多原子离子
离子是具有一定量的正电荷或负电荷的化学实体。术语“离子”可以指附着有非零净电荷的原子或分子。因此,所有离子要么在它们的整体原子或分子结构中含有比电子更多的质子,要么在它们的原子/分子结构中含有比质子更多的电子。已知质子数比电子数多的离子具有净正电荷。这些离子通常称为阳离子。另一方面,具有比质子更多的电子的离子已知具有净负电荷。这些离子通常被称为阴离子。
How are Ions formed?
Ions can be prepared in a variety of ways. For example, spontaneous collisions between molecules in a liquid or gaseous fluid can result in one of an atom’s/electrons molecule’s being knocked off. As a result, a positively charged ion and a free electron are formed. Physical ionisation is the most common type of ionisation. The liberated electron could potentially bind to another atom or molecule, resulting in the production of a new negatively charged anion.
Chemical interactions are another major way in which ions can be produced. When an ionic compound, such as salt, is dissolved in a suitable solvent, the atoms that make up the salt dissociate and generate free ions. When common salt, commonly known as sodium chloride, dissolves in water, it dissociates to produce sodium cations and chloride anions. It should be noted that sodium cations are represented by the symbol Na+, whereas chloride anions are represented by the symbol Cl–.
多原子离子
A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalently bound set of two or more atoms, or a metal complex, that behaves as a single unit and has a net charge greater than zero. This chemical species is an ion, as opposed to a molecule, which has a net charge of zero.
由一个氧原子和一个氢原子组成并具有一个净电荷的氢氧根离子是多原子离子的一个简单例子。它的化学式是OH-。
另一方面,铵离子的电荷为+1,由一个氮原子和四个氢原子组成;其化学式为NH 4 + 。在酸碱化学和盐的生产中,经常使用多原子离子。多原子离子通常被认为是中性分子的共轭酸或碱。
多原子离子的结构
多原子离子可以被认为是单原子离子。通过获得或失去电子而被电离的原子称为单原子离子。离子具有净电荷,因为原子核中的电子总数不等于质子总数。结果,与中性原子相比,在带负电的阴离子的情况下,我们有额外的电子,或者在带正电的阳离子的情况下,我们没有足够的电子。例如,中性氯原子的原子序数为 17,这意味着它拥有 17 个质子和 17 个电子。当中性原子获得一个额外的电子时,就会形成氯阴离子。氯阴离子在获得一个电子后现在有 17 个质子和 18 个电子。离子的净电荷为 1,因为与质子数相比,多了一个电子。
另一方面,多原子离子可能被认为是通过获得或失去电子而被电离的分子。因为分子中的电子总数不等于分子中质子的总数,所以多原子离子中的共价键原子团具有净电荷。
考虑多原子离子OH - ,也称为氢氧化物。左图为氢氧根离子的点状结构。它由一个氧原子和一个氢原子组成。连接它们的单线表示共价键,它由 H 和 O 共享的两个电子组成。 O 周围的点代表孤电子对。氢氧化物中的氧具有三个孤对电子,总共有六个孤对电子。通过将完整的点结构括在方括号中并将电荷放在右上角来显示氢氧根离子上的净电荷。我们可以观察到氢氧化物带有 1- 电荷,这意味着该离子比氢原子核加氧原子多一个电子。
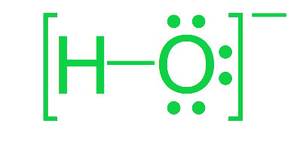
氢氧根离子的路易斯点结构
多原子离子的例子
- 多原子阳离子:大多数常见的多原子阴离子是含氧阴离子,它们是含氧酸(衍生自非金属元素氧化物的酸)的共轭碱。例如,硫酸根阴离子SO 4 -2来源于H 2 SO 4 ,可以认为是SO 3 + H 2 O。
- 多原子阴离子:铵 (NH 4 ) 是唯一的阳离子多原子离子。
Formula | Name |
| NH4+ | Ammonium |
| NO2– | Nitrite |
| NO3– | Nitrate |
| SO32- | Sulphite |
| SO42- | Sulphate |
| OH– | Hydroxide |
| CN– | Cyanide |
| CO32- | Carbonate |
示例问题
问题1:哪个是离子化合物?
回答:
Ionic compounds are just that: they’re made up of ions. These ions are electron-gaining or electron-losing atoms with a net positive or negative charge. Metals lose electrons and become cations when they have a net positive charge. Non-metals tend to acquire electrons, resulting in anions with a net negative charge.
问题2:离子化合物的组成部分是什么?
回答:
Ionic compounds are made up of ions, which are charged particles that occur when an atom (or group of atoms) acquires or loses electrons. A cation is a positively charged ion, while an anion is a negatively charged ion.
问题3:什么是简单离子?
回答:
Simple ions are ions that are made up of only a single atom.
问题4:什么是复合离子?
回答:
Compound ions are ions that are produced by joining together groups of atoms.
问题5:什么是多原子离子?
回答:
Polyatomic ions can be thought of in terms of monatomic ions. An atom that has been ionised by gaining or losing electrons is known as a monatomic ion. The ion has a net charge because the total number of electrons in the nucleus is not equal to the total number of protons.