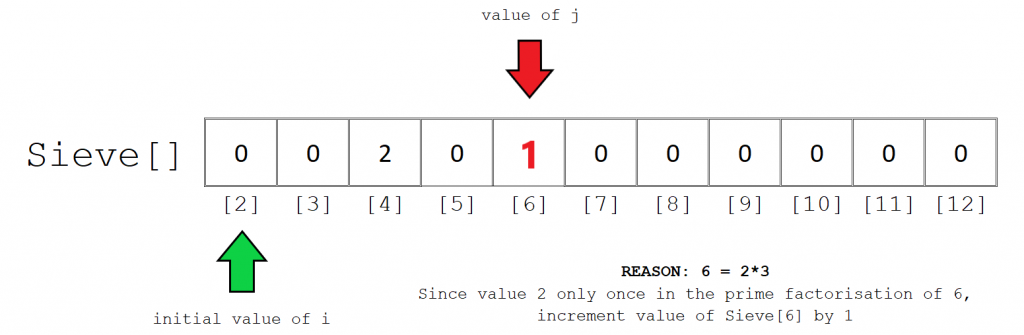
最终计算出的Sieve数组应如下所示。请注意,任何存储值为0的索引都表示一个数字,该数字不是2个或多个质数的乘积。这包括所有质数0和1。
要注意的第二件事是,我们只需要检查

下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to check if each element of
// the given array is a product of exactly
// K prime factors
#include
#define MAX 1000000
using namespace std;
// initialise the global sieve array
int Sieve[MAX] = { 0 };
// Function to generate Sieve
void constructSieve()
{
// NOTE: k value is necessarily more than 1
// hence, 0, 1 and any prime number cannot be
// represented as product of
// two or more prime numbers
for (int i = 2; i <= MAX; i++) {
if (Sieve[i] == 0) {
for (int j = 2 * i; j <= MAX; j += i) {
int temp = j;
while (temp > 1 && temp % i == 0) {
Sieve[j]++;
temp = temp / i;
}
}
}
}
}
// Function to check if each number of array
// satisfies the given condition
void checkElements(int A[], int n, int k)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (Sieve[A[i]] == k) {
cout << "YES\n";
}
else {
cout << "NO\n";
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// first construct the sieve
constructSieve();
int k = 3;
int A[] = { 12, 36, 42, 72 };
int n = sizeof(A) / sizeof(int);
checkElements(A, n, k);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to check if each element of
// the given array is a product of exactly
// K prime factors
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1000000;
// initialise the global sieve array
static int[] Sieve = new int[MAX+1];
// Function to generate Sieve
static void constructSieve()
{
// NOTE: k value is necessarily more than 1
// hence, 0, 1 and any prime number cannot be
// represented as product of
// two or more prime numbers
for (int i = 2; i <= MAX; i++)
{
if (Sieve[i] == 0)
{
for (int j = 2 * i; j <= MAX; j += i)
{
int temp = j;
while (temp > 1 && temp % i == 0)
{
Sieve[j]++;
temp = temp / i;
}
}
}
}
}
// Function to check if each number of array
// satisfies the given condition
static void checkElements(int A[], int n, int k)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (Sieve[A[i]] == k)
{
System.out.println("YES");
}
else
{
System.out.println("No");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// first construct the sieve
constructSieve();
int k = 3;
int A[] = {12, 36, 42, 72};
int n = A.length;
checkElements(A, n, k);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-JiPython3
# Python3 program to check if each element of
# the given array is a product of exactly
# K prime factors
MAX = 1000000
# initialise the global sieve array
Sieve = [0]*(MAX + 1)
# Function to generate Sieve
def constructSieve() :
# NOTE: k value is necessarily more than 1
# hence, 0, 1 and any prime number cannot be
# represented as product of
# two or more prime numbers
for i in range(2, MAX + 1) :
if (Sieve[i] == 0) :
for j in range(2*i, MAX + 1, i) :
temp = j;
while (temp > 1 and temp % i == 0) :
Sieve[j] += 1;
temp = temp // i;
# Function to check if each number of array
# satisfies the given condition
def checkElements(A, n, k) :
for i in range(n) :
if (Sieve[A[i]] == k) :
print("YES");
else :
print("NO");
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
# first construct the sieve
constructSieve();
k = 3;
A = [ 12, 36, 42, 72 ];
n = len(A);
checkElements(A, n, k);
# This code is contributed by AnkitRai01C#
// C# program to check if each element of
// the given array is a product of exactly
// K prime factors
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1000000;
// initialise the global sieve array
static int[] Sieve = new int[MAX+1];
// Function to generate Sieve
static void constructSieve()
{
// NOTE: k value is necessarily more than 1
// hence, 0, 1 and any prime number cannot be
// represented as product of
// two or more prime numbers
for (int i = 2; i <= MAX; i++)
{
if (Sieve[i] == 0)
{
for (int j = 2 * i; j <= MAX; j += i)
{
int temp = j;
while (temp > 1 && temp % i == 0)
{
Sieve[j]++;
temp = temp / i;
}
}
}
}
}
// Function to check if each number of array
// satisfies the given condition
static void checkElements(int []A, int n, int k)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (Sieve[A[i]] == k)
{
Console.WriteLine("YES");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// first construct the sieve
constructSieve();
int k = 3;
int []A = {12, 36, 42, 72};
int n = A.Length;
checkElements(A, n, k);
}
}
// This code contributed by anuj_67...YES
NO
YES
NO
时间复杂度: O(n * log(logn))
空间复杂度:O(MAX),其中MAX为10 6 。