给定两个字符串str1和str2以及以下可以在str1上执行的操作。找到将“ str1”转换为“ str2”所需的最少编辑(操作)次数。
- 插
- 去掉
- 代替
以上所有操作费用均相等。
例子:
Input: str1 = “geek”, str2 = “gesek”
Output: 1
We can convert str1 into str2 by inserting a ‘s’.
Input: str1 = “cat”, str2 = “cut”
Output: 1
We can convert str1 into str2 by replacing ‘a’ with ‘u’.
Input: str1 = “sunday”, str2 = “saturday”
Output: 3
Last three and first characters are same. We basically
need to convert “un” to “atur”. This can be done using
below three operations.
Replace ‘n’ with ‘r’, insert t, insert a
在这种情况下,有哪些子问题?这个想法是从两个字符串的左侧或右侧逐一凝视所有字符。让我们从右上角遍历,遍历每对字符有两种可能性。以下是条件:
- 如果两个字符串的最后一个字符相同,则无事可做。忽略最后一个字符,并获得剩余字符串的计数。因此,我们递归长度为m-1和n-1。
- 否则(如果最后一个字符不同),我们考虑对“ str1”的所有操作,考虑对第一个字符串的最后一个字符的所有三个操作,递归计算所有三个操作的最小开销,并取三个值中的最小值。
- 插入:重复出现m和n-1
- 删除:重复执行m-1和n
- 替换:重复执行m-1和n-1
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// A Naive recursive C++ program to find minimum number
// operations to convert str1 to str2
#include
using namespace std;
// Utility function to find minimum of three numbers
int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
return min(min(x, y), z);
}
int editDist(string str1, string str2, int m, int n)
{
// If first string is empty, the only option is to
// insert all characters of second string into first
if (m == 0)
return n;
// If second string is empty, the only option is to
// remove all characters of first string
if (n == 0)
return m;
// If last characters of two strings are same, nothing
// much to do. Ignore last characters and get count for
// remaining strings.
if (str1[m - 1] == str2[n - 1])
return editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1);
// If last characters are not same, consider all three
// operations on last character of first string, recursively
// compute minimum cost for all three operations and take
// minimum of three values.
return 1 + min(editDist(str1, str2, m, n - 1), // Insert
editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n), // Remove
editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1) // Replace
);
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
// your code goes here
string str1 = "sunday";
string str2 = "saturday";
cout << editDist(str1, str2, str1.length(), str2.length());
return 0;
} Java
// A Naive recursive Java program to find minimum number
// operations to convert str1 to str2
class EDIST {
static int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x <= y && x <= z)
return x;
if (y <= x && y <= z)
return y;
else
return z;
}
static int editDist(String str1, String str2, int m, int n)
{
// If first string is empty, the only option is to
// insert all characters of second string into first
if (m == 0)
return n;
// If second string is empty, the only option is to
// remove all characters of first string
if (n == 0)
return m;
// If last characters of two strings are same, nothing
// much to do. Ignore last characters and get count for
// remaining strings.
if (str1.charAt(m - 1) == str2.charAt(n - 1))
return editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1);
// If last characters are not same, consider all three
// operations on last character of first string, recursively
// compute minimum cost for all three operations and take
// minimum of three values.
return 1 + min(editDist(str1, str2, m, n - 1), // Insert
editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n), // Remove
editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1) // Replace
);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
String str1 = "sunday";
String str2 = "saturday";
System.out.println(editDist(str1, str2, str1.length(), str2.length()));
}
}Python
# A Naive recursive Python program to fin minimum number
# operations to convert str1 to str2
def editDistance(str1, str2, m, n):
# If first string is empty, the only option is to
# insert all characters of second string into first
if m == 0:
return n
# If second string is empty, the only option is to
# remove all characters of first string
if n == 0:
return m
# If last characters of two strings are same, nothing
# much to do. Ignore last characters and get count for
# remaining strings.
if str1[m-1]== str2[n-1]:
return editDistance(str1, str2, m-1, n-1)
# If last characters are not same, consider all three
# operations on last character of first string, recursively
# compute minimum cost for all three operations and take
# minimum of three values.
return 1 + min(editDistance(str1, str2, m, n-1), # Insert
editDistance(str1, str2, m-1, n), # Remove
editDistance(str1, str2, m-1, n-1) # Replace
)
# Driver program to test the above function
str1 = "sunday"
str2 = "saturday"
print editDistance(str1, str2, len(str1), len(str2))C#
// A Naive recursive C# program to
// find minimum numberoperations
// to convert str1 to str2
using System;
class GFG {
static int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x <= y && x <= z)
return x;
if (y <= x && y <= z)
return y;
else
return z;
}
static int editDist(String str1, String str2, int m, int n)
{
// If first string is empty, the only option is to
// insert all characters of second string into first
if (m == 0)
return n;
// If second string is empty, the only option is to
// remove all characters of first string
if (n == 0)
return m;
// If last characters of two strings are same, nothing
// much to do. Ignore last characters and get count for
// remaining strings.
