原子的组成
原子是物质可以在不释放带电粒子的情况下被分割成的最小单位。它也是具有化学元素特征的最小物质单位。因此,原子是物质的基本组成部分。原子非常小,无法通过肉眼或普通显微镜看到。原子中的大部分空间都是空的。其余部分由带正电的质子和中子核组成,周围环绕着带负电的电子云。与电子相比,原子核小而密,电子是自然界中最轻的带电粒子。电子被它们的电力吸引到任何正电荷。在原子中,电力将电子与原子核结合。
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. More than 99.94 % of an atom’s mass is in the nucleus.
原子的组成
由于量子力学的性质,没有一个理论可以完全令人满意地可视化原子的各种特性,这迫使物理学家使用原子的互补图像来解释不同的特性。在某些方面,原子中的电子表现得像绕核运行的粒子。在其他情况下,电子的行为就像围绕原子核的波。这种波型被称为轨道。并且这些轨道具有最大的电子概率。原子的行为受到这些轨道特性的强烈影响,其化学特性由称为壳的轨道群决定。
简单来说,原子的结构可以描述为类似于我们的太阳行星,行星围绕太阳旋转。由于地球以太阳为中心围绕太阳旋转。以类似的方式,电子围绕原子核旋转。因为太阳比太阳系的所有行星都重。以类似的方式,原子核包含原子的大部分质量。但也有一个不同之处,即太阳在我们的太阳系中具有足够的大小,而另一方面,原子核的大小相对于原子几乎可以忽略不计。
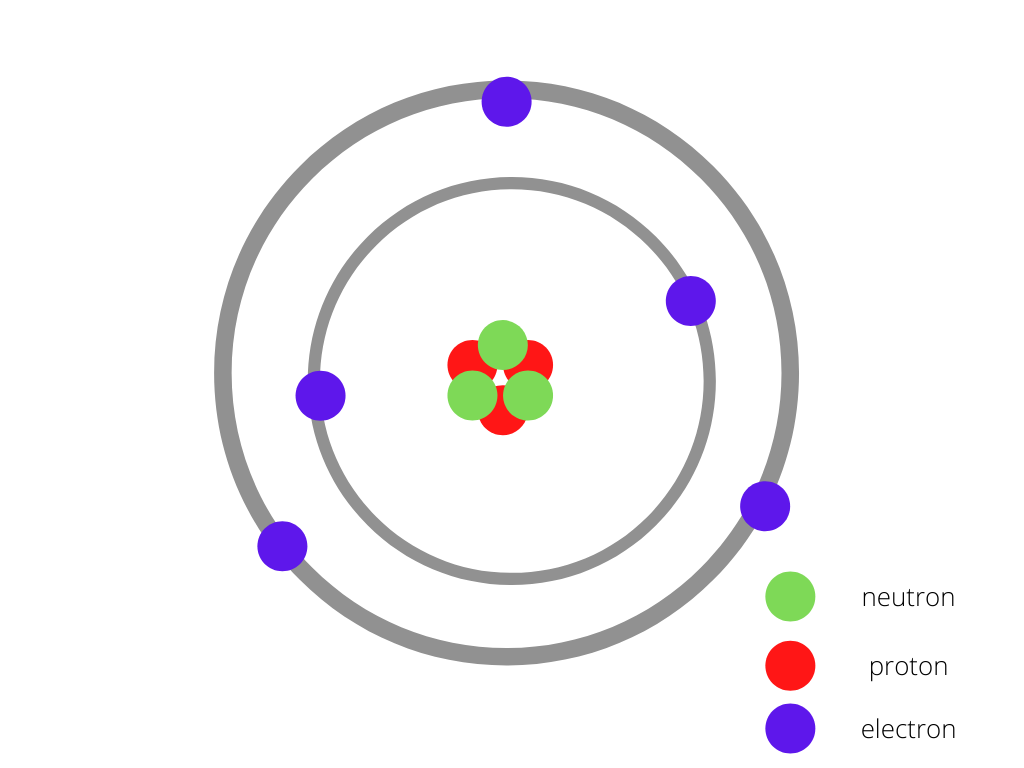
原子模型
不同原子中质子、电子和中子数量的变化
每个元素的原子在电子、质子和中子的数量上是不同的。随着我们在元素周期表中前进,原子序数增加。同样地,质子、中子、电子的数量也增加了,因此尺寸也增加了。
电子:电子是一种亚原子粒子,其电荷为负一个基本电荷。电子属于轻子粒子家族的第一代,通常被认为是基本粒子,因为它们没有已知的成分或子结构。
质子:质子是一种亚原子粒子,符号 p 或 p⁺,带有 +1e 基本电荷的正电荷,质量略小于中子。质子和中子的质量都约为一个原子质量单位,它们被统称为“核子”。
中子:中子是原子核中的粒子,质量 = 1,电荷 = 0。中子与原子核中的质子一起被发现。原子中的中子数决定了它的同位素。
尽管中子具有净中性电荷,但它确实由带电成分组成,这些成分在电荷方面相互抵消。
There can be mainly three types of changes in element:
- When the number of protons in an atom is changed, you will change the atom from one element to a different element.
