在Python中使用 SQLite 聚合函数
在本文中,我们将了解如何在 SQLite Python中使用聚合函数。聚合函数是一种数据库管理函数,它将许多行的值组合成一个汇总值。 Average(即算术平均值)、sum、max、min、Count 是常用的聚合函数。 SQLite 为我们提供了许多用于统计分析的聚合函数。
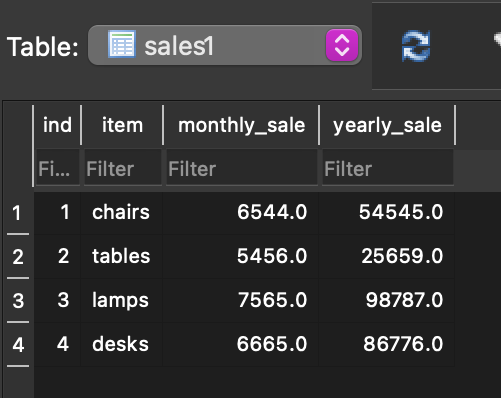
用于演示的数据库:要下载数据库,请单击此处。
最大()函数
max()函数返回我们指定的列中所有值的最大值。
Syntax: max(name_of_the_column)
Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# Obtain a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Find the maximum yearly_sale
max_sale = "select max(yearly_sale) from sales1"
cursor.execute(max_sale)
print("The maximum yearly sale is is:")
print(cursor.fetchone()[0])
# Closing database connection
connection.close()Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# Obtain a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# minimum yearly sale
min_sale = "select min(yearly_sale) from sales1"
cursor.execute(min_sale)
# Print the minimum score
print("The minimum yearly sale is:")
# fetching the result
print(cursor.fetchone()[0])
# Closing database connection
connection.close()Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# creating a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# average value of yearly_sales
avg_sale = "select avg(yearly_sale) from sales1"
cursor.execute(avg_sale)
print("The average yearly sales is:")
print(cursor.fetchone())
# Closing database connection
connection.close()Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# creating a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# total monthly_sale
Total_mon_sale= "select total(monthly_sale) from sales1"
cursor.execute(Total_mon_sale)
# Print the total score
print("The total monthly sale of all items is:")
print(cursor.fetchone()[0])
# Closing database connection
connection.close()Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# creating a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# sum of all the yearly sale
sum_yearly_sale = "select sum(yearly_sale) from sales1"
cursor.execute(sum_yearly_sale)
# Print the sum of scores
print("The sum of yearly sale is :")
print(cursor.fetchone()[0])
# Closing database connection
connection.close()Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# creating a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# count of all the rows of the database
count = "select count(*) from sales1"
cursor.execute(count)
print("The count of all rows of the table :")
print(cursor.fetchone()[0])
# Closing database connection
connection.close()输出:
The maximum yearly sale is is:
98787.0Min()函数
min()函数返回我们指定的列中所有值的最小值。
Syntax: min(name_of_the_column)
Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# Obtain a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# minimum yearly sale
min_sale = "select min(yearly_sale) from sales1"
cursor.execute(min_sale)
# Print the minimum score
print("The minimum yearly sale is:")
# fetching the result
print(cursor.fetchone()[0])
# Closing database connection
connection.close()
输出:
The minimum yearly sale is:
25659.0平均()函数
avg()函数返回我们指定的列中所有值的平均值或算术平均值。如果列中存在任何空值,则将其排除在外。
Syntax: avg(name_of_the_column)
Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# creating a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# average value of yearly_sales
avg_sale = "select avg(yearly_sale) from sales1"
cursor.execute(avg_sale)
print("The average yearly sales is:")
print(cursor.fetchone())
# Closing database connection
connection.close()
输出:
The average yearly sales is:
(66441.75,)总计()函数
total()函数返回列的所有值的总和或总和。
Syntax: total(name_of_the_column)
Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# creating a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# total monthly_sale
Total_mon_sale= "select total(monthly_sale) from sales1"
cursor.execute(Total_mon_sale)
# Print the total score
print("The total monthly sale of all items is:")
print(cursor.fetchone()[0])
# Closing database connection
connection.close()
输出:
The total monthly sale of all items is:
26230.0Sum()函数
sum()函数返回列的所有值的总和,如果所有值都为 null ,则返回 null。所以,total()函数是一个比较好的函数。
Syntax: sum(name_of_the_column)
Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# creating a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# sum of all the yearly sale
sum_yearly_sale = "select sum(yearly_sale) from sales1"
cursor.execute(sum_yearly_sale)
# Print the sum of scores
print("The sum of yearly sale is :")
print(cursor.fetchone()[0])
# Closing database connection
connection.close()
输出:
The sum of yearly sale is :
265767.0计数()函数
count()函数返回特定列或整个表中非空值的数量。
count of all rows in a table:
count(*)
count of all rows in a specified column:
count(name_of_the_column)
Python3
# import the sqlite module
import sqlite3
# establishing a connection to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("sales.db")
# creating a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# count of all the rows of the database
count = "select count(*) from sales1"
cursor.execute(count)
print("The count of all rows of the table :")
print(cursor.fetchone()[0])
# Closing database connection
connection.close()
输出:
The count of all rows of the table :
4