if (str1[m - 1] == str2[n - 1])
return editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1);
// If last characters are not same, consider all three
// operations on last character of first string, recursively
// compute minimum cost for all three operations and take
// minimum of three values.
return 1 + min(editDist(str1, str2, m, n - 1), // Insert
editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n), // Remove
editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1) // Replace
);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
String str1 = "sunday";
String str2 = "saturday";
Console.WriteLine(editDist(str1, str2, str1.Length,
str2.Length));
}
}C++
// A memoization program to find minimum number
// operations to convert str1 to str2
#include
using namespace std;
// Maximum 2-D array coloumn size
const int maximum = 1000;
// Utility function to find minimum of three numbers
int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
return min(min(x, y), z);
}
int editDist(string str1, string str2, int m, int n, int dp[][maximum])
{
// If first string is empty, the only option is to
// insert all characters of second string into first
if (m == 0)
return n;
// If second string is empty, the only option is to
// remove all characters of first string
if (n == 0)
return m;
// if the recursive call has been
// called previously, then return
// the stored value that was calculated
// previously
if (dp[m - 1][n - 1] != -1)
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
// If last characters of two strings are same, nothing
// much to do. Ignore last characters and get count for
// remaining strings.
// Store the returned value at dp[m-1][n-1]
// considering 1-based indexing
if (str1[m - 1] == str2[n - 1])
return dp[m - 1][n - 1] = editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1, dp);
// If last characters are not same, consider all three
// operations on last character of first string, recursively
// compute minimum cost for all three operations and take
// minimum of three values.
// Store the returned value at dp[m-1][n-1]
// considering 1-based indexing
return dp[m - 1][n - 1] = 1 + min(editDist(str1, str2, m, n - 1, dp), // Insert
editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n, dp), // Remove
editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1, dp) // Replace
);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
string str1 = "sunday";
string str2 = "saturday";
int m = str1.length();
int n = str2.length();
// Declare a dp array which stores
// the answer to recursive calls
int dp[m][maximum];
// initially all index with -1
memset(dp, -1, sizeof dp);
// Function call
// memoization and top-down approach
cout << editDist(str1, str2, m, n, dp);
return 0;
} Python3
# A memoization program to find minimum number
# operations to convert str1 to str2
def editDistance(str1, str2, m, n, d = {}):
key = m, n
# If first string is empty, the only option
# is to insert all characters of second
# string into first
if m == 0:
return n
# If second string is empty, the only
# option is to remove all characters
# of first string
if n == 0:
return m
if key in d:
return d[key]
# If last characters of two strings are same,
# nothing much to do. Ignore last characters
# and get count for remaining strings.
if str1[m - 1] == str2[n - 1]:
return editDistance(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1)
# If last characters are not same, consider
# all three operations on last character of
# first string, recursively compute minimum
# cost for all three operations and take
# minimum of three values.
# Store the returned value at dp[m-1][n-1]
# considering 1-based indexing
d[key] = 1 + min(editDistance(str1, str2, m, n - 1), # Insert
editDistance(str1, str2, m - 1, n), # Remove
editDistance(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1)) # Replace
return d[key]
# Driver code
str1 = "sunday"
str2 = "saturday"
print(editDistance(str1, str2, len(str1), len(str2)))
