continue语句用于跳过循环的当前迭代,程序的控制流转到下一个迭代。
的语法continue语句是:
continue [label]; 注意: label是可选的,很少使用。
JavaScript的工作继续声明
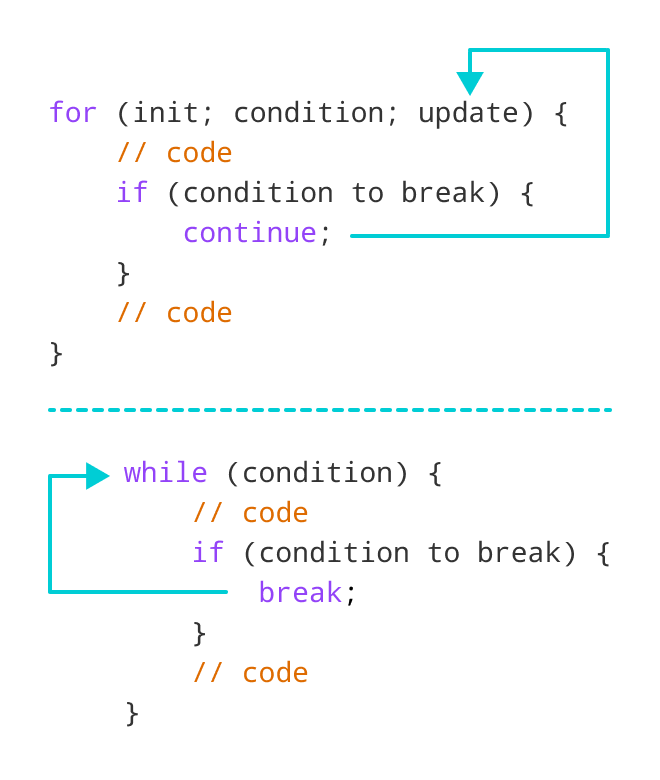
继续for循环
在for循环, continue跳过当前迭代和控制流跳转到updateExpression。
示例1:打印i的值
// program to print the value of i
for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// condition to continue
if (i == 3) {
continue;
}
console.log(i);
}输出
1
2
4
5在以上程序中, for循环用于在每次迭代中打印i的值。
注意循环内的continue语句。
if(i == 3) {
continue;
}这意味着
- 当i等于3时 ,
continue语句将跳过第三次迭代。 - 然后,
i变为4 ,并再次评估测试条件和continue语句。 - 因此,在接下来的两次迭代中将打印4和5 。
注意 : continue语句几乎总是与决策语句一起使用。要了解更多信息,请访问JavaScript if … else语句。
要了解有关for循环的更多信息,请访问JavaScript for循环。
注意 : break语句完全终止循环。但是, continue语句仅跳过当前迭代。
继续while循环
在while循环中, continue跳过当前迭代,程序的控制流跳回到while条件。
对于while和do...while循环, continue语句的工作方式相同。
示例2:计算正数
// program to calculate positive numbers only
// if the user enters a negative number, that number is skipped from calculation
// negative number -> loop terminate
// non-numeric character -> skip iteration
let sum = 0;
let number = 0;
while (number >= 0) {
// add all positive numbers
sum += number;
// take input from the user
number = parseInt(prompt('Enter a number: '));
// continue condition
if (isNaN(number)) {
console.log('You entered a string.');
number = 0; // the value of number is made 0 again
continue;
}
}
// display the sum
console.log(`The sum is ${sum}.`);输出
Enter a number: 1
Enter a number: 2
Enter a number: hello
You entered a string.
Enter a number: 5
Enter a number: -2
The sum is 8. 在上述程序中,用户输入一个数字。 while循环用于打印用户输入的正数的总和。
注意continue语句的使用。
if (isNaN(number)) {
continue;
}- 当用户输入非数字数字/ 字符串,
continue语句将跳过当前迭代。然后程序的控制流程进入while循环的条件 。 - 当用户输入小于0的数字时,循环终止。
在上面的程序中, isNaN()用于检查用户输入的值是否为数字。
要了解更多关于while循环的信息,请访问JavaScript while循环。
继续嵌套循环
当continue由两个嵌套循环的内部使用, continue跳过内环的当前迭代。例如,
// nested for loops
// first loop
for (let i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
// second loop
for (let j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (j == 2) {
continue;
}
console.log(`i = ${i}, j = ${j}`);
}
}输出
i = 1, j = 1
i = 1, j = 3
i = 2, j = 1
i = 2, j = 3
i = 3, j = 1
i = 3, j = 3在上面的程序中,当执行continue语句时,它将跳过内部循环中的当前迭代,并且程序的控制流移至内部循环的updateExpression 。
因此, j = 2的值永远不会显示在输出中。
JavaScript标签为继续
使用嵌套循环时,可以跳过当前迭代,并且可以将程序的控制流传递给 label语句的updateExpression 。
但是在JavaScript中很少使用标有continue标记,因为这会使代码更难以阅读和理解。
如果您想了解更多有关带有标签的continue语句的信息,请访问带有标签的continue。