- If you change the number of electrons in an atom, you will get an ion of the element.
- If the numbers of neutrons are changed without changing the number of protons and electrons, then isotopes are formed. The difference in the number of neutrons between the various isotopes of an element means that the various isotopes have different masses.
With the overall combined effect, we can say that atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons.
现在让我们考虑以下示例来理解上述概念:
Example 1: Carbon (C)
The number of protons in a Carbon atom = 6
The number of electrons in a Carbon atom = 6
The number of neutrons in a Carbon atom = 6
The figure given below shows the structure of the carbon atom has 6 protons and 6 neutrons at the centre surrounded by 6 electrons.
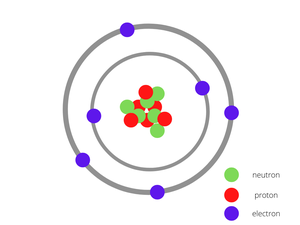
Carbon Atom
Example 2: Hydrogen (H)
The number of protons in a Hydrogen atom = 1
The number of electrons in a Hydrogen atom = 1
The number of neutrons in a Hydrogen atom = 0
The figure is given below shows the structure of a hydrogen atom having single protons at the centre and an electron revolving around it.
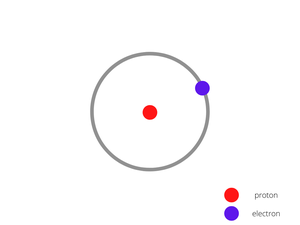
Hydrogen Atom
Example 3: Sodium
The number of protons in a Sodium atom = 11
The number of electrons in a Sodium atom = 11
The number of neutrons in a Sodium atom = 12
The figure given below shows the structure of the Sodium atom has 11 protons and 12 neutrons at the centre surrounded by 11 electrons.
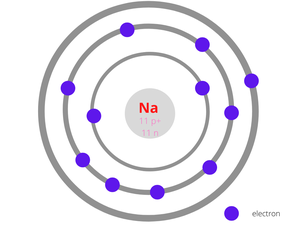
Sodium Atom
Example 4: Neon
The number of protons in a Neon atom = 10
The number of electrons in a Neon atom = 10
The number of neutrons in a Neon atom = 10
The figure given below shows the structure of the Neon atom which is an inert gas having 10 protons and 10 neutrons at the centre surrounded by 10 electrons.

Neon Atom
示例问题
问题 1:计算原子序数为 35 和质量数为 80 的溴中的质子数、电子数、中子数。
回答:
Step 1: In this step we will find the number of protons of the given sample:
Number of protons of a sample = Atomic Number of the element = 35
Step 2: In this step we will find the number of electrons of the given sample:
Number of electrons of a sample = Number of protons = 35
Step 3: In this step we will find the number of neutrons of the given sample:
Number of neutrons of a sample = (Mass number – Atomic Number) of the element
Number of neutrons of a sample = 80 – 35 = 45
So, here we got our required values.
The values are:
Number of proton, p = 35
Number of neutron, n = 45
Number of electron, e = 35
问题2:计算钛中的电子数、质子数和中子数(原子序数=22,质量数=48)。
回答:
The formula to calculate the number of neutrons is:
Number of neutrons = (A – Z)
where,
A = Mass number
Z = Atomic number
As the atomic number of Titanium is 22 which means the number of protons or electrons in this element is also 22.
Calculation of number of neutrons in Titanium (Ti) as follows:-
Given that Atomic number (Z) of Ti = 22, Mass number (A) of Ti = 48
Number of neutrons = (A – Z)
Number of neutrons in Ti = (48 – 22) = 26
Therefore the number of electrons, protons and neutrons in Titanium are 22, 22 and 26 respectively.
问题 3:求13 Al 27原子核中的质子数、电子数和中子数。
回答:
Atomic mass (A) = 27
Atomic number (Z) = 13
So, number of proton =13
Number of neutrons = (A – Z)
neutron = 27−13=14
electron = 13
But, there are only proton and neutron in the nucleus.
So, 13 protons ,14 neutrons and no electrons are present in nucleus of Al .
问题 4:求 12 g 的6 C 12中质子、电子和中子的总数。
回答:
6C12 contains 6 NA protons, 6NA electrons and 6NA neutrons.
where NA is Avogadro number.
Since 1g element contains 1 mole atoms and,
1 mole = 6.023 × 1023
So, Total number of particles =18NA
=18 × 6.023 × 1023
=1.08 × 1025
So, total number of electrons, protons and neutrons is 1.08 x 1025 .
问题 5:5 个中子的铍的质量数是多少?
回答:
Through the periodic table, by observing in sequence you will find that atomic number of beryllium is 4.
Given , number of neutrons is 5.
Mass number = atomic number + number of neutrons
= 5+4
= 9
So, the mass number for beryllium with 5 neutrons is 9.