# This code is contributed by puranjanprithu输出:
3上述解决方案的时间复杂度是O(3 ^ n),它是指数级的。当两个字符串的字符都不匹配时,会发生最坏的情况。下面是最坏情况的递归调用图。
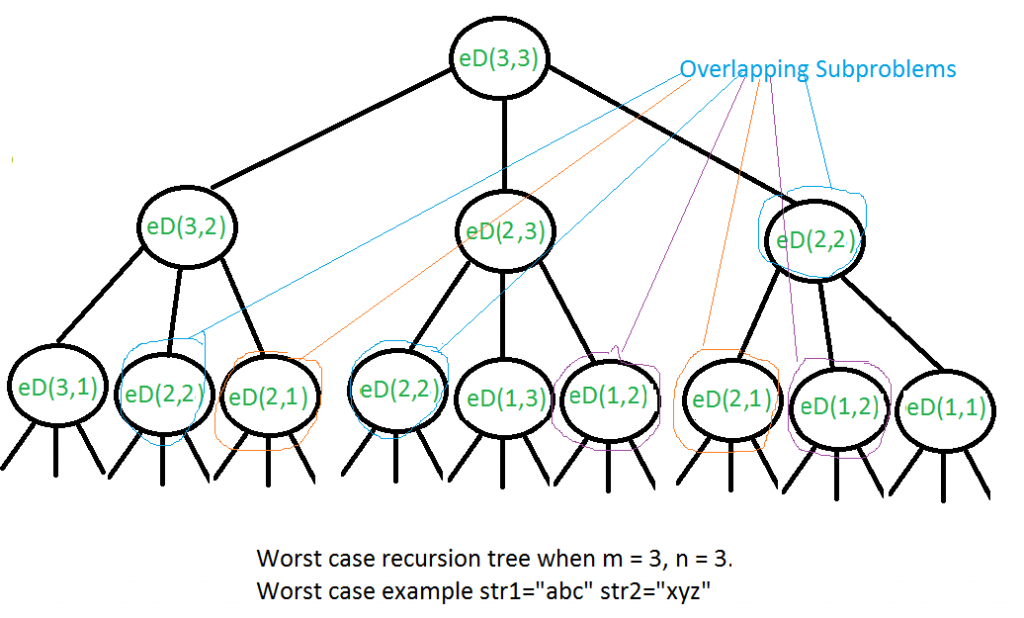
我们可以看到,许多子问题被一次又一次地解决了,例如,eD(2,2)被调用了三次。由于再次调用了相同的问题,因此此问题具有“重叠子问题”属性。因此,“编辑距离”问题具有动态编程问题的两个属性(请参阅此内容)。像其他典型的动态编程(DP)问题一样,可以通过构造存储子问题结果的临时数组来避免相同子问题的重新计算。自下而上的方法可以在这里找到。
也可以使用自上而下的动态编程和备忘录来解决该问题。在递归代码中,可以使用备注来避免重叠问题。如果在第一次调用时存储该值,则可以在O(1)中计算多个重复调用。在观察递归代码时,可以看到在每个递归调用中最多有两个参数正在更改其值。在某些情况下,先前已调用过相同的递归调用。由于两个参数不是恒定的,因此可以使用二维数组来避免重复调用。因此,返回值存储在某些二维数组中。步骤如下:
- 使用所有索引的-1初始化大小为m * n的2-D DP数组。
- 在每个递归调用上,将返回值存储在dp [m] [n]中,这样,如果再次调用func(m,n) ,则可以在O(1)中对其进行应答,而无需使用递归。
- 通过检查dp [m] [n]上的值,检查是否以前访问过递归调用。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// A memoization program to find minimum number
// operations to convert str1 to str2
#include
using namespace std;
// Maximum 2-D array coloumn size
const int maximum = 1000;
// Utility function to find minimum of three numbers
int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
return min(min(x, y), z);
}
int editDist(string str1, string str2, int m, int n, int dp[][maximum])
{
// If first string is empty, the only option is to
// insert all characters of second string into first
if (m == 0)
return n;
// If second string is empty, the only option is to
// remove all characters of first string
if (n == 0)
return m;
// if the recursive call has been
// called previously, then return
// the stored value that was calculated
// previously
if (dp[m - 1][n - 1] != -1)
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
// If last characters of two strings are same, nothing
// much to do. Ignore last characters and get count for
// remaining strings.
// Store the returned value at dp[m-1][n-1]
// considering 1-based indexing
if (str1[m - 1] == str2[n - 1])
return dp[m - 1][n - 1] = editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1, dp);
// If last characters are not same, consider all three
// operations on last character of first string, recursively
// compute minimum cost for all three operations and take
// minimum of three values.
// Store the returned value at dp[m-1][n-1]
// considering 1-based indexing
return dp[m - 1][n - 1] = 1 + min(editDist(str1, str2, m, n - 1, dp), // Insert
editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n, dp), // Remove
editDist(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1, dp) // Replace
);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
string str1 = "sunday";
string str2 = "saturday";
int m = str1.length();
int n = str2.length();
// Declare a dp array which stores
// the answer to recursive calls
int dp[m][maximum];
// initially all index with -1
memset(dp, -1, sizeof dp);
// Function call
// memoization and top-down approach
cout << editDist(str1, str2, m, n, dp);
return 0;
}
Python3
# A memoization program to find minimum number
# operations to convert str1 to str2
def editDistance(str1, str2, m, n, d = {}):
key = m, n
# If first string is empty, the only option
# is to insert all characters of second
# string into first
if m == 0:
return n
# If second string is empty, the only
# option is to remove all characters
# of first string
if n == 0:
return m
if key in d:
return d[key]
# If last characters of two strings are same,
# nothing much to do. Ignore last characters
# and get count for remaining strings.
if str1[m - 1] == str2[n - 1]:
return editDistance(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1)
# If last characters are not same, consider
# all three operations on last character of
# first string, recursively compute minimum
# cost for all three operations and take
# minimum of three values.
# Store the returned value at dp[m-1][n-1]
# considering 1-based indexing
d[key] = 1 + min(editDistance(str1, str2, m, n - 1), # Insert
editDistance(str1, str2, m - 1, n), # Remove
editDistance(str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1)) # Replace
return d[key]
# Driver code
str1 = "sunday"
str2 = "saturday"
print(editDistance(str1, str2, len(str1), len(str2)))
# This code is contributed by puranjanprithu
输出:
3时间复杂度:O(M * N)
辅助空间:O(M